Action Potential Definition Anatomy
That property is called the excitability. An action potential is defined as a sudden fast transitory and propagating change of the resting membrane potential.
To get an electrical signal started the membrane potential has to change.
Action potential definition anatomy. This starts with a channel opening for na in the membrane. In the neuron an action potential produces the nerve impulse and in the muscle cell it produces the contraction required for all movement. Action potential definition the change in electrical potential that occurs between the inside and outside of a nerve or muscle fiber when it is stimulated serving to transmit nerve signals.
Sodium and potassium channels. As a result the polarity of the neuron is maintained as mentioned above. Action potential the brief about one thousandth of a second reversal of electric polarization of the membrane of a nerve cell neuron or muscle cell.
The action potential is a rapid and reversible reversal of the electrical potential difference across the plasma membrane of excitable cells such as neurons muscle cells and some endocrine cells. The action potential resting membrane potential describes the steady state of the cell which is a dynamic process that is balanced by ion leakage and ion pumping. An electric impulse consisting of a self propagating series of polarizations and depolarizations transmitted across the plasma membranes of a nerve fiber during the transmission of a nerve impulse and across the plasma membranes of a muscle cell during contraction or another activity.
When myelination is present the action potential propagates differently. Only neurons and muscle cells are capable of generating an action potential. Without any outside influence it will not change.
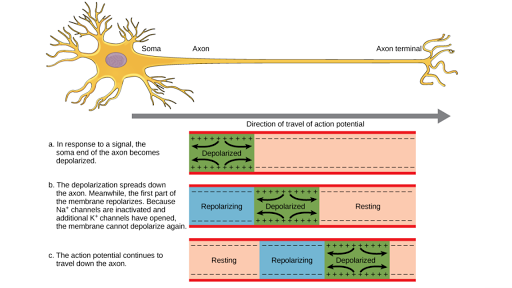
Open or close in response to changes in membrane potential. Propagation as described above applies to unmyelinated axons. The action potential must propagate toward the axon terminals.
Without any outside influence it will not change. Resting membrane potential describes the steady state of the cell which is a dynamic process that is balanced by ion leakage and ion pumping. To get an electrical signal started the membrane potential has to change.
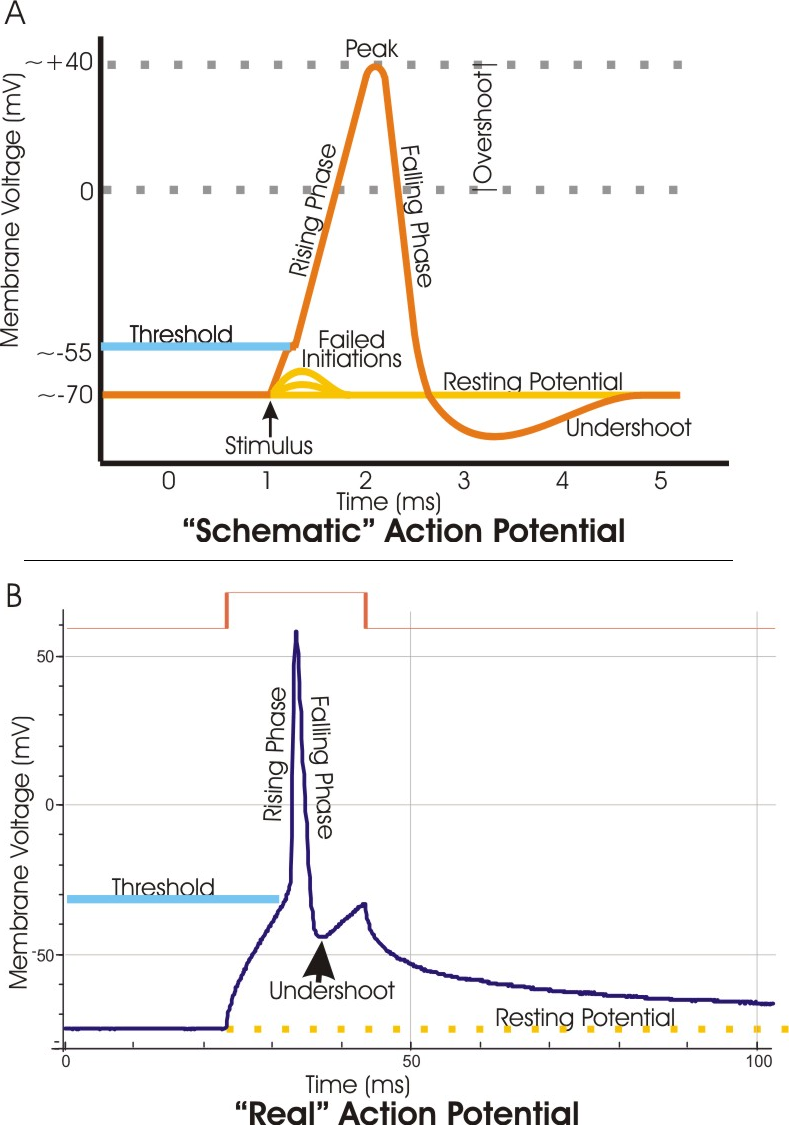
Throughout but more in the axon especially in the axon hillock. In a neuronal action potential the membrane potential rapidly changes from its resting level of approximately 70 mv to around 50 mv and subsequently rapidly returns to the resting level again.
