Surface Anatomy Of Foot
The tuberosity of the fifth metatarsal is. The medial tubercle of the calcaneus can be palpated by grasping the heel.
 Surface Anatomy Barchart Santa Fe Community College Bookstore
Surface Anatomy Barchart Santa Fe Community College Bookstore
First metatarsalphalangeal joint 11.
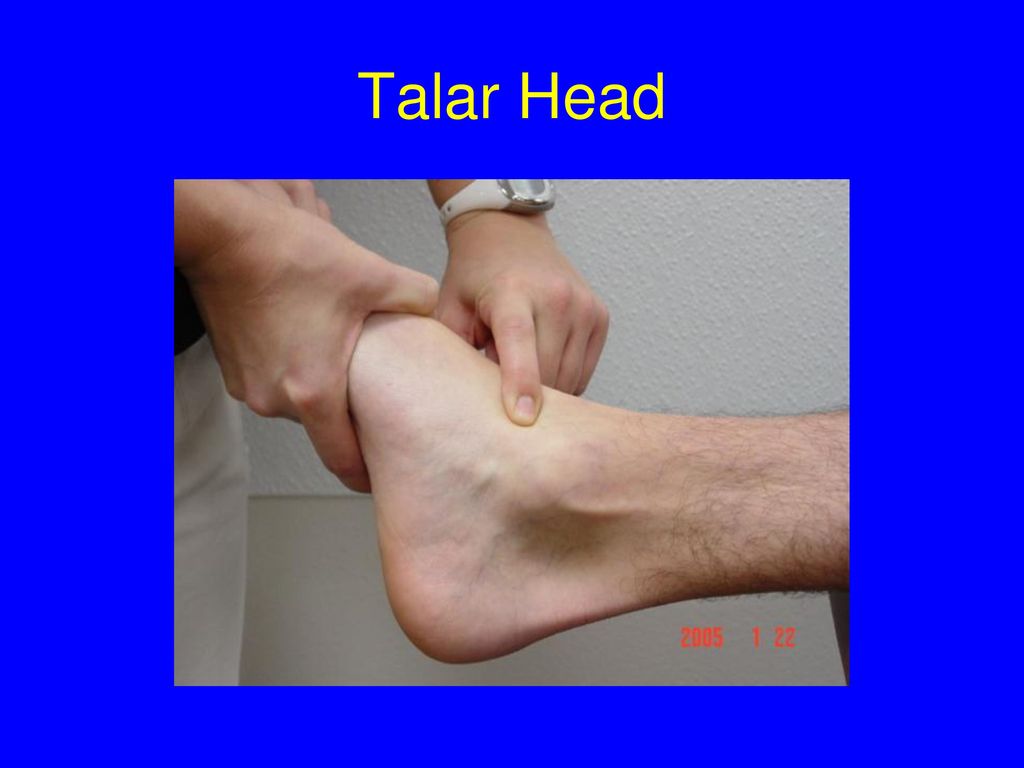
Surface anatomy of foot. The forefoot meets the midfoot at the five tarsometatarsal tmt joints. The head of the talus can be palpated just below the lateral malleolus when the foot is inverted. Foot surface anatomy 1.
You can palpate medically examine by touch the following bones in the foot. There is relatively thin skin over the medial. Broken bones in the foot usually call for rest ice compression and elevation to reduce any swelling.
Surface anatomy of the foot for the clinician and operator an exact knowledge of surface anatomy is absolutely essential. The most common broken bones in the foot are broken toes which may occur after hitting a toe on a hard or sharp surface while walking running swimming or playing sports. These muscles arise from the calca the skin specialized skin on the plan skin thickness.
It can readily be acquired because the various bony points and tendons are usually evident both to touch and sight. Foot surface anatomy 2. In addition to the phalanges and metatarsals the forefoot contains two small oval shaped sesamoid bones just beneath the head of the first metatarsal on the plantar surface or underside of the foot that are held in place by tendons and ligaments.
