Striations Anatomy
Hence the word skeletal. Marked with striations or striae.
Skeletal muscle is the tissue that most muscles attached to bones are made of.

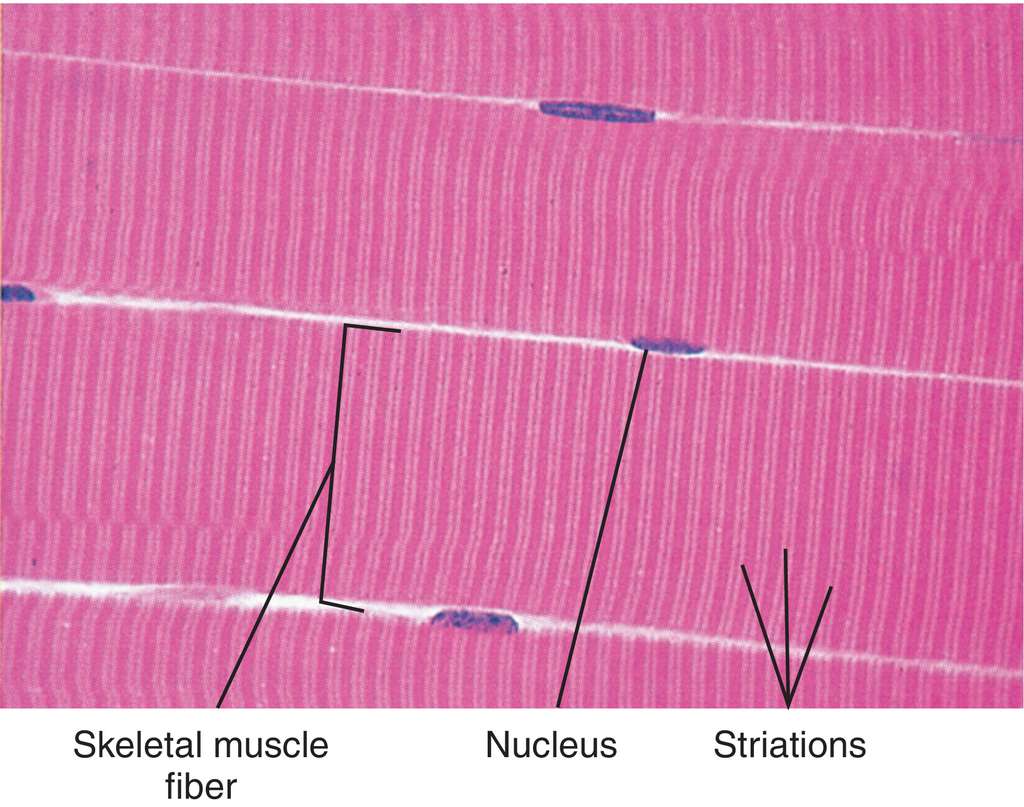
Striations anatomy. Striated definition is marked with striations or striae. Its long thin multinucleated fibres are crossed with a regular pattern of fine red and white lines. The light bands contain actin and are called i bands because they are isotropic to polarized light.
Unlike smooth muscle and cardiac muscle skeletal muscle is under voluntary control. Skeletal muscle also called voluntary muscle in vertebrates most common of the three types of muscle in the body. When used in the context of the anatomy of muscle structures the word striations refers to the stripe like visual features found in skeletal muscle.
Strīāshənz npl the transverse alternating light and dark bands of skeletal muscles that result from differences in light absorption. Striations means a series of ridges furrows or linear marks and is used in several ways. In the case of skeletal muscle cells the stripes are created by a repeating series of dark and light bands.
Striation geology a striation as a result of a geological fault. The striation is due to the regular alternation of the contractile proteins actin and myosin along with the structural proteins that couple the contractile proteins to connective tissues. Any of a number of scratches or parallel grooves on the surface of a rock resulting from the action of moving ice as of a glacier.
In hyperbolic geometry a striation is a reflection across two parallel mirrors. Separate one sarcomere from the next. In anatomy striated muscle.