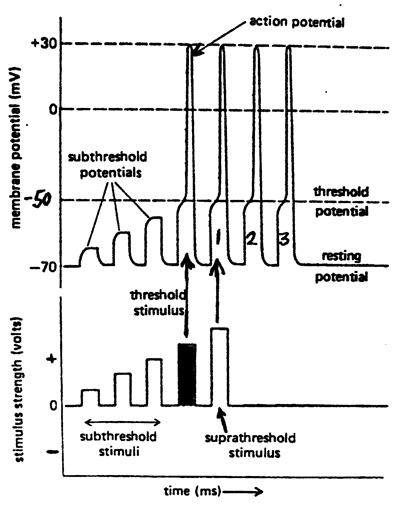 Subthreshold Threshold And Suprathreshold Stimuli
Subthreshold Threshold And Suprathreshold Stimuli
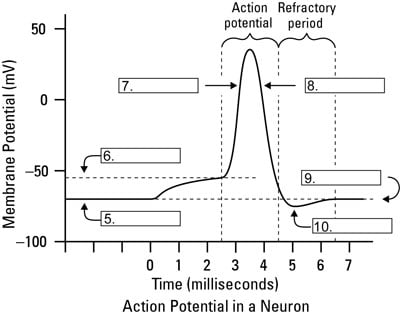 Action Potential Of Neurons Dummies
Action Potential Of Neurons Dummies
 Cnap Compound Nerve Action Potential
Cnap Compound Nerve Action Potential
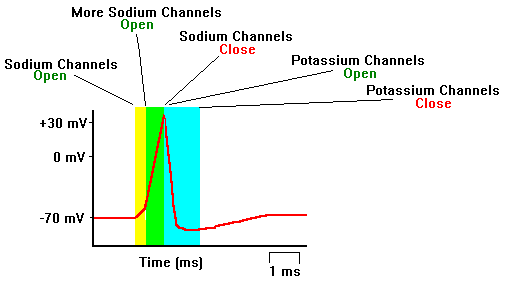 Neuroscience For Kids Action Potential
Neuroscience For Kids Action Potential
Difference Between Depolarization And Repolarization
 Graded Potential An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Graded Potential An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
 Cardiac Electrophysiology Action Potential Automaticity
Cardiac Electrophysiology Action Potential Automaticity
 The Nervous System Chapter Ppt Video Online Download
