Ear Anatomy External
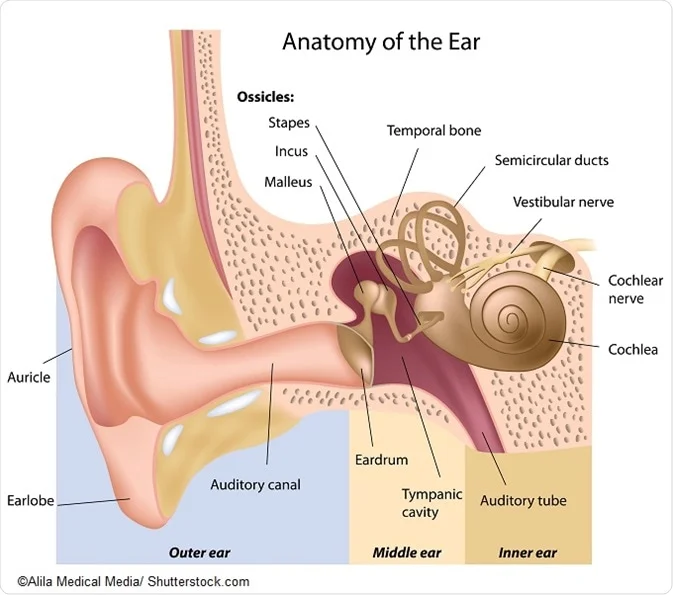
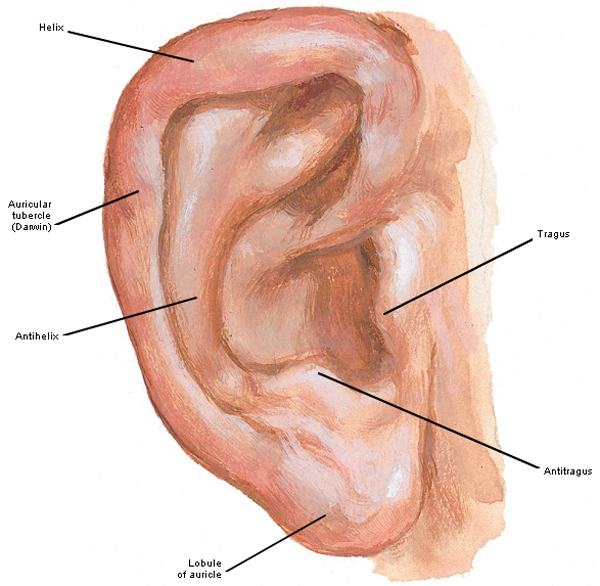
Auricle pinna auricle is composed of thin plate of elastic cartilage covered by layer of skin. The external ear functions to collect and amplify sound which then gets transmitted to the middle ear.
 Healthcare Health Solution External Ear Anatomy And Function
Healthcare Health Solution External Ear Anatomy And Function
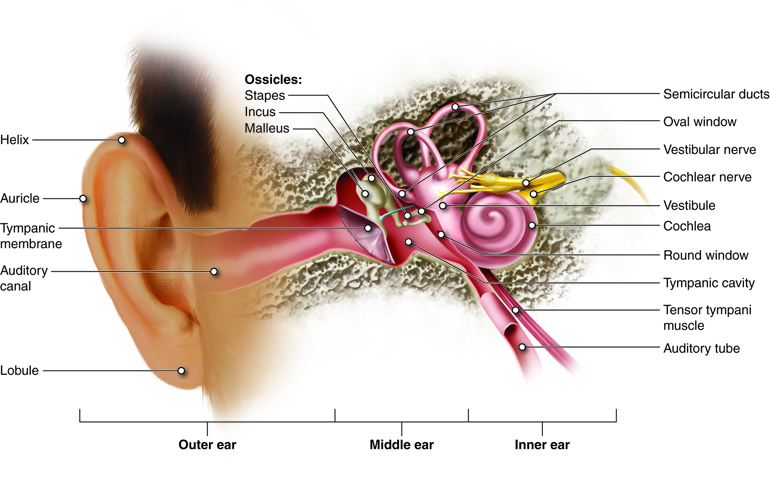
Sound causes the eardrum and its tiny attached bones in the middle portion of the ear to vibrate.
