Neck Of Femur Anatomy
A fractured neck of femur nof is a common orthopaedic presentation. Over 65000 hip fractures each year are recorded in the uk alone and they are becoming increasingly frequent due to an aging population.
In the female in consequence of the increased width of the pelvis the neck of the femur forms more nearly a right angle with the body than it does in the male.

Neck of femur anatomy. A fractured neck of femur is classified as either intracapsular or extracapsular. The femoral aspect of the hip is made up of the femoral head with its articular cartilage and the femoral neck which connects the head to the shaft in the region of the lesser and greater. The femoral neck is strengthened by a thickening of bone called the calcar femorale present along its concavity.
With associated lengthy hospital stays and an estimated cost of over 7500 per fracture. The head forms a ball and socket joint with the hip at the acetabulum being held in place by a ligament ligamentum teres femoris within the socket and by strong surrounding ligaments. The proximal end consists of a head neck and two trochantersthe head faces superiorward medialward and slightly anteriorward the proximal area of the femur forms the hip joint with the pelvis.
A fracture of the femoral neck is classified as a type of hip fracture. The classical clinical finding is that of an externally rotated shortened leg. The angle facilitates movements of the hip joint.
In the vast majority of cases a hip fracture is a fragility fracture due to a fall or minor trauma in someone with weakened osteoporotic bone. It is often due to osteoporosis. There are also two bony ridges connecting the two trochanters.
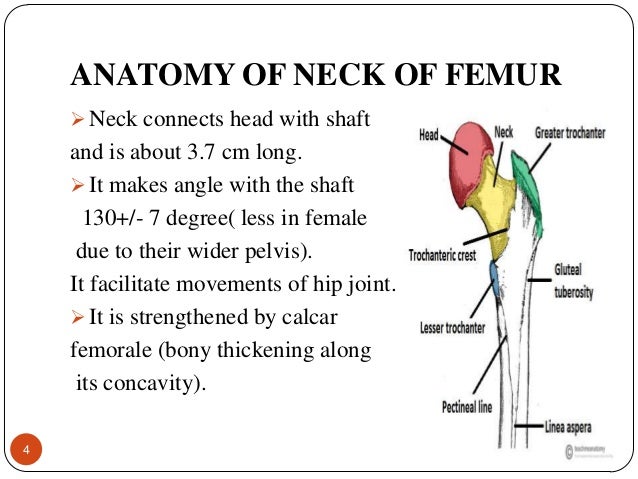
Fractures of the neck of femur are very common injuries which mainly occur in elderly females with osteoporotic bones. In humans the neck of the femur connects the shaft and head at a femur upper bone of the leg or hind leg. The neck is about is about 3 35 cms long and connects head with the shaft.
Head connects with the acetabulum of the pelvis to make the hip joint. In the adult the neck forms an angle of about 125 with the body but this varies in inverse proportion to the development of the pelvis and the stature. The neck forms an angle with the shaft known as neck shaft angle and is about 125 in adults lesser in females.
