Anatomy Of Middle Ear
The middle ear also known as the tympanic cavity or the tympanum is a pneumatized air filled region of the temporal bone that lies just medial to the tympanic membrane ear drum and lateral to the promontory caused by the turns of the cochlea of the ear. The area is pressurized.
Structure And Function Of The Middle Ear
Semicircular ducts filled with fluid.

Anatomy of middle ear. Also known as the tympanic cavity the middle ear is an air filled membrane lined space located between the ear canal and the eustachian tube cochlea and auditory nerve. The ossicles directly couple sound energy from the ear drum to the oval window of the cochlea. It is also membrane lined interplanetary cavity situated between the ear canal and the eustachian tube cochlea and auditory nerve.
The outer ear is called the pinna and is made of ridged cartilage covered by skin. Auditory tube drains fluid from the. Middle ear tympanic cavity anatomy duration.
They are also referred to as the hammer anvil and stirrup respectively. The bones are called. The ossicles were given their latin names for their distinctive shapes.
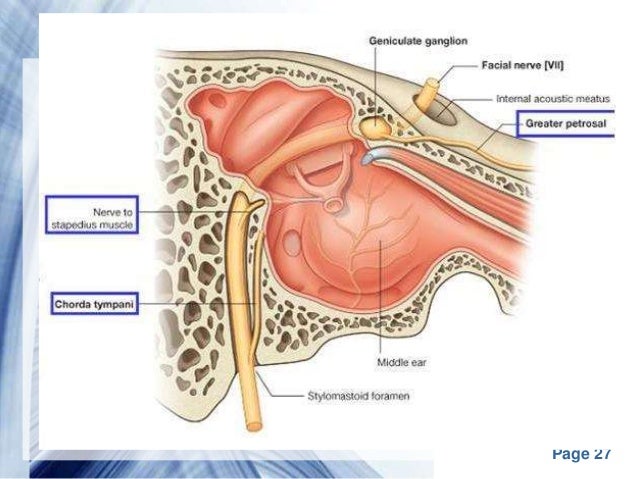
Middle ear anatomy tympanic cavity is an air filled cavity. Oval window connects the middle ear with the inner ear. The middle ear contains three tiny bones known as the ossicles.
Sam webster 38861 views. Middle ear tympanic cavity consisting of. The cochlea is shaped like a snail and is divided into two chambers by a membrane.
Sound funnels through the pinna into the external auditory. Three small bones that are connected and transmit the sound waves to the inner ear. The ear has external middle and inner portions.
Malleus incus and stapes. The eardrum splits this cavity from the ear canal. Cochlea spiral shaped organ of hearing.
Attached to cochlea and nerves. A canal that links the middle ear with the back of the nose. The cochlea which is the hearing portion and the semicircular canals is the balance portion.
The inner ear includes. Ear anatomy inner ear. The eustachian tube helps to equalize the pressure in.
The chambers are full of fluid which vibrates when sound comes in and causes the small hairs which line the membrane to vibrate and send electrical impulses to the brain. Transforms sound into signals that get sent to the brain. The eardrum acts as a natural boundary between the middle ear and the ear canal.
The eardrum separates this space from the ear canal.