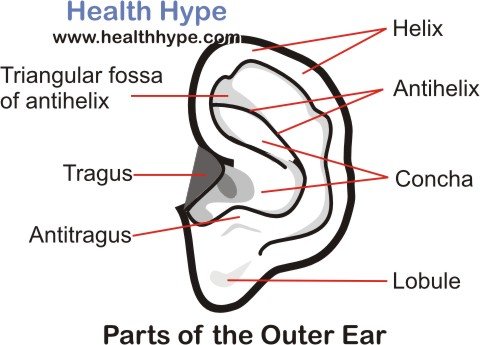
Ear anatomy external. Sound travels through the auricle and the auditory canal a short tube that ends at the eardrum. The funnel like curves of auricle collects sound wave and direct them to middle ear. The outer ear includes.
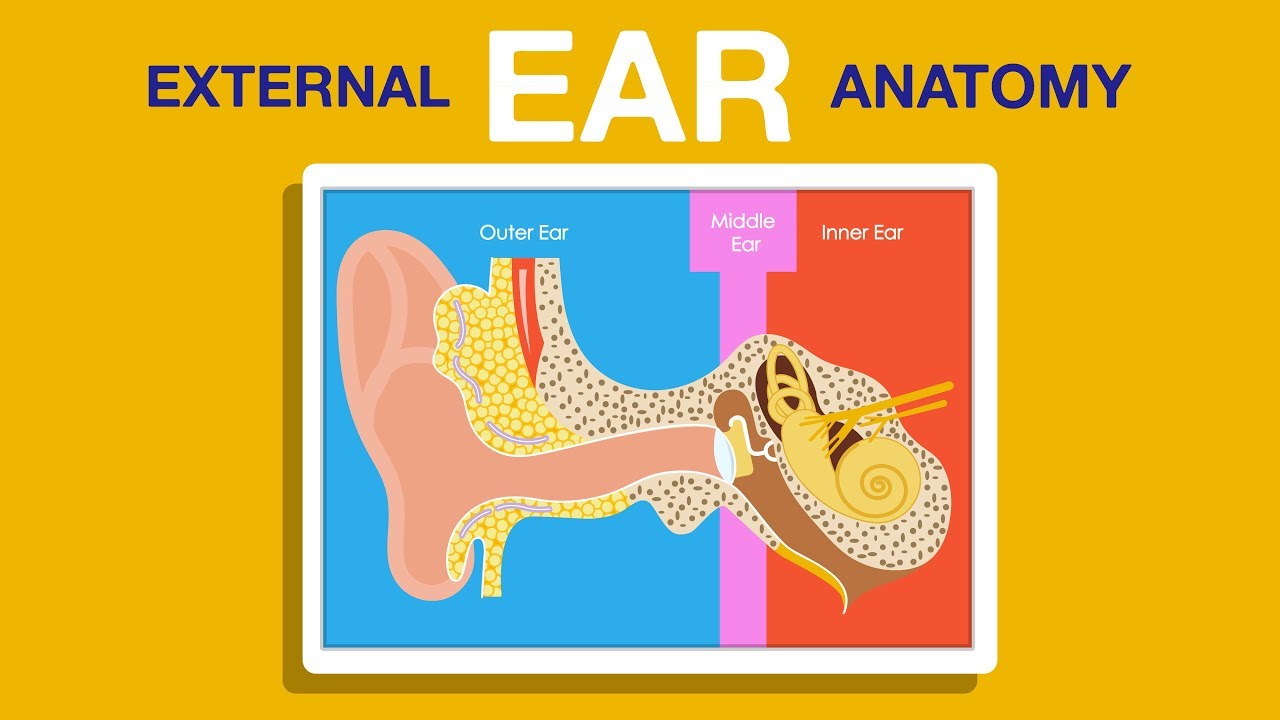
Ear anatomy outer ear. Under the skin the outer one third of the canal is cartilage and inner two thirds is bone. The external ear can be divided functionally and structurally into two parts.