Of relating to or being striated muscle see the full definition. A term applied to skeletal muscle to indicate that these muscles are generally under conscious control by the higher brain centers. Striation fatigue in material.
Striated musculature is comprised of two types of tissues. Striation valley in antarctica. Under the light microscope muscle cells appear striated with many nuclei squeezed along the membranes.
Skeletal muscle and cardiac muscle. These visual features consist of alternating light and dark striations that can be observed using just a simple light microscope. Similar to cardiac muscle however skeletal muscle is striated.
Skeletal muscles are attached to bones by tendons and they produce all the movements of body parts in relation to each other. Thin filaments attach series of ridges furrows or linear marks one of the cross striations in the striated muscle that contai lighter areas of non overlap between actin and myosin that con the region of a striated muscle fibre that contains only thick striations series of ridges furrows.
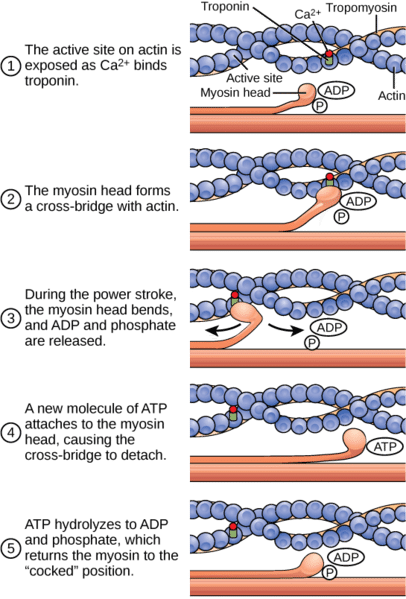 Ultrastructure Of Muscle Skeletal Sliding Filament
Ultrastructure Of Muscle Skeletal Sliding Filament
 9 3 Skeletal Muscle Fibers Contain Calcium Regulated
9 3 Skeletal Muscle Fibers Contain Calcium Regulated
 Anatomy Review Skeletal Muscle Tissue Sinoe Medical Homepage
Anatomy Review Skeletal Muscle Tissue Sinoe Medical Homepage
 Root Anatomy Of Epidendrum Radicans A Transverse Section
Root Anatomy Of Epidendrum Radicans A Transverse Section
Ch 09 General Muscle Terminology
 Obliquely Striated Muscle Anatomy Britannica
Obliquely Striated Muscle Anatomy Britannica
 Types Of Muscle Tissues Anatomy And Physiology
Types Of Muscle Tissues Anatomy And Physiology
