Anterior Hip Anatomy
Anteroposterior and lateral radiographs of the hip. Using the femoral head as a landmark the anterior synovial recess is identified.
Study of the anterior hip region.
Anterior hip anatomy. Lateral or external rotation 30 with the hip extended 50 with the hip flexed. The 2 hip bones form the bony pelvis. The hip is a ball and socket joint in the engine room of human locomotion.
Muscles of the hip. Illustration of the right hip demonstrates the location and size of the incision for the direct anterior approach. The approach continues between the sartorius and tensor fascia lata muscles an internervous plane avoiding the risk of denervation of the involved muscles.
When the cartilage in the hip joint starts to deteriorate the implications are profound. This joint serves as the main connection between the lower extremity and the trunk and typically works in a closed kinematic chain. This approach involves a 3 to 4 inch incision on the front of the hip that allows the joint to be replaced by moving muscles aside along their natural tissue planes without detaching any tendons.
The natural motion of the hip allows us to walk run swim cycle dance for those of us with rhythm and enjoy our lives as upright bipeds with grace. The muscles of the thigh and lower back work together to keep the hip stable. Adduct and externally rotate the hip to place the capsule on stretch.
Retract rectus femoris and iliopsoas medially and gluteus medius laterally to expose the hip capsule. Anatomy of the hip the hip joint. In hip replacement surgery the hip can be reached through the back of the hip posterior approach the side of the hip lateral or anterolateral approach the front of the leg anterior approach or through a combination of approaches.
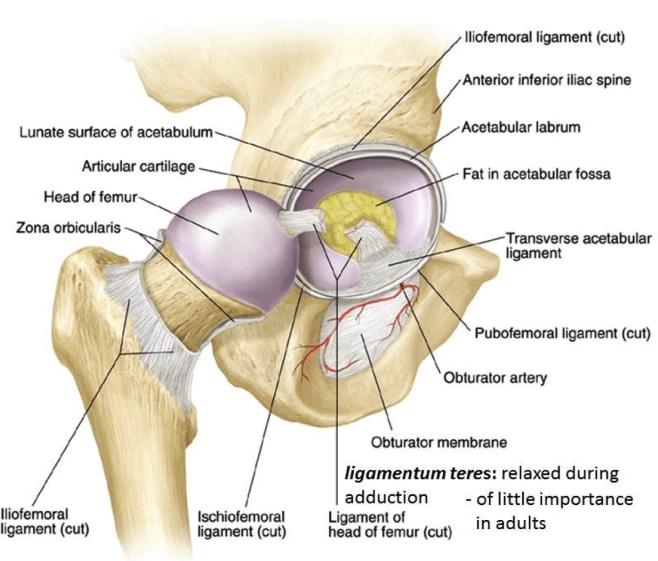
The hip joint is a ball and socket type joint. The hip articulation is true diarthroidal ball and socket style joint formed from the head of the femur as it articulates with the acetabulum of the pelvis. The hip joint is the articulation of the pelvis with the femur which connects the axial skeleton with the lower extremity.
Detach rectus femoris from both its origins. The stability of the hip is increased by the strong ligaments that encircle the hip. As a result today there is a range of surgical approaches being utilized by orthopedic surgeons.
The adult os coxae or hip bone is formed by the fusion of the ilium the ischium and the pubis which occurs by the end of the teenage years. The movements of the hip joint is thus performed by a series of muscles which are here presented in order of importance with the range of motion from the neutral zero degree position indicated. Direct anterior hip replacement is a minimally invasive surgical technique.
In physiological conditions it is virtual whereas it is distended by anechoic fluid in the presence of joint effusion. Identify plane between rectus femoris and gluteus medius.