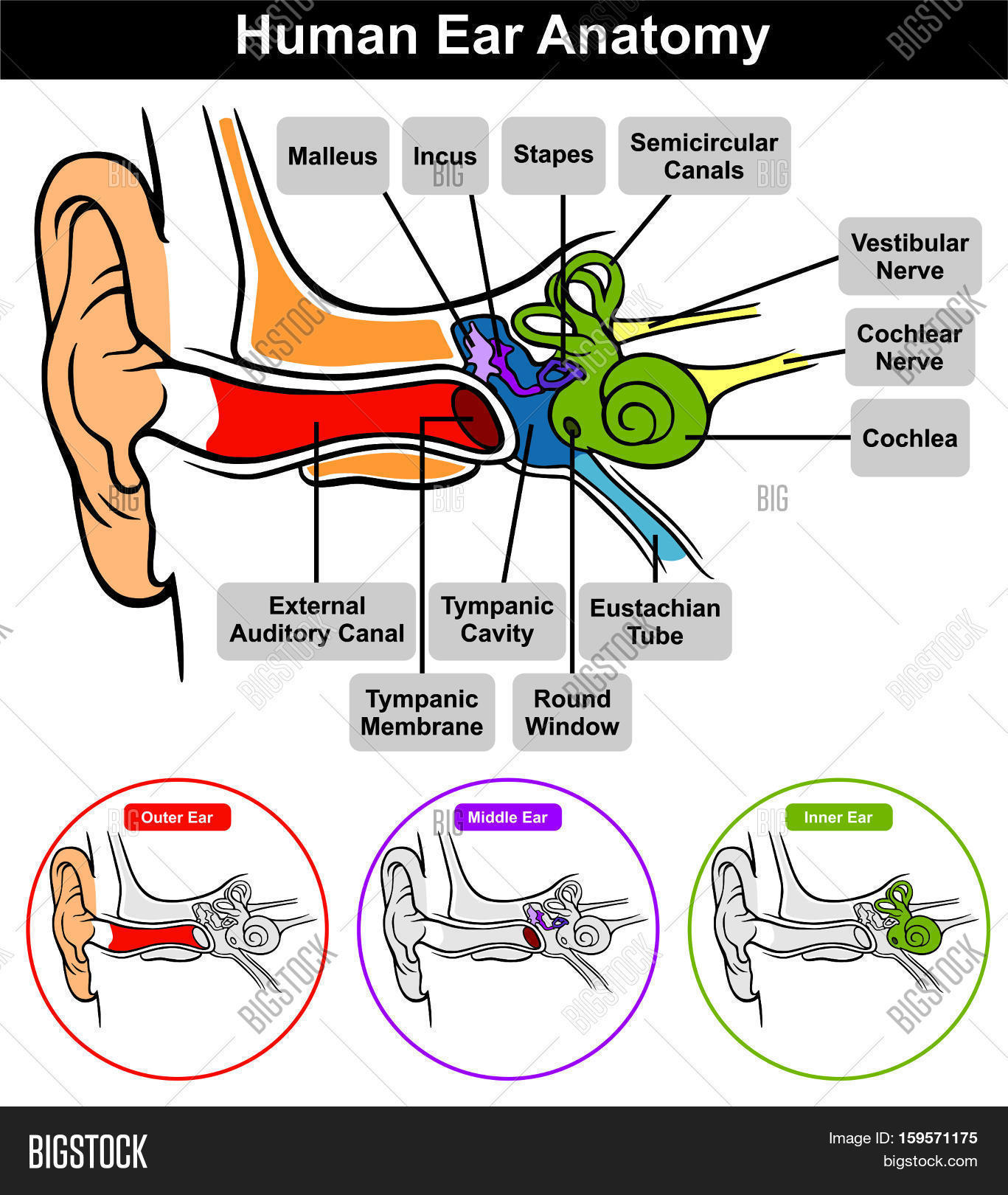
Auricle cartilage covered by skin placed on opposite sides of the head auditory canal also called the ear canal eardrum outer layer also called the tympanic membrane the outer part of the ear collects sound. Ear canal the ear canal starts at the outer ear and ends at the ear drum. The cochlea is shaped like a snail and is divided into two chambers by a membrane.