 Royalty Free Femur Stock Images Photos Vectors Shutterstock
Royalty Free Femur Stock Images Photos Vectors Shutterstock
:watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/anatomy_term/neck-of-the-femur-2/LukBjJXw3ht7ngp8bPhkA_Neck_of_Femur_01.png) Femur Bone Anatomy Proximal Distal And Shaft Kenhub
Femur Bone Anatomy Proximal Distal And Shaft Kenhub
 Hip Anatomy Recon Orthobullets
Hip Anatomy Recon Orthobullets
 Proximal Femur Approach Lateral Approach Femoral Neck
Proximal Femur Approach Lateral Approach Femoral Neck
 Femoral Nerve Block Landmarks And Nerve Stimulator
Femoral Nerve Block Landmarks And Nerve Stimulator
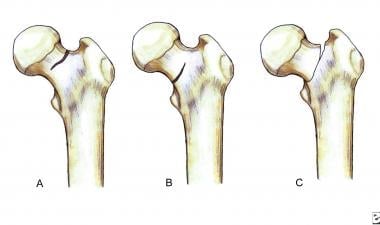 Femoral Neck Fracture Background Epidemiology Functional
Femoral Neck Fracture Background Epidemiology Functional
 Hip Fracture Anatomy Causes And Consequences Intechopen
Hip Fracture Anatomy Causes And Consequences Intechopen
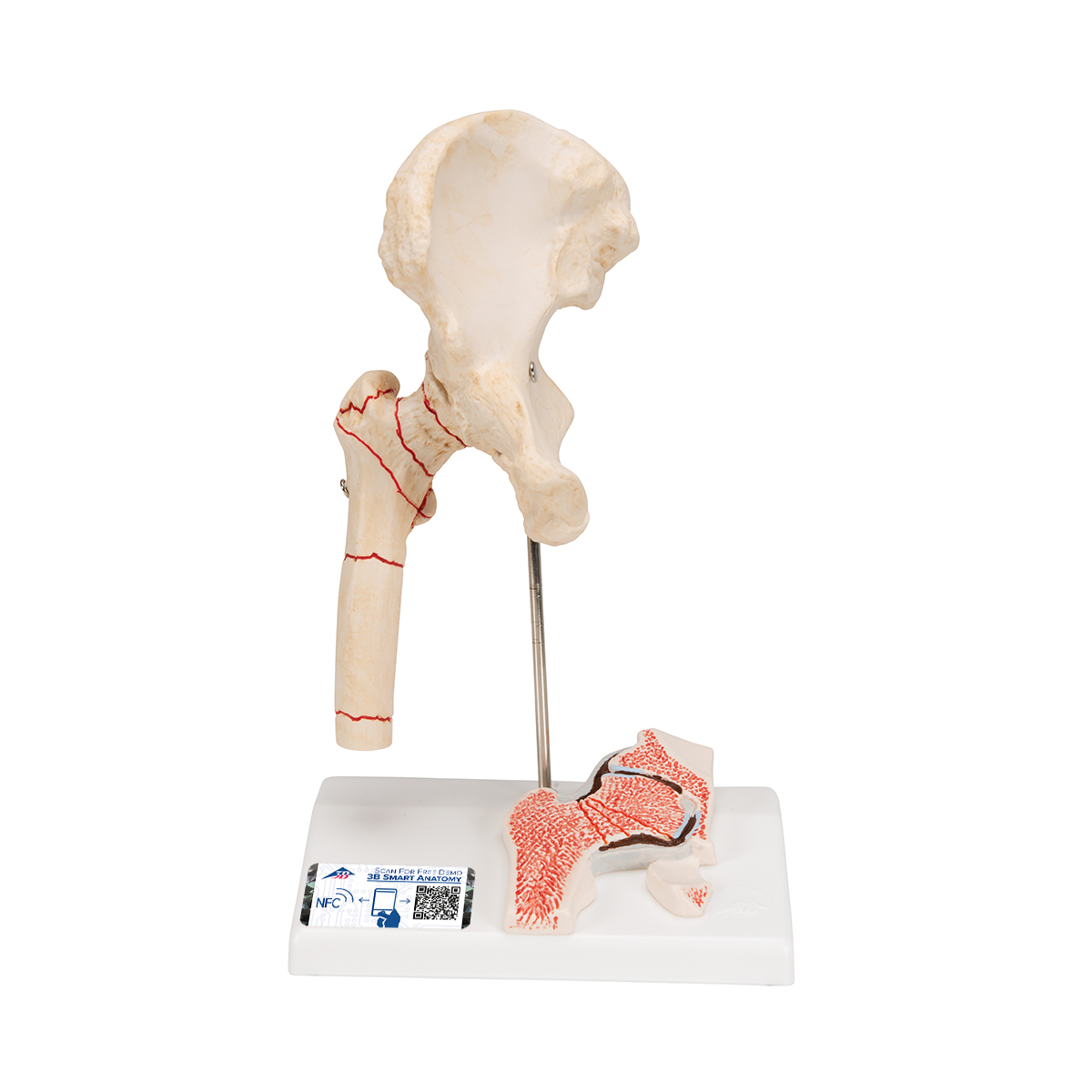 Anatomical Teaching Models Plastic Human Joint Models
Anatomical Teaching Models Plastic Human Joint Models