The Nervous System Chapter Ppt Video Online Download
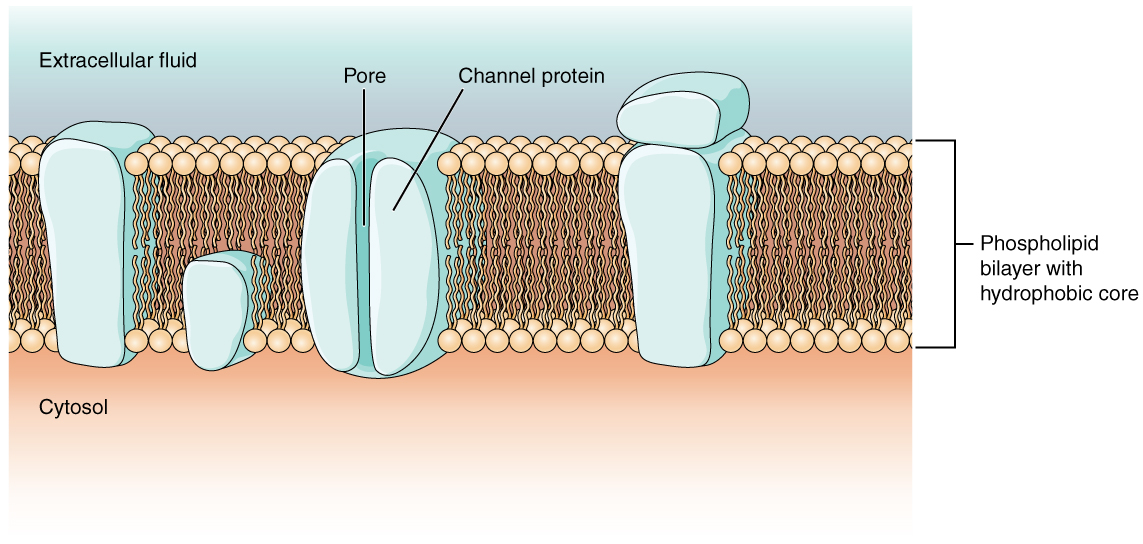 12 4 The Action Potential Anatomy And Physiology
12 4 The Action Potential Anatomy And Physiology
 Action Potential In The Neuron
Action Potential In The Neuron
Ch 11 Histology Of The Neurons Axon
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-172594438-56a796f13df78cf7729768ee.jpg) All Or None Law For Nerves And Muscles
All Or None Law For Nerves And Muscles
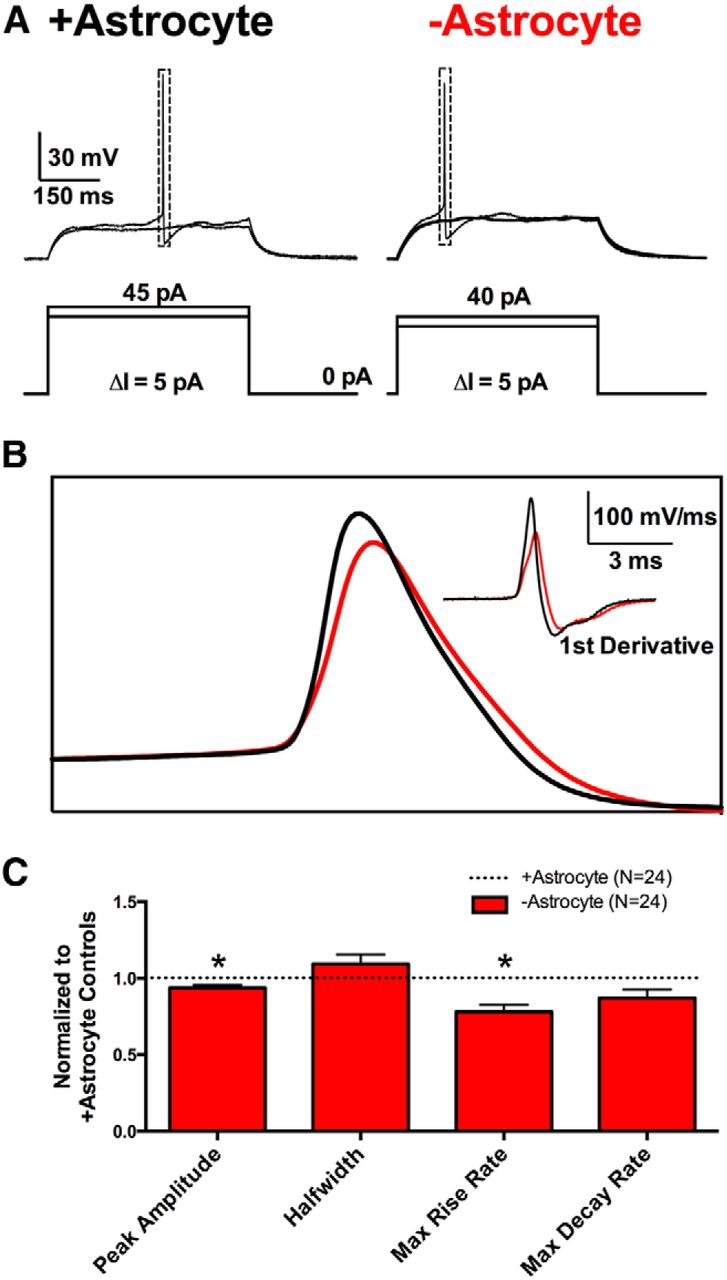 Loss Of Local Astrocyte Support Disrupts Action Potential
Loss Of Local Astrocyte Support Disrupts Action Potential
 Action Potential Definition Steps Facts Britannica
Action Potential Definition Steps Facts Britannica
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/11527/anatomy-neurons-basic-types_english.jpg) Action Potential Definition Steps Phases Kenhub