Ear anatomy inner ear. The chambers are full of fluid which vibrates when sound comes in and causes the small hairs which line the membrane to vibrate and send electrical impulses to the brain. The skin of the ear canal is very sensitive to pain and pressure.
The outer ear is called the pinna and is made of ridged cartilage covered by skin. Picture of the ear. The auricle and external acoustic meatus or external auditory canal compose the external ear.
The auricle or pinna and the external acoustic meatus which ends at the tympanic membrane. The cochlea which is the hearing portion and the semicircular canals is the balance portion. External ear is composed of auricle and external auditory canal meatus.
Sound funnels through the pinna into the external auditory canal a short tube that ends at the eardrum tympanic membrane. By teachmeseries ltd 2019. The asymmetric shape of the external auricle introduces delays in the path of sound that assist in sound localization.
The outer ear external ear or auris externa is the external portion of the ear which consists of the auricle also pinna and the ear canal. It gathers sound energy and focuses it on the eardrum tympanic membrane. The canal is approximately an inch in length.
 Hearing And Equilibrium Anatomy And Physiology
Hearing And Equilibrium Anatomy And Physiology
 Types Of Hearing Impairment University Of Iowa Hospitals
Types Of Hearing Impairment University Of Iowa Hospitals
 Sense Of Hearing Anatomy And Physiology 1 2 With Mrs
Sense Of Hearing Anatomy And Physiology 1 2 With Mrs
 Human Ear Anatomy Image Photo Free Trial Bigstock
Human Ear Anatomy Image Photo Free Trial Bigstock
 Chapter 47 Diseases Of The External Ear Current Diagnosis
Chapter 47 Diseases Of The External Ear Current Diagnosis
 Ear Auricle The Human Outer Ear Anatomy Stock Photo
Ear Auricle The Human Outer Ear Anatomy Stock Photo
 Anatomy And Physiology Of The Ear Children S Wisconsin
Anatomy And Physiology Of The Ear Children S Wisconsin
 Picture Of The Ear Ear Conditions And Treatments
Picture Of The Ear Ear Conditions And Treatments
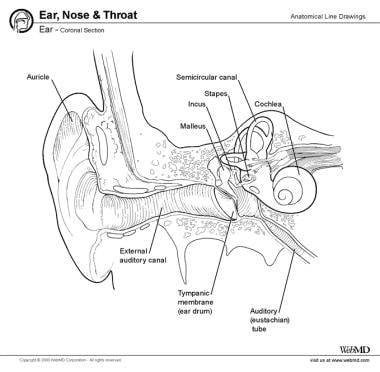 Ear Anatomy Overview Embryology Gross Anatomy