Wheeless Textbook Of Orthopaedics
 Anatomy Of The Human Proximal Femur Upper Third Of The
Anatomy Of The Human Proximal Femur Upper Third Of The
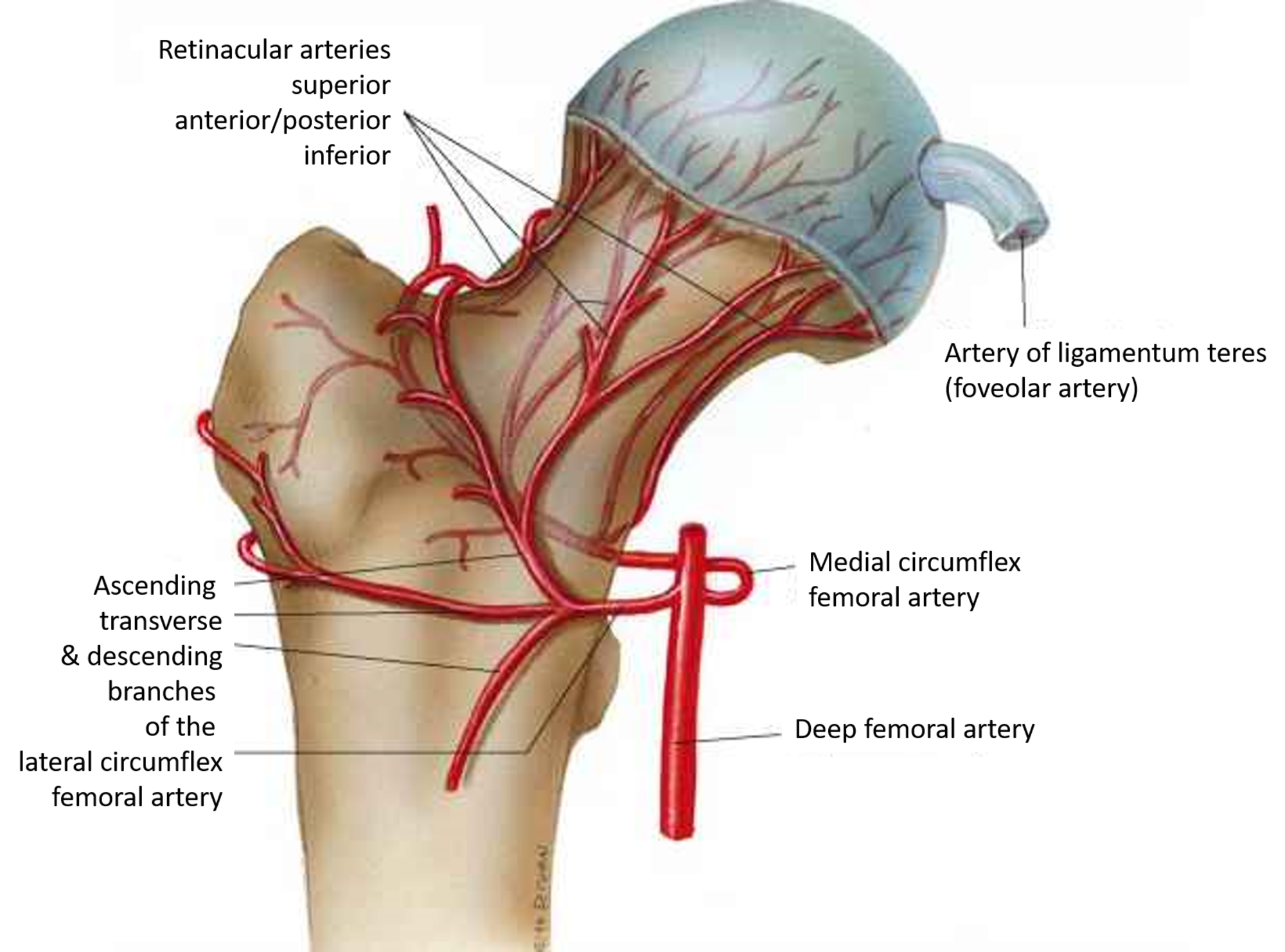 Cureus Osteonecrosis Of The Femoral Head Etiology
Cureus Osteonecrosis Of The Femoral Head Etiology
 Femur Anatomy Greater Trochanter Neck Head Retinacular
Femur Anatomy Greater Trochanter Neck Head Retinacular
Femoral Neck Fracture Fracture Of Hip
 Anatomy Of The Hip Central Coast Orthopedic Medical Group
Anatomy Of The Hip Central Coast Orthopedic Medical Group
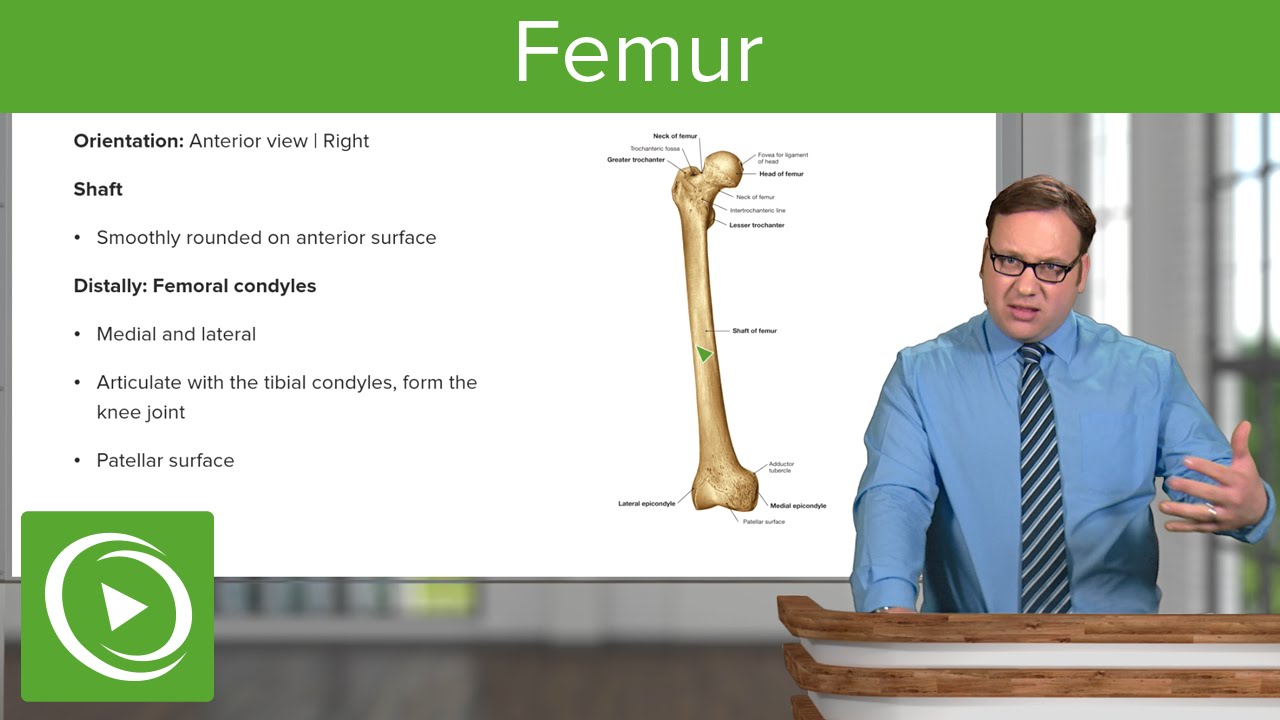 Femur Anatomy Medical Education Videos
Femur Anatomy Medical Education Videos
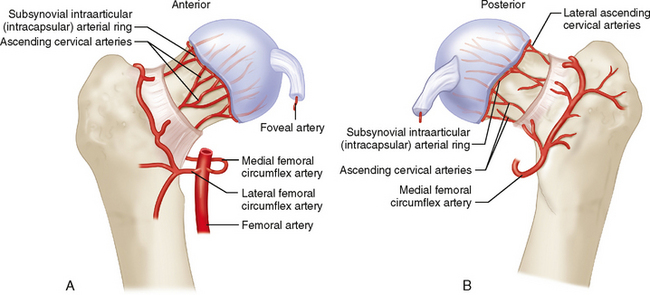 17 Femoral Neck Fractures Musculoskeletal Key
17 Femoral Neck Fractures Musculoskeletal Key
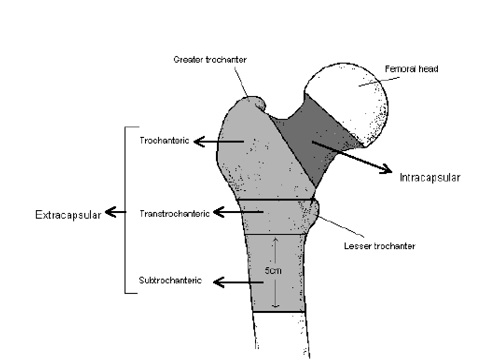 Fractured Neck Of Femur Rcemlearning
Fractured Neck Of Femur Rcemlearning
 Femoral Neck Stress Fractures Knee Sports Orthobullets
Femoral Neck Stress Fractures Knee Sports Orthobullets

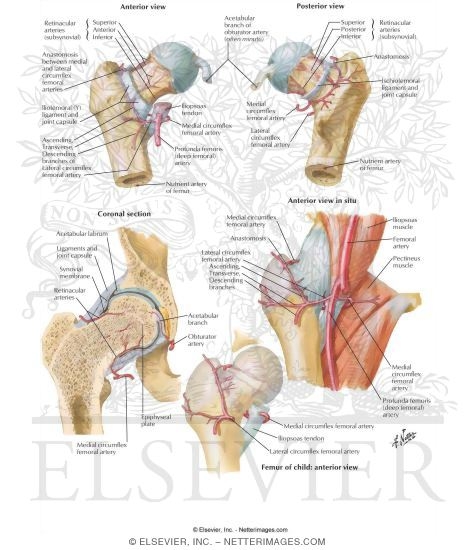



Belum ada Komentar untuk "Neck Of Femur Anatomy"
Posting Komentar