 Pain At The Front Of The Hip Sartorius Psoas Strain
Pain At The Front Of The Hip Sartorius Psoas Strain
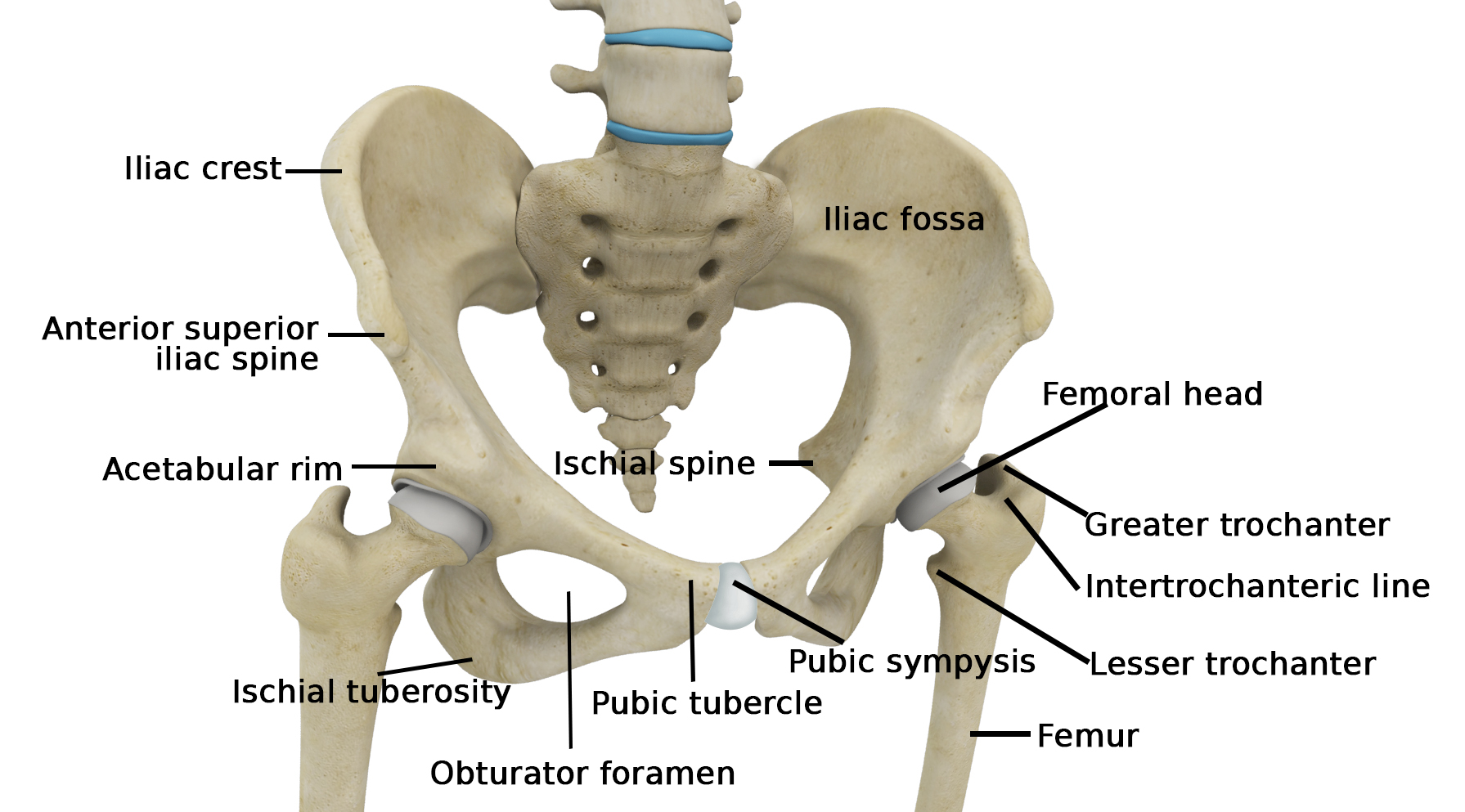
 Hip Anatomy Recon Orthobullets
Hip Anatomy Recon Orthobullets
:watermark(/images/watermark_5000_10percent.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/atlas_overview_image/747/2iEeCHPsxbas46QC7ze0g_muscles-pelvis-hip-femur_english.jpg) Hip And Thigh Bones Joints Muscles Kenhub
Hip And Thigh Bones Joints Muscles Kenhub