Ear Anatomy Overview Embryology Gross Anatomy
:watermark(/images/watermark_only.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/anatomy_term/meatus-acusticus-externus-2/cNYVakPkJkzvw8J3mO7HA_Meatus_acusticus_externus_01.png) Ear Anatomy Parts And Functions Kenhub
Ear Anatomy Parts And Functions Kenhub
 2 Anatomy Of The Of The External Ear Doctor Online 2016
2 Anatomy Of The Of The External Ear Doctor Online 2016
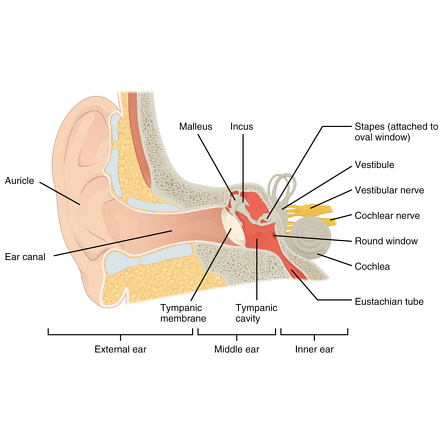 Middle Ear Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org
Middle Ear Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org
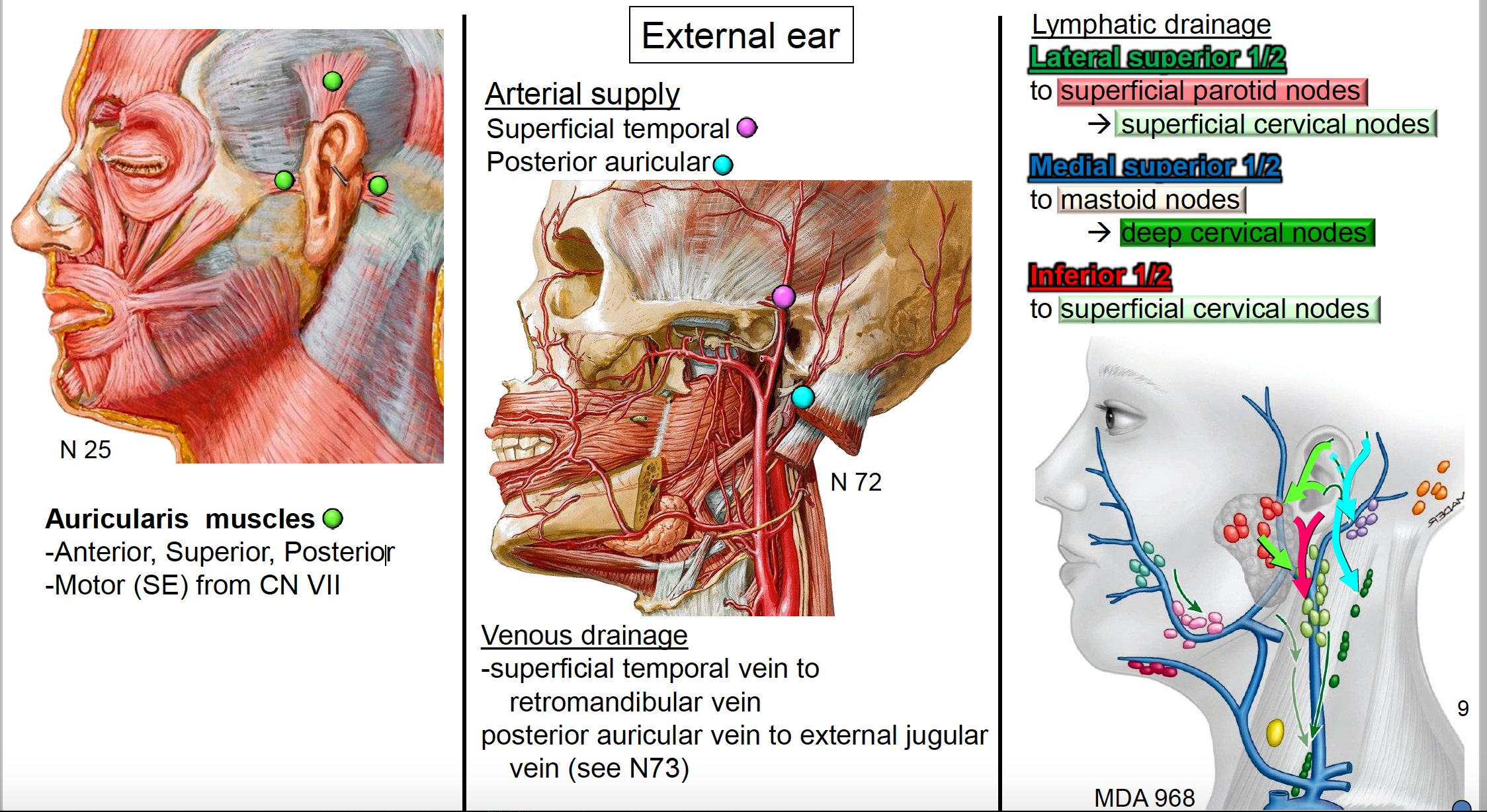
 Pdf Anatomy And Orientation Of The Human External Ear
Pdf Anatomy And Orientation Of The Human External Ear
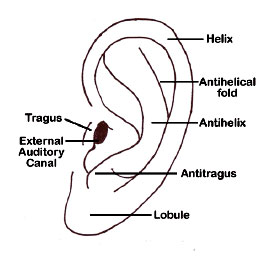 Hearing Outer Ear Development Embryology
Hearing Outer Ear Development Embryology
 Special Senses External Middle Ear Anatomy
Special Senses External Middle Ear Anatomy
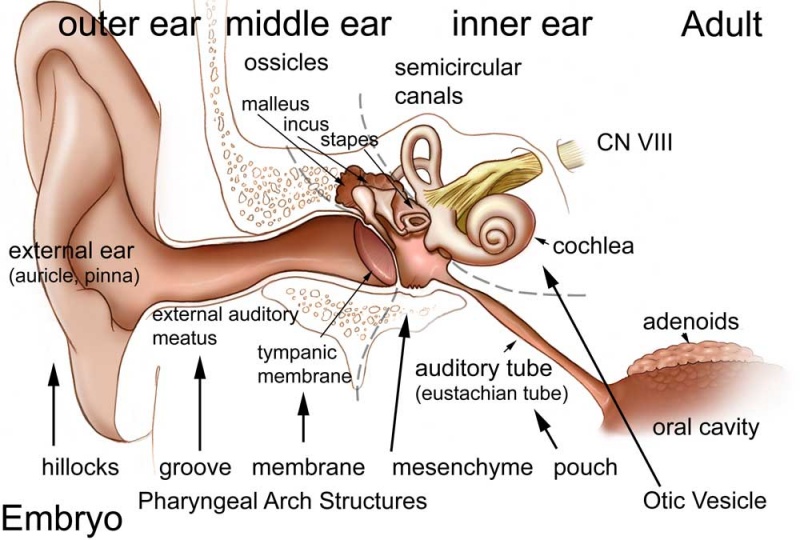 Lecture Sensory Development Embryology
Lecture Sensory Development Embryology