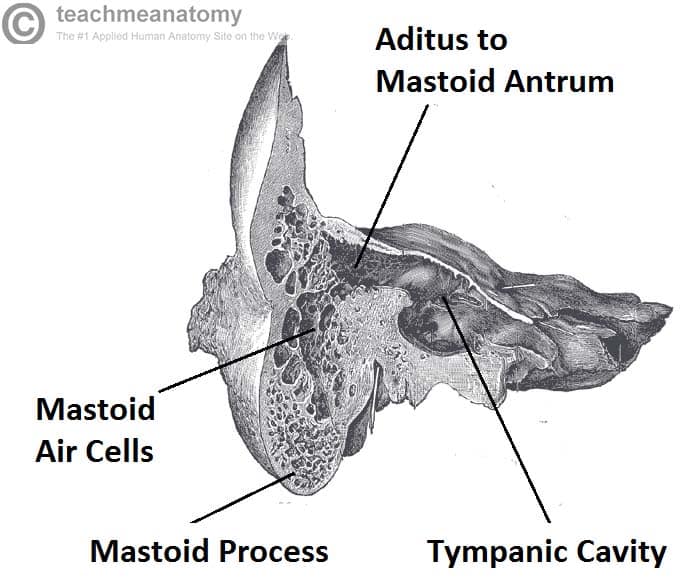 The Middle Ear Parts Bones Muscles Teachmeanatomy
The Middle Ear Parts Bones Muscles Teachmeanatomy
 The Human Ear Consists Of Three Parts The Outer Ear Middle Ear
The Human Ear Consists Of Three Parts The Outer Ear Middle Ear
 Middle Ear Anatomy At Grand Valley State University Studyblue
Middle Ear Anatomy At Grand Valley State University Studyblue
 External And Middle Ear Anatomy Diagram Quizlet
External And Middle Ear Anatomy Diagram Quizlet
 Middle Ear Anatomy Ear Anatomy Middle Ear Anatomy
Middle Ear Anatomy Ear Anatomy Middle Ear Anatomy
