Joints Anatomy
These joints are divided into three categories based on the number of axes of motion provided by each. For example between vertebrae in the spine.
 What Is The Si Joint Si Joint Anatomy Si Bone
What Is The Si Joint Si Joint Anatomy Si Bone
These joints occur where the connection between the articulating bones is made up of cartilage.

Joints anatomy. They have varying shapes but the important thing about them is the movement they allow. Joints can be grouped by their structure into fibrous cartilaginous and synovial joints 1 a synchrondosis is an immovable cartilaginous joint. A tissue called the synovial membrane lines the joint.
These joints are called immovable joints and are primarily meant for growth and they permit molding during child birth. A fibrous joint is where the bones are bound by a tough fibrous tissue. Strong ligaments tough elastic bands of connective tissue surround.
There are more joints in a child then in an adult because as growth proceeds some of the bones fuse together eg. 2 a symphysis consists of a compressable fibrocartilaginous pad that connects two bones. Sutures are immovable joints synarthrosis and are only found between the flat plate like bones of the skull.
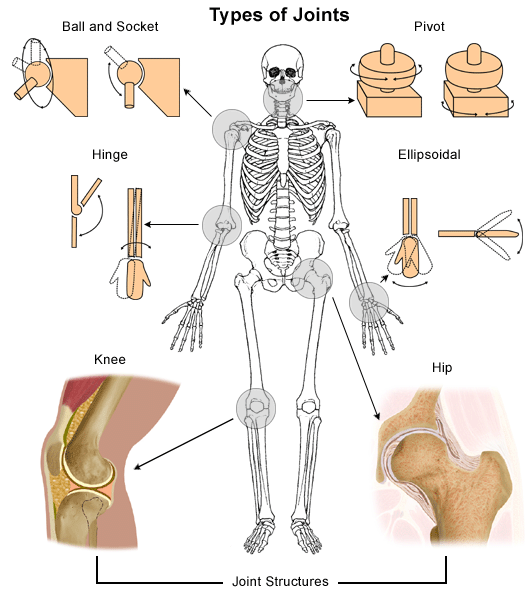
Since the cartilage is smooth and slippery the bones move against each other easily and without pain. Joints between skeletal elements exhibit a great variety of form and function and are classified into three general morphologic types. There are 6 types of synovial joints.
Fibrous joints can be further sub classified into sutures gomphoses and syndesmoses. Joints consist of the following. Transverse frontal and sagittal.
The ischium ilium and pubis fuse together to form the pelvic bone hip bone. These are typically joints that require strength. Lets go through each joint.
An axis in anatomy is described as the movements in reference to the three anatomical planes. Anatomy the place of union usually more or less movable between two or more rigid skeletal components bones cartilage or parts of a single bone. Synchondroses are temporary joints which are only present in children up until the end of puberty.
The joints may be classified anatomically into the following groups. Hip anatomy function and common problems. Cartilaginous synchondroses and symphyses.
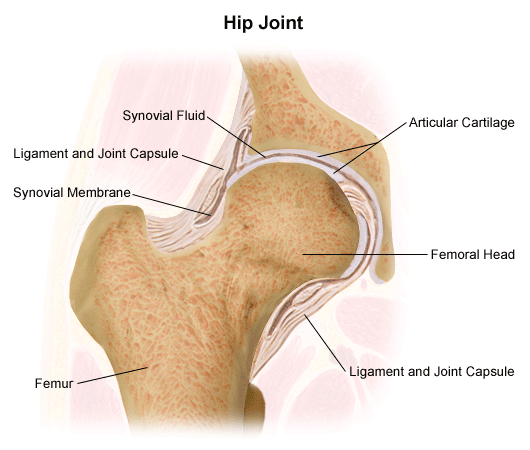
Most diarthrotic joints are found in the appendicular skeleton and thus give the limbs a wide range of motion. Large ligaments tendons and muscles around the hip joint called the joint capsule hold the bones ball and socket in place and keep it from dislocating. This is a type of tissue that covers the surface of a bone at a joint.
 Bones Of The Leg And Foot Interactive Anatomy Guide
Bones Of The Leg And Foot Interactive Anatomy Guide
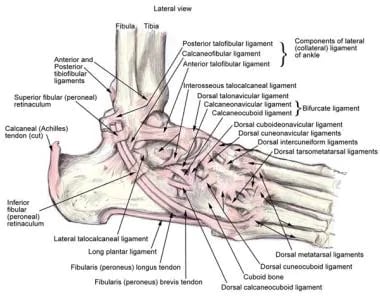 Ankle Joint Anatomy Overview Lateral Ligament Anatomy And
Ankle Joint Anatomy Overview Lateral Ligament Anatomy And
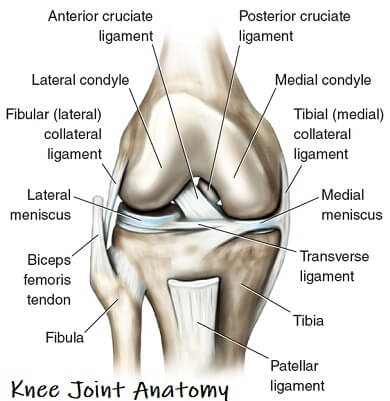 Knee Joint Anatomy Motion Knee Pain Explained
Knee Joint Anatomy Motion Knee Pain Explained
 Skeletal System And Ligaments Of The Joints Anatomical
Skeletal System And Ligaments Of The Joints Anatomical
Anatomy 101 Finger Joints The Handcare Blog
 Types Of Synovial Joints Biology For Majors Ii
Types Of Synovial Joints Biology For Majors Ii
 Lecture 11 Lower Limb Articulations I Body Joints
Lecture 11 Lower Limb Articulations I Body Joints
 Human Skeleton Structure Skull Spine Rib Cage Pelvis Joints Anatomy And Medicine 3d Vector Icon Set
Human Skeleton Structure Skull Spine Rib Cage Pelvis Joints Anatomy And Medicine 3d Vector Icon Set
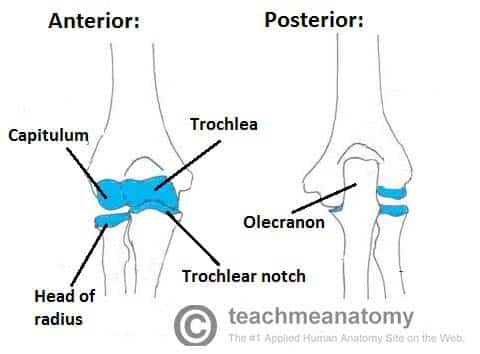 The Elbow Joint Structure Movement Teachmeanatomy
The Elbow Joint Structure Movement Teachmeanatomy
 Elbow Joint Anatomy Pictures And Information
Elbow Joint Anatomy Pictures And Information
Human Being Anatomy Skeleton Types Of Synovial Joints
 Anatomy Of The Foot North Arkansas Podiatry
Anatomy Of The Foot North Arkansas Podiatry
 Anatomy 7 Bones Cartilage And Joints Medicine 1st Year
Anatomy 7 Bones Cartilage And Joints Medicine 1st Year
 Knee Joint Picture Image On Medicinenet Com
Knee Joint Picture Image On Medicinenet Com
 Ligaments Of The Joints Chart 20x26
Ligaments Of The Joints Chart 20x26
Anatomy 101 Wrist Joints The Handcare Blog



Belum ada Komentar untuk "Joints Anatomy"
Posting Komentar