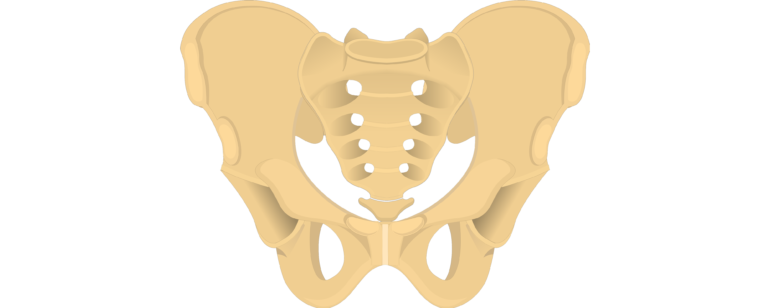 Hip Bone Anatomy Anterior Markings
Hip Bone Anatomy Anterior Markings
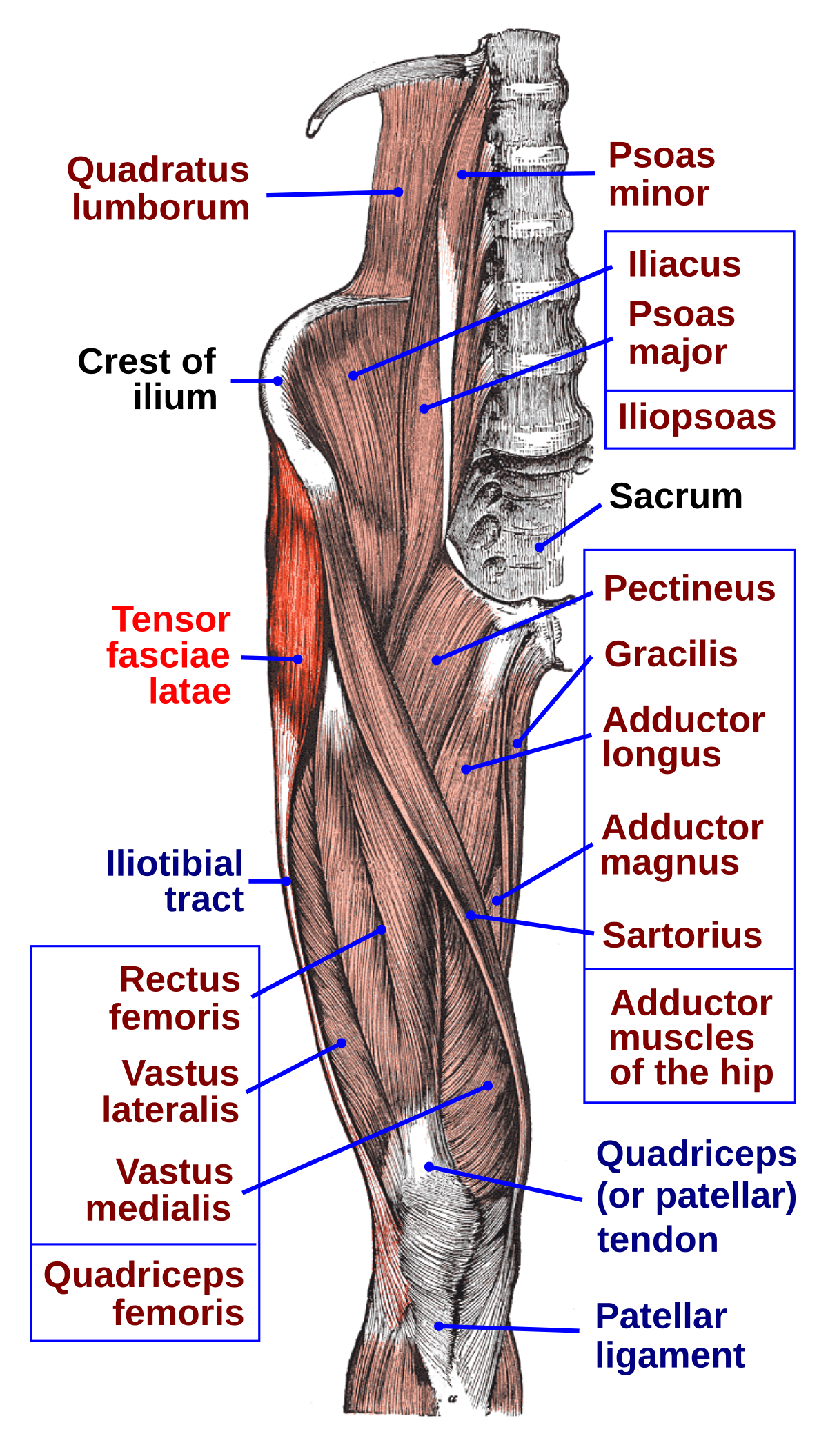 Tensor Fasciae Latae Muscle Wikipedia
Tensor Fasciae Latae Muscle Wikipedia
 Muscles Advanced Anatomy 2nd Ed
Muscles Advanced Anatomy 2nd Ed
 Hip Flexors An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Hip Flexors An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
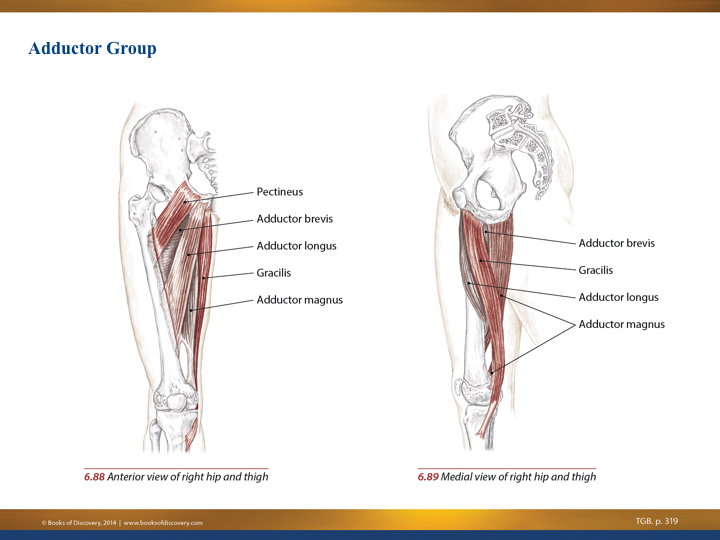 Hip Adductors Anatomy And Exercises
Hip Adductors Anatomy And Exercises