 Middle Ear Anatomy Annotated Ct Radiology Case
Middle Ear Anatomy Annotated Ct Radiology Case
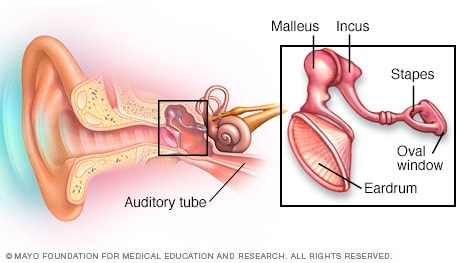 Slide Show How You Hear Mayo Clinic
Slide Show How You Hear Mayo Clinic
 Anatomy And Physiology Of The Middle Ear Youtube
Anatomy And Physiology Of The Middle Ear Youtube
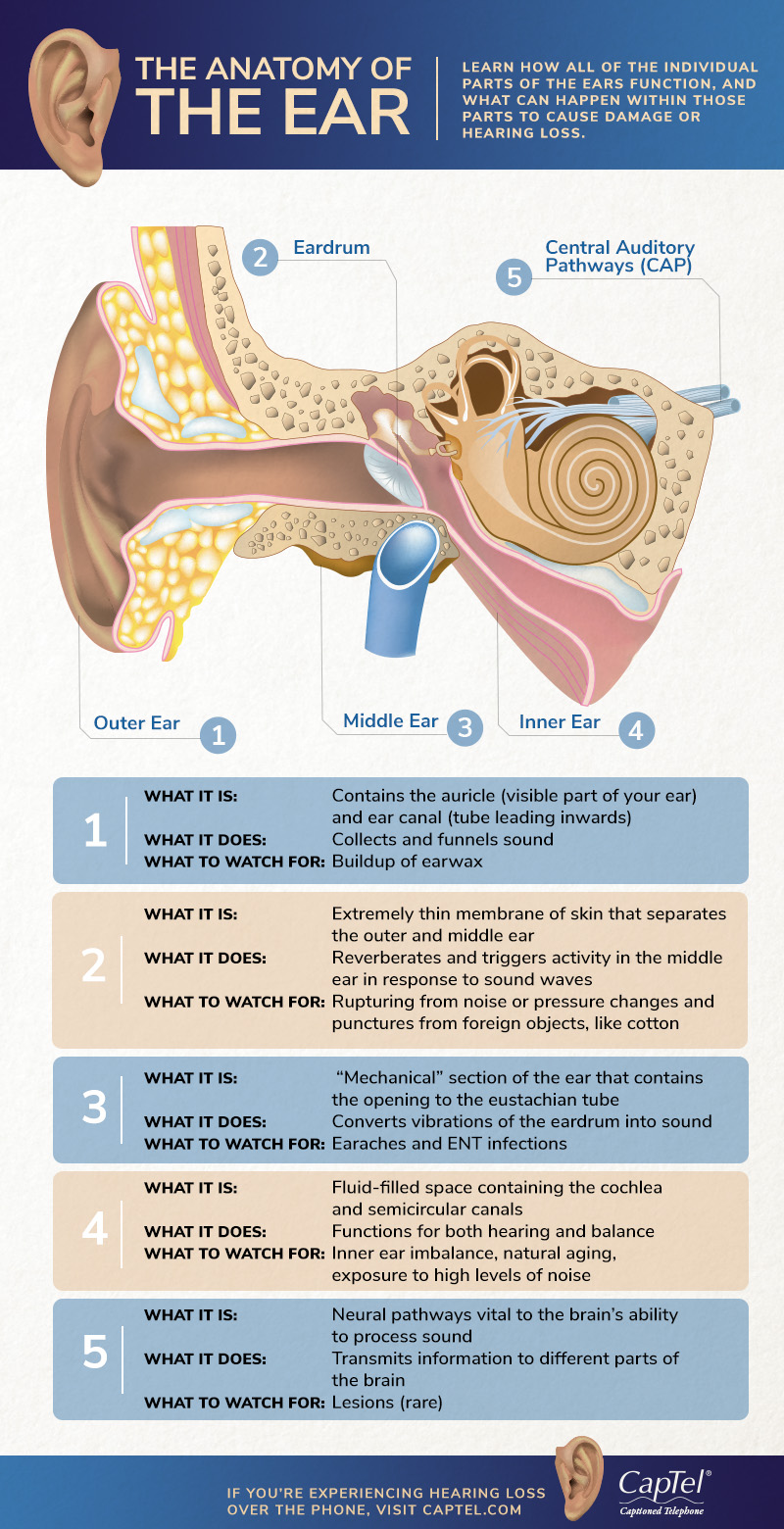 The Anatomy Of The Ear Infographic
The Anatomy Of The Ear Infographic
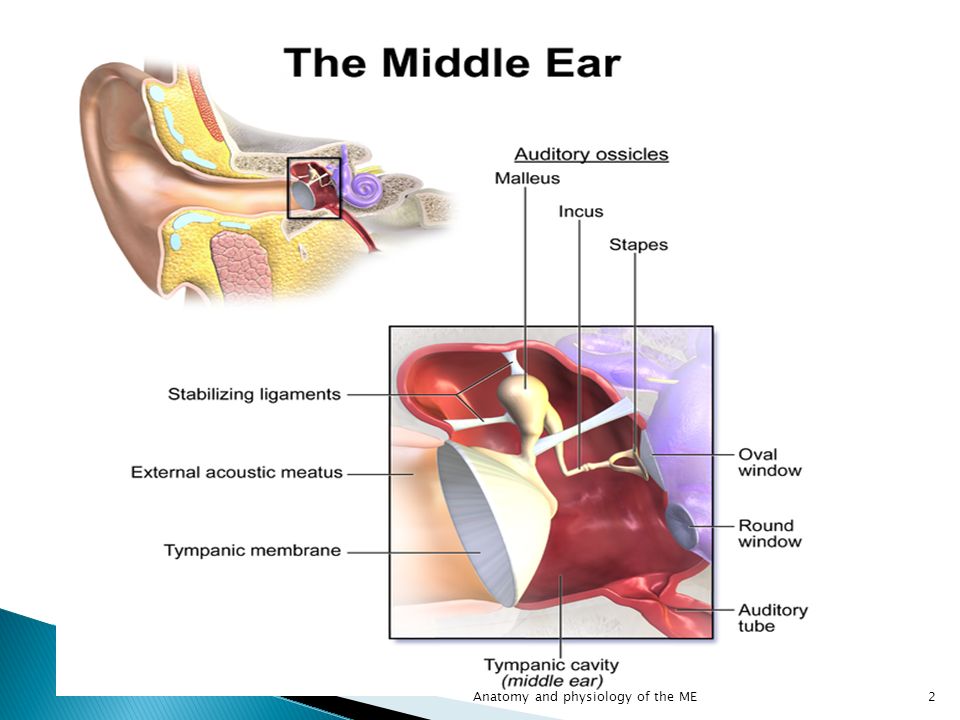 Anatomy And Physiology Of The Middle Ear Ppt Video Online
Anatomy And Physiology Of The Middle Ear Ppt Video Online