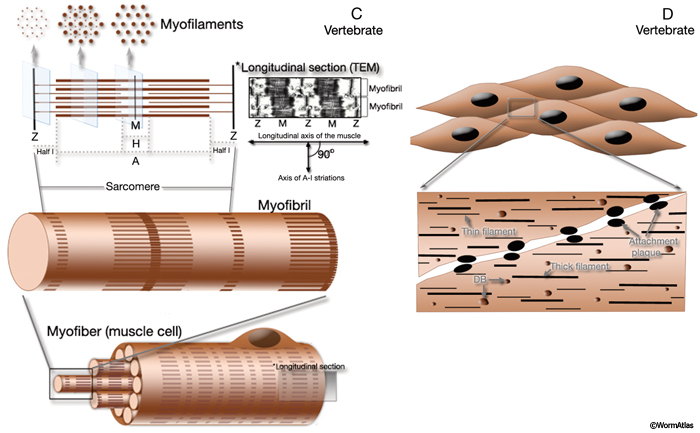 Handbook Muscle System Introduction
Handbook Muscle System Introduction
 Physiology And Anatomy Of Muscles
Physiology And Anatomy Of Muscles
 Difference Between Striated Non Striated And Cardiac Muscles
Difference Between Striated Non Striated And Cardiac Muscles
 Anatomy 2a Quiz 4 2 Answers Ppt Video Online Download
Anatomy 2a Quiz 4 2 Answers Ppt Video Online Download
 Sarcomere Definition Structure Function And Quiz
Sarcomere Definition Structure Function And Quiz
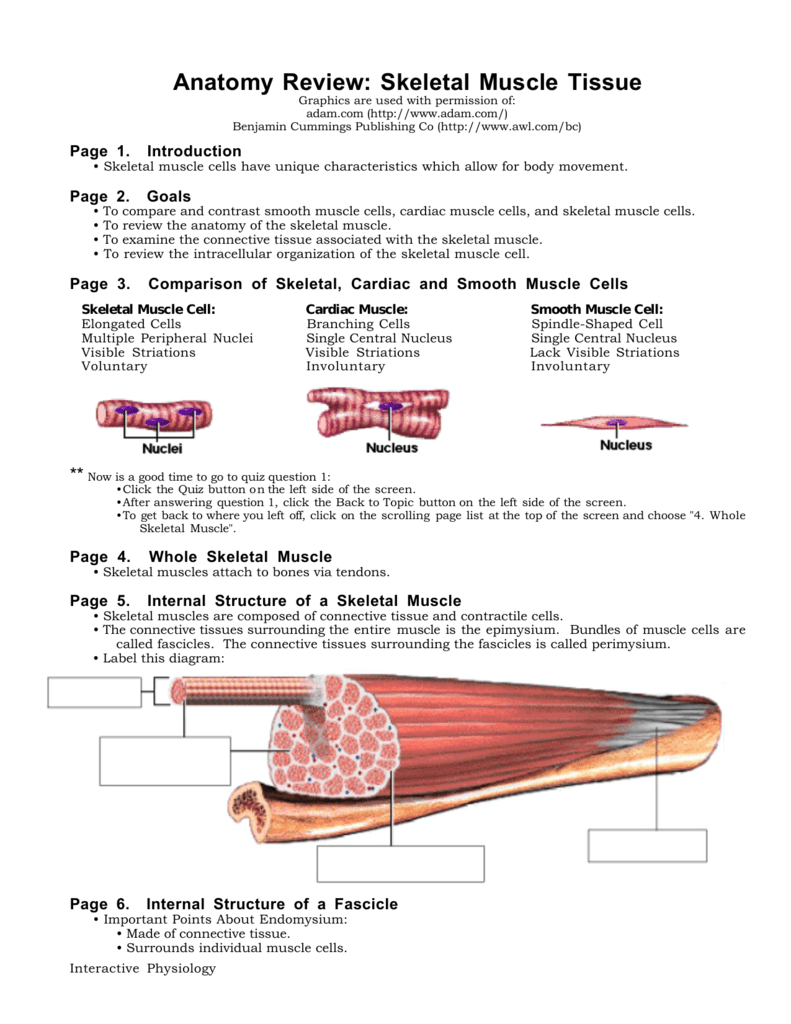 Anatomy Review Skeletal Muscle Tissue
Anatomy Review Skeletal Muscle Tissue
 Non Striated Muscle Stock Photos Non Striated Muscle Stock
Non Striated Muscle Stock Photos Non Striated Muscle Stock
 Striated Muscle Stock Photos Download 225 Royalty Free Photos
Striated Muscle Stock Photos Download 225 Royalty Free Photos
 Somso Transversely Striated Muscular Fibre With Motor End Plate
Somso Transversely Striated Muscular Fibre With Motor End Plate
 Striated Muscle Stock Photos Download 225 Royalty Free Photos
Striated Muscle Stock Photos Download 225 Royalty Free Photos
Ch 09 General Muscle Terminology

 Cardiac Muscle Definition Function And Structure
Cardiac Muscle Definition Function And Structure
 Anatomy Neurobiology Ana 812 Lab Session Muscle Tissue
Anatomy Neurobiology Ana 812 Lab Session Muscle Tissue
 Cardiac Muscle Striations Nuclei And Intercalated Discs
Cardiac Muscle Striations Nuclei And Intercalated Discs
 Types Of Muscle Tissue And Fibers Biology For Majors Ii
Types Of Muscle Tissue And Fibers Biology For Majors Ii
 Full Size Picture Striated Muscle Jpg
Full Size Picture Striated Muscle Jpg





Belum ada Komentar untuk "Striations Anatomy"
Posting Komentar