Urinary Bladder Anatomy
Sphincter of the urinary bladder. In placental mammals a special duct the urethra leads from the urinary bladder to the exterior.
 The Urinary Bladder Human Anatomy
The Urinary Bladder Human Anatomy
The appearance of the bladder varies depending on the amount of urine stored.
Urinary bladder anatomy. Urinary bladder the urinary bladder is an organ that serves to collect urine to be voided through urination after the urine is filtered through the kidneys where the necessary ions are reabsorbed if physiologically needed through feedback mechanisms found throughout the body and in the nephrons of the kidneys such as the macula densa. Urine is received into the body of the. The urinary bladder is made of several distinct tissue layers.
Urine leaves the bladder via the urethra a single muscular tube ending in an opening the urinary meatus. In females the urethra is separate from the genital tract. Interior of the bladder.
It temporarily stores urine conveyed by the ureters from the kidneys until the body is ready to expel it through the urethra. The urinary bladder shape of the bladder. The bladders job in the urinary system is to store the urine produced by your body until it is released from the body when you urinate.
The vasculature of the bladder is primarily derived from the internal iliac vessels. It fulfills the excretory function of the more primitive cloaca. In humans the bladder is a hollow muscular organ situated at the base of the pelvis.
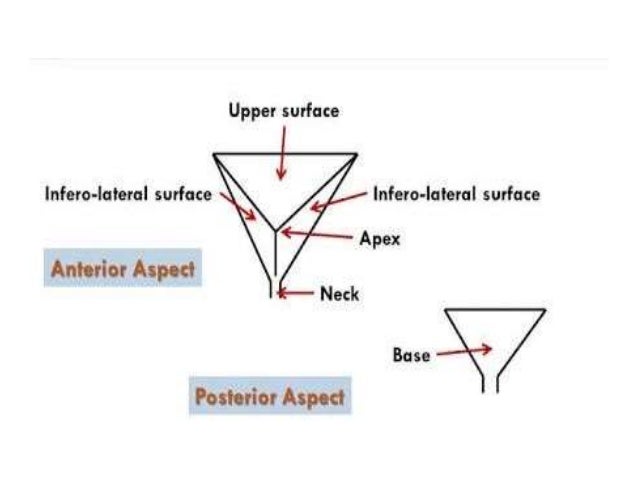
The interior of the bladder are the trigone of the bladder. Gross anatomy of the bladder surface anatomy of the bladder. When empty the bladder is about the size and shape of a pear.
The urinary bladder is hollow and somewhat pear shaped in appearance. The urinary bladder is a muscular sac in the pelvis just above and behind the pubic bone. The visceral muscles of the muscularis layer.
It has a muscular elastic wall which allows it to expand and distend when filled. In males the vas deferens sperm carrying tubes empty into the urethra. The sphincter of the urinary bladder consists of smooth.
Surrounding the mucosal layer is the submucosa a layer of connective tissue with blood vessels. The superolateral aspect of the bladder drains into the external. The bladder has a volume capacity of 400500 ml and is.
Urine collects in the bladder fed from the two ureters that connect the bladder with the kidneys. The urinary bladder is a hollow muscular organ. The urinary bladder usually just called the bladder is a major part of the bodys urinary system1 3 it is a hollow organ that is made mostly out of muscle.
The innermost layer of the bladder is the mucosa layer that lines the hollow lumen.
 Easy Notes On Urinary Bladder Learn In Just 4 Minutes
Easy Notes On Urinary Bladder Learn In Just 4 Minutes
 The Urinary System In Mammals Anatomy And Function Petcoach
The Urinary System In Mammals Anatomy And Function Petcoach
 25 2 Gross Anatomy Of Urine Transport Anatomy And Physiology
25 2 Gross Anatomy Of Urine Transport Anatomy And Physiology
 Symptoms Causes Of Bladder Control Problems Urinary
Symptoms Causes Of Bladder Control Problems Urinary
 Bladder Position Relations Gross Structure The Urinary
Bladder Position Relations Gross Structure The Urinary
 Anatomy And Physiology Of The Kidneys Urinary Bladder Ureters Urethra And Nephron
Anatomy And Physiology Of The Kidneys Urinary Bladder Ureters Urethra And Nephron
 Anatomy Of The Lower Urinary Tract
Anatomy Of The Lower Urinary Tract
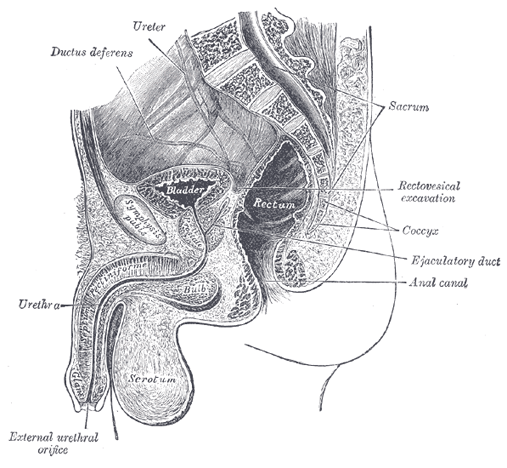
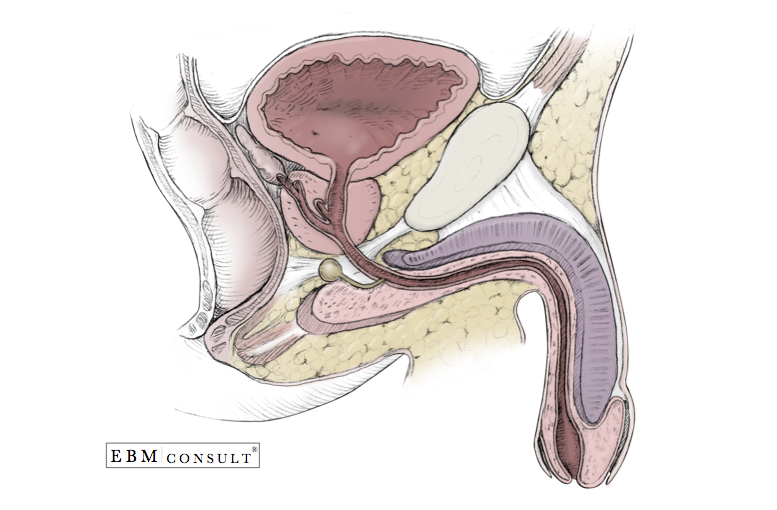 Male Genitourinary Anatomy Bladder Prostate Penis In
Male Genitourinary Anatomy Bladder Prostate Penis In
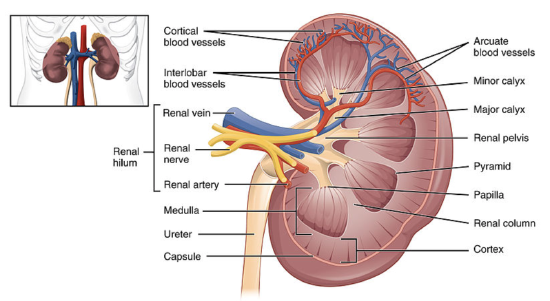 19 4 Ureters Urinary Bladder And Urethra Biology Libretexts
19 4 Ureters Urinary Bladder And Urethra Biology Libretexts