 Middle Ear Tympanic Cavity Anatomy
Middle Ear Tympanic Cavity Anatomy
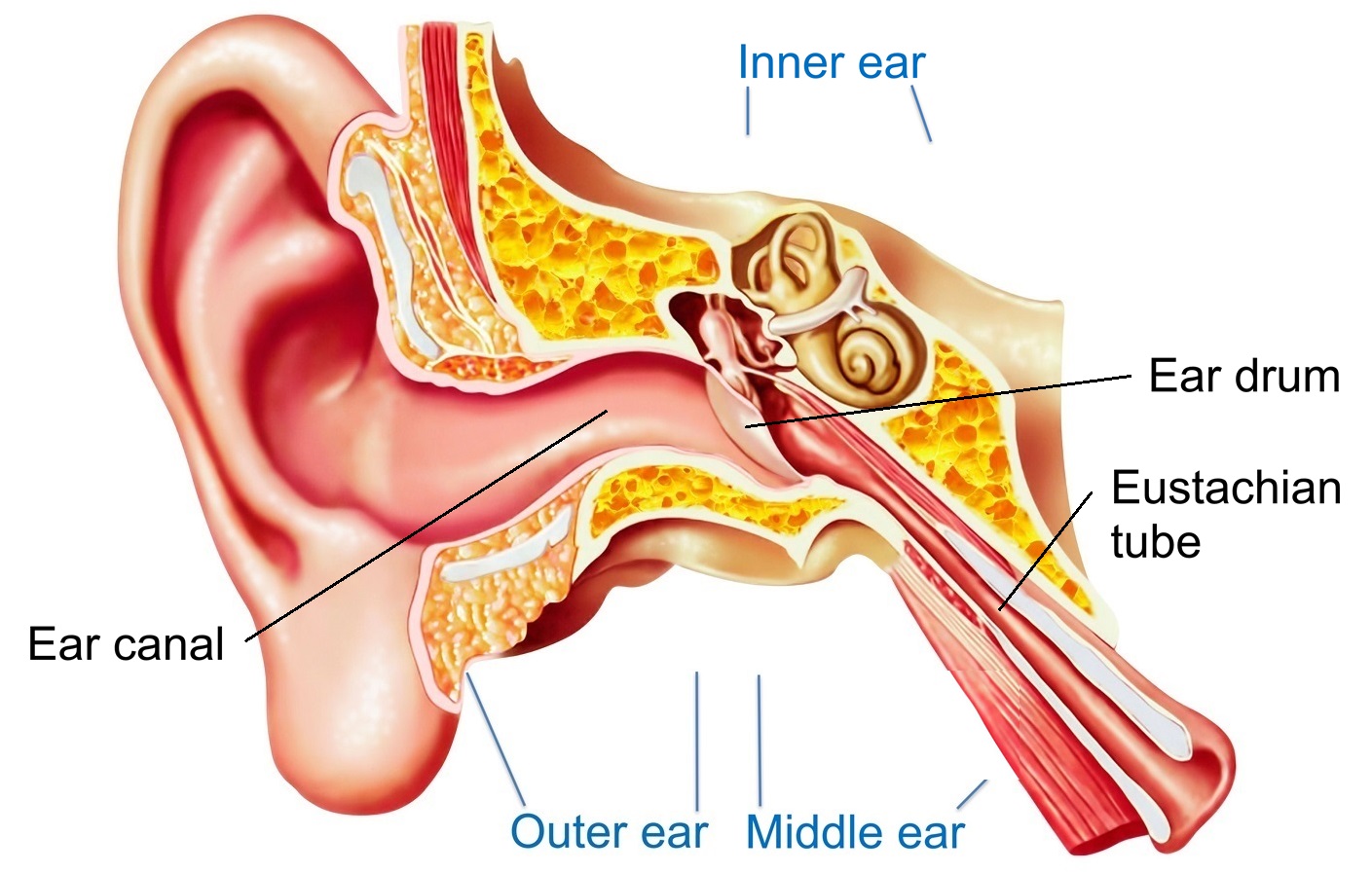 Ear Infection Middle Ear Symptoms Treatment Southern
Ear Infection Middle Ear Symptoms Treatment Southern
Structure And Function Of The Middle Ear
Ear Anatomy Causes Of Hearing Loss Hearing Aids Audiology
 Special Senses Figure 24 13 Anatomy Of The External And
Special Senses Figure 24 13 Anatomy Of The External And

 Anatomy Of The Middle Ear A Schematic Of A Sauropsid
Anatomy Of The Middle Ear A Schematic Of A Sauropsid