There is relatively thin skin over the medial plantar aponeurosis. Deep anatomy of the sole the glabrous skin on the sole of the foot lacks the hair and pigmentation found elsewhere on the body and it has a high concentration of sweat pores. The toenail surface anatomy peer review orthopaedicsone peer review workflow is an innovative platform that allows the process of peer review to occur right within an orthopaedicsone article in an open transparent and flexible manner.
Bony palpation medial aspect 3. The sole contains the thickest layers of skin on the body due to the weight that is continually placed on it. The thinner part of the plantar fascia ru weight bearing maintaining the arch of the foot and moving t layer 1.
 Talocrural Articulation Or Ankle Joint Human Anatomy
Talocrural Articulation Or Ankle Joint Human Anatomy
 Regional Anatomy Foot At Texas Woman S University Studyblue
Regional Anatomy Foot At Texas Woman S University Studyblue
 Fg Anatomy G48 Anterior Lateral Leg Anatomy Unit 6
Fg Anatomy G48 Anterior Lateral Leg Anatomy Unit 6
 Synovial Sheaths And Tendons At Ankle C Surface Anatomy Of
Synovial Sheaths And Tendons At Ankle C Surface Anatomy Of
 3d Printed Foot Structures Of The Plantar Surface
3d Printed Foot Structures Of The Plantar Surface
 Foot Surface Anatomy Ppt Download
Foot Surface Anatomy Ppt Download
 Surface Anatomy Of The Lower Extremity Prohealthsys
Surface Anatomy Of The Lower Extremity Prohealthsys
 Evidence Based Surface Anatomy For Acupuncture Huang And
Evidence Based Surface Anatomy For Acupuncture Huang And
 Lateral Aspect Of Leg And Foot A Surface Anatomy
Lateral Aspect Of Leg And Foot A Surface Anatomy
 Section 8 Atlas Of Surface Anatomy Hadzic S Peripheral
Section 8 Atlas Of Surface Anatomy Hadzic S Peripheral
 Photo By Medical Rf A Superior Anterolateral View Left Side Of The Bones Of The Left Foot The Surface Anatomy Of The Body Is Semi Transparent And
Photo By Medical Rf A Superior Anterolateral View Left Side Of The Bones Of The Left Foot The Surface Anatomy Of The Body Is Semi Transparent And
 Duke Anatomy Lab 2 Pre Lab Exercise
Duke Anatomy Lab 2 Pre Lab Exercise
 The Anatomy Of The Human Foot Sciencedirect
The Anatomy Of The Human Foot Sciencedirect
 Foot And Ankle Surface Anatomy
Foot And Ankle Surface Anatomy
 Foot And Ankle Musculoskeletal Key
Foot And Ankle Musculoskeletal Key
 Region Of The Knee Surface Anatomy
Region Of The Knee Surface Anatomy
 Patient Education Concord Orthopaedics
Patient Education Concord Orthopaedics
 Anatomy Of The Foot And Ankle Orthopaedia
Anatomy Of The Foot And Ankle Orthopaedia
 Atlas Of Surface Anatomy Hadzic S Peripheral Nerve Blocks
Atlas Of Surface Anatomy Hadzic S Peripheral Nerve Blocks
 Surface Anatomy Atlas Of Anatomy
Surface Anatomy Atlas Of Anatomy
 Patient Education Concord Orthopaedics
Patient Education Concord Orthopaedics
 Male And Female Anatomical Body Surface Anatomy Human Body
Male And Female Anatomical Body Surface Anatomy Human Body
 11 Surface Anatomy Of The Medial Ankle Mm Medial Malleolus
11 Surface Anatomy Of The Medial Ankle Mm Medial Malleolus
 Ch 12 Diagram Surface Anatomy Anterior Leg Foot
Ch 12 Diagram Surface Anatomy Anterior Leg Foot



Belum ada Komentar untuk "Surface Anatomy Of Foot"
Posting Komentar