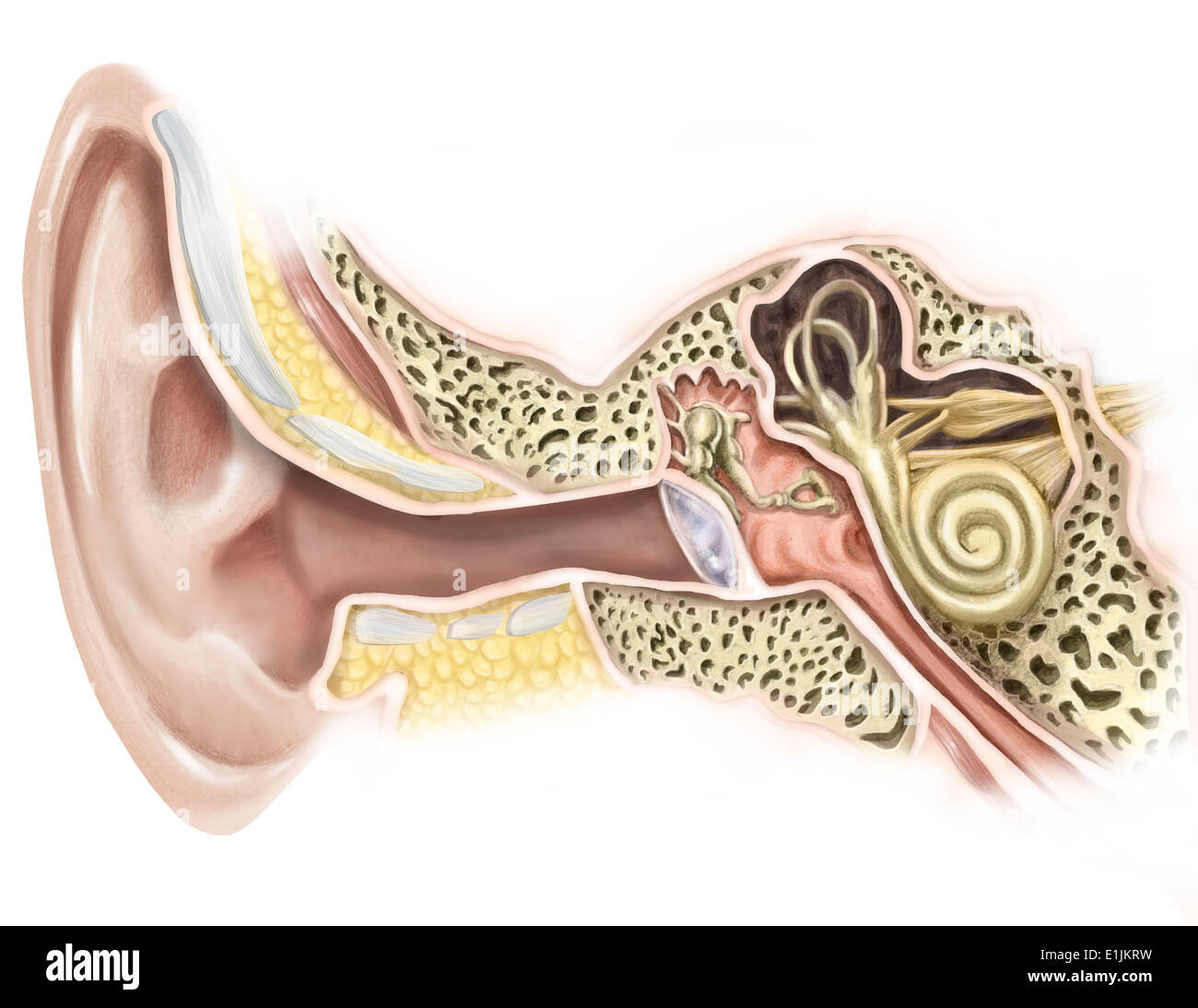 External Auditory Canal Of Human Ear Stock Photo 69866829
External Auditory Canal Of Human Ear Stock Photo 69866829
 Do You Hear What I Hear Signs And Symptoms Of Tinnitus
Do You Hear What I Hear Signs And Symptoms Of Tinnitus
 External Ear Anatomy And Function In 2019 External Ear
External Ear Anatomy And Function In 2019 External Ear

 Exam 12 Chap 15 Hearing Anatomy Physiology Kaap309
Exam 12 Chap 15 Hearing Anatomy Physiology Kaap309
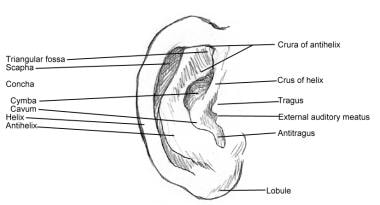 Ear Anatomy Overview Embryology Gross Anatomy
Ear Anatomy Overview Embryology Gross Anatomy
 Anatomy Of The Ear S External Structures
Anatomy Of The Ear S External Structures
 Human Ear Anatomy Parts Outer Middle Inner Diagram
Human Ear Anatomy Parts Outer Middle Inner Diagram
 Outer External Part Of Human Ear Structure Picture And Definitions
Outer External Part Of Human Ear Structure Picture And Definitions
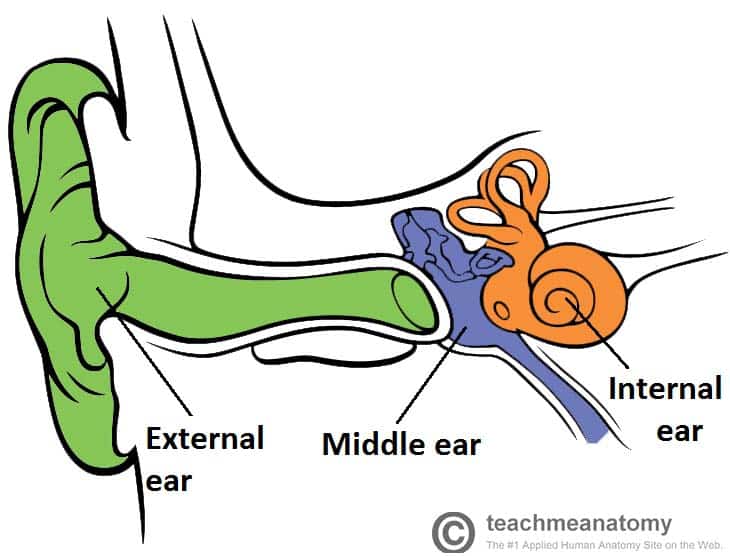 The External Ear Structure Function Innervation
The External Ear Structure Function Innervation


Belum ada Komentar untuk "Ear Anatomy External"
Posting Komentar