Direct Anterior Hip Replacement Oak Lawn Bone And Joint
Hip Pain Orthopedics University Of Colorado Denver
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/11030/Hip_and_thigh_1.png) Hip And Thigh Bones Joints Muscles Kenhub
Hip And Thigh Bones Joints Muscles Kenhub
 Acetabular Fractures Orthoinfo Aaos
Acetabular Fractures Orthoinfo Aaos

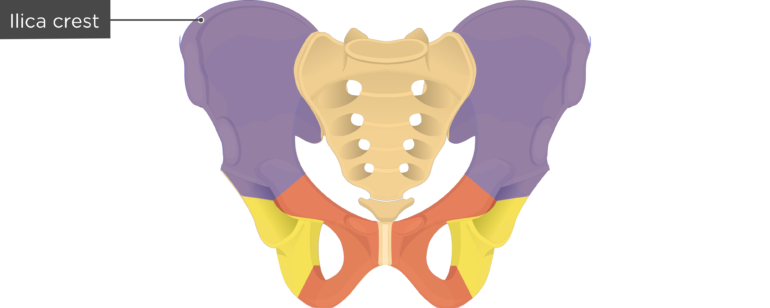 Hip Bone Anatomy Anterior Markings
Hip Bone Anatomy Anterior Markings
 Hip Surgeon Springfield Hip Replacement East Longmeadow