 Middle Ear An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Middle Ear An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
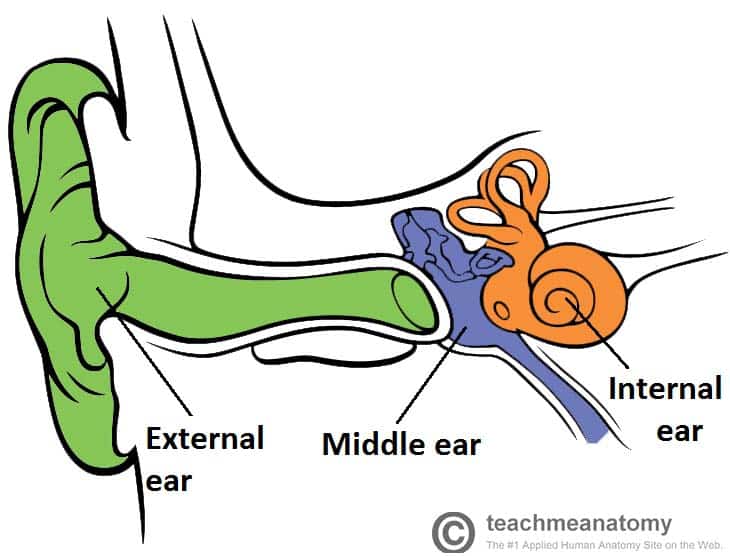 The Middle Ear Parts Bones Muscles Teachmeanatomy
The Middle Ear Parts Bones Muscles Teachmeanatomy
 Anatomy Of The Ear Professional Hearing Services
Anatomy Of The Ear Professional Hearing Services
 Types Of Hearing Impairment University Of Iowa Hospitals
Types Of Hearing Impairment University Of Iowa Hospitals
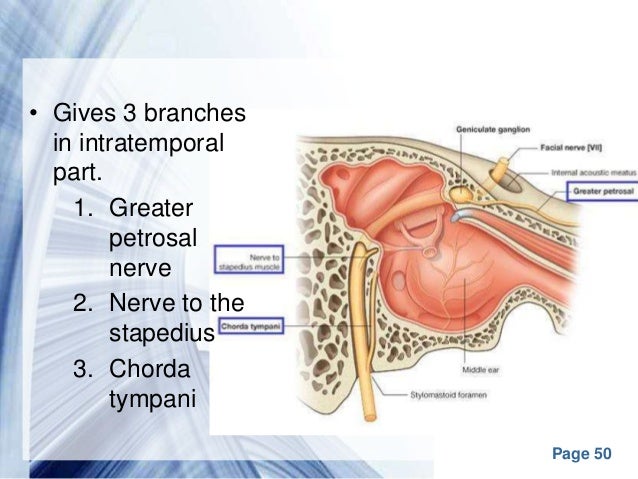
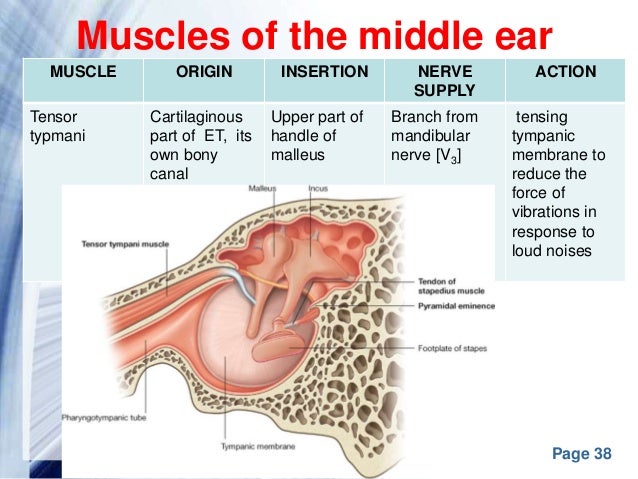



Belum ada Komentar untuk "Anatomy Of Middle Ear"
Posting Komentar