Action Potential Definition Steps Phases Kenhub
Difference Between Depolarization And Repolarization
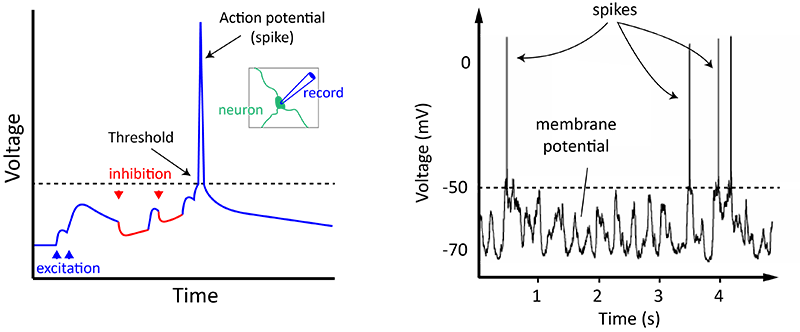 Action Potentials And Synapses Queensland Brain Institute
Action Potentials And Synapses Queensland Brain Institute
 How To Label An Action Potential Graph Showing
How To Label An Action Potential Graph Showing
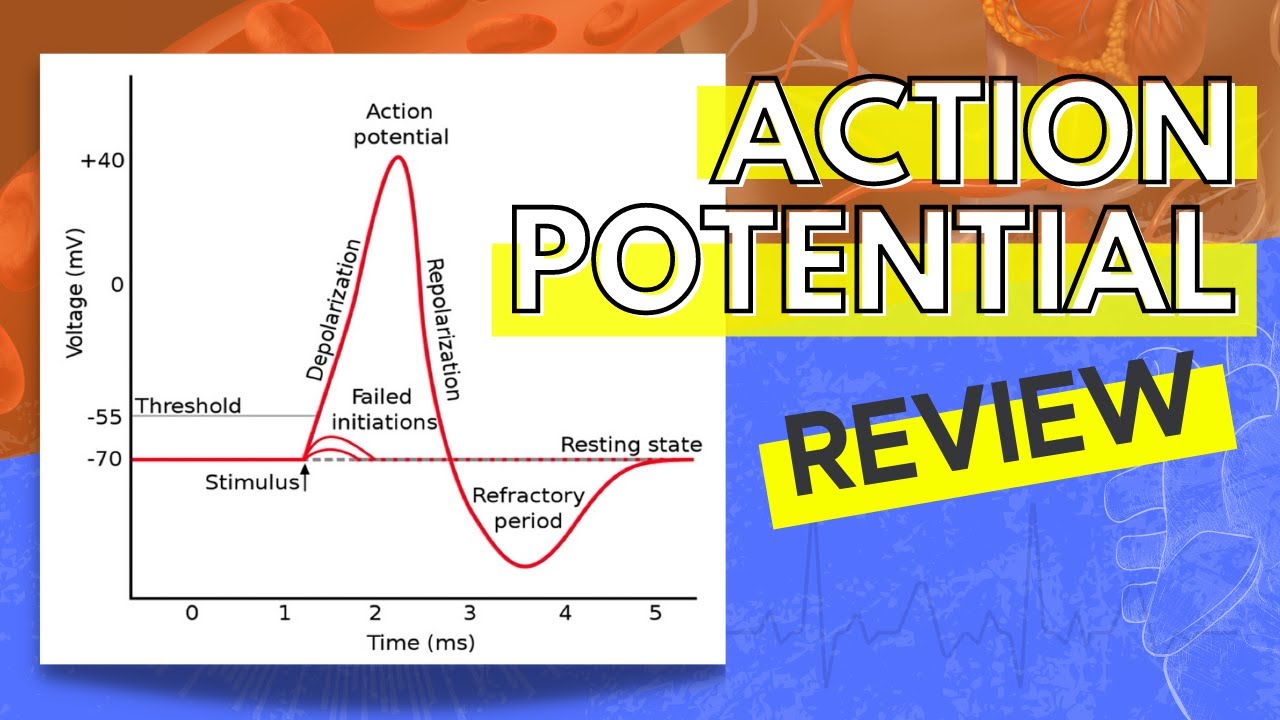 The Action Potential Anatomy And Physiology I
The Action Potential Anatomy And Physiology I
 Action Potential Definition Steps Facts Britannica
Action Potential Definition Steps Facts Britannica
 Best Action Potential Explanation
Best Action Potential Explanation



Belum ada Komentar untuk "Action Potential Definition Anatomy"
Posting Komentar