Hip Surgeon Springfield Hip Replacement East Longmeadow
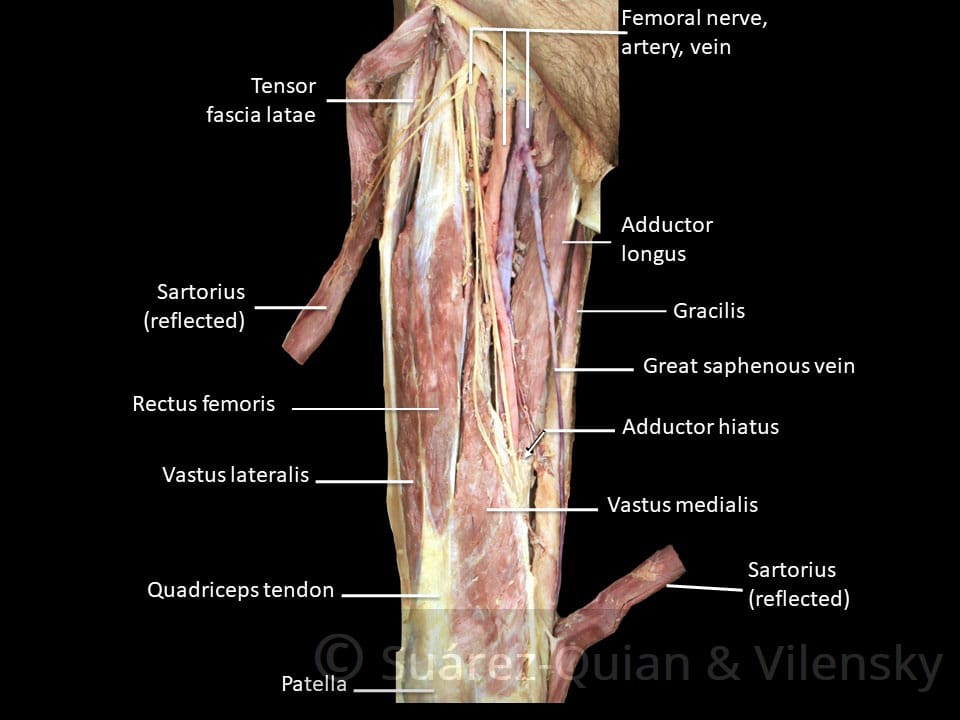 Muscles Of The Anterior Thigh Quadriceps Teachmeanatomy
Muscles Of The Anterior Thigh Quadriceps Teachmeanatomy
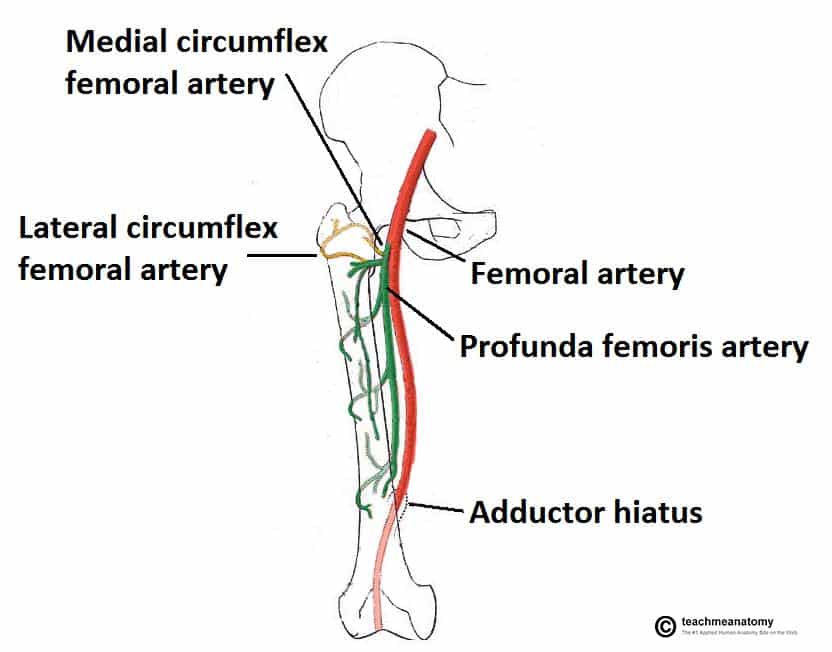 The Hip Joint Articulations Movements Teachmeanatomy
The Hip Joint Articulations Movements Teachmeanatomy
 Male Hip Bone Anatomy Anterior View Stock Vector Royalty
Male Hip Bone Anatomy Anterior View Stock Vector Royalty
