Turtle Anatomy Shell
Turtle shell anatomy scutes turtles are reptiles whose protection comes from a shell. Instead turtles breathe in two ways.
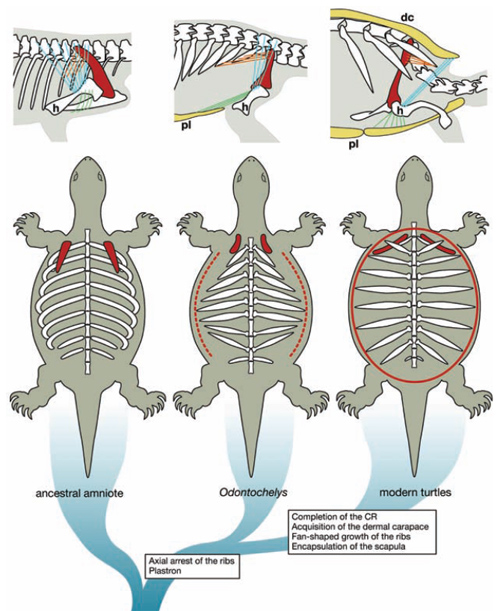
 How The Turtle Got Its Shell Through Skeletal Shifts And
How The Turtle Got Its Shell Through Skeletal Shifts And
Box turtles can also retract their head and limbs into their shells and close the shell for added protection.
Turtle anatomy shell. The lower shell that encases the belly is called the plastron. Most aquatic turtles are generally flatter allowing them to move faster through the water. The upper shell of the turtle is called the carapace.
The bone of the shell consists of both skeletal and dermal bone showing that the complete enclosure of the shell probably evolved by including dermal armor into the rib c. The shell shapes of turtles differ with each species and are often related to habitat. The shell is composed of hard bone plates covered by scutes.
The turtle shell has a top and a bottom. Most aquatic turtles are generally flatter allowing them to move faster through the water. The rigid shell means turtles cannot breathe as other reptiles do by changing the volume of their chest cavity via expansion and contraction of the ribs.
The carapace and plastron are bony structures that usually join one another along each side of the body creating a rigid skeletal box. First they employ buccal pumping pulling air into their mouth then pushing it into the lungs via oscillations of the floor of the throat. There are two parts to the shell.
The top part of the shell the carapace is a dome made from the actual back bones and ribs which have expanded and fused together. It is constructed of modified bony elements such as the ribs parts of the pelvis and other bones found in most reptiles. Turtles overcome this problem with muscles that increase the space surrounding their lungs as they breathe in.
The carapace and plastron are joined together on the turtles sides by bony structures called bridges. The turtle shell is a highly complicated shield for the ventral and dorsal parts of turtles tortoises and terrapins completely enclosing all the vital organs of the turtle and in some cases even the head. The scutes are made of keratin the primary substance in hair nails and hooves of other animals.
Turtle order testudines any reptile with a body encased in a bony shell including tortoises. Although numerous animals from invertebrates to mammals have evolved shells none has an architecture like that of turtles. This provides room for the lungs to expand.
The shells are either oval or heart shaped and are very hard except the leatherback species which has a soft leathery tissue and a set of bony plates beneath it. Box turtles have a hard shell that protects their organs. A turtles shell constricts the expansion of its ribs for breathing.
The plastron or ventral part of the shell is the lower area of the turtle and it has a light yellow color and a thinner and more sensitive tissue.
 Episode 3 Field Guide What S A Reptile Past Time Paleo
Episode 3 Field Guide What S A Reptile Past Time Paleo
 Can You Remove A Turtle From Its Shell Without Killing It
Can You Remove A Turtle From Its Shell Without Killing It
 Zoology For High Schools And Colleges Zoology Anatomt Of
Zoology For High Schools And Colleges Zoology Anatomt Of
 Turtle Shell Anatomy Turtle Tortoises Fierce Animals
Turtle Shell Anatomy Turtle Tortoises Fierce Animals
 One Tiny Turtle Beach En En En Hatch Language Arts
One Tiny Turtle Beach En En En Hatch Language Arts
 Sea Turtle Anatomy Sea Turtle Facts And Information
Sea Turtle Anatomy Sea Turtle Facts And Information
 Anatomy And Diseases Of Turtle And Tortoise Shells Petcoach
Anatomy And Diseases Of Turtle And Tortoise Shells Petcoach
 Green Sea Turtle National Geographic
Green Sea Turtle National Geographic
 Facts About Aquatic Turtle Turtle Anatomy And Health
Facts About Aquatic Turtle Turtle Anatomy And Health
 What S Inside A Turtle Shell A Complete Overview All
What S Inside A Turtle Shell A Complete Overview All
 All About Box Turtles Welcome Wildlife
All About Box Turtles Welcome Wildlife
 Self Righting Potential And The Evolution Of Shell Shape In
Self Righting Potential And The Evolution Of Shell Shape In
 Top Ten Facts About Turtle Shells Earth Rangers Wild Wire Blog
Top Ten Facts About Turtle Shells Earth Rangers Wild Wire Blog
 Spiny Softshell Turtle National Wildlife Federation
Spiny Softshell Turtle National Wildlife Federation
 Turtles Read Biology Ck 12 Foundation
Turtles Read Biology Ck 12 Foundation
 16 Fun Facts About Tortoises Mental Floss
16 Fun Facts About Tortoises Mental Floss
 Factsheet On Green Sea Turtle Us Fish Wildlife Service S
Factsheet On Green Sea Turtle Us Fish Wildlife Service S
 Tortoise Scoot Shell Anatomy Tortoise Sulcata Tortoise
Tortoise Scoot Shell Anatomy Tortoise Sulcata Tortoise
 All About Box Turtles Welcome Wildlife
All About Box Turtles Welcome Wildlife

Belum ada Komentar untuk "Turtle Anatomy Shell"
Posting Komentar