 Direct Anterior Hip Replacement Carmel Ny Hip Surgery
Direct Anterior Hip Replacement Carmel Ny Hip Surgery
 Hip Anatomy Recon Orthobullets
Hip Anatomy Recon Orthobullets
 Muscles Of The Hips And Thighs Human Anatomy And
Muscles Of The Hips And Thighs Human Anatomy And
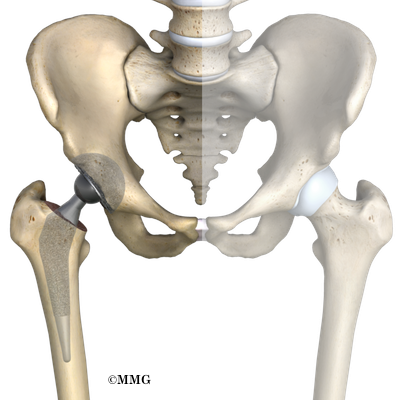 Artificial Joint Replacement Of The Hip Anterior Approach
Artificial Joint Replacement Of The Hip Anterior Approach
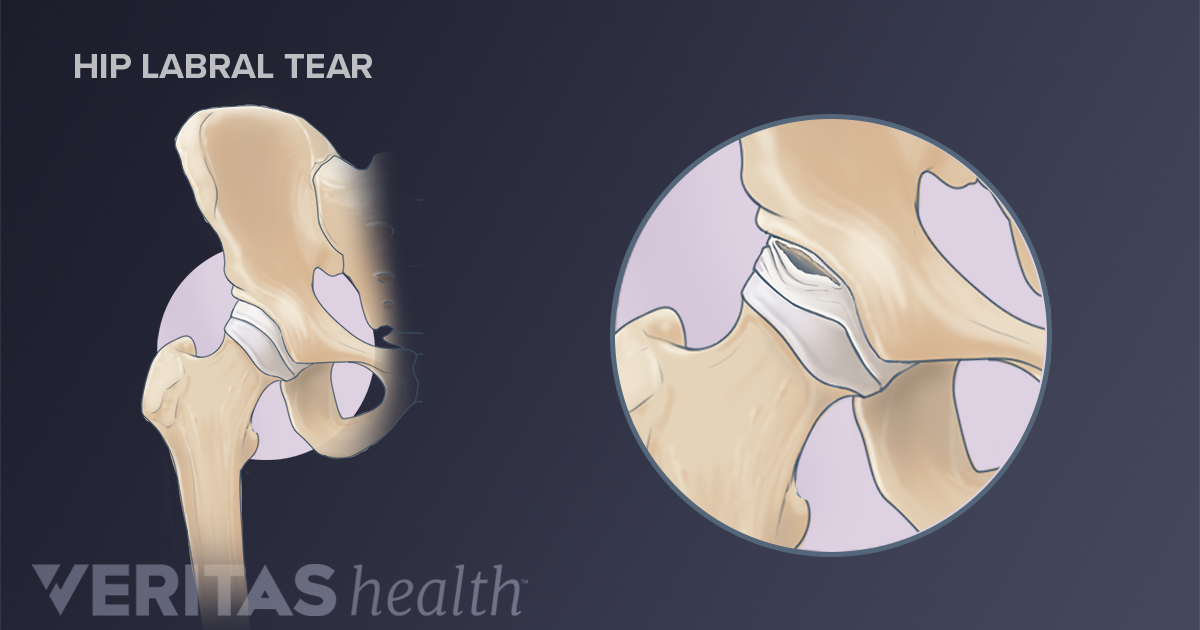


Belum ada Komentar untuk "Anterior Hip Anatomy"
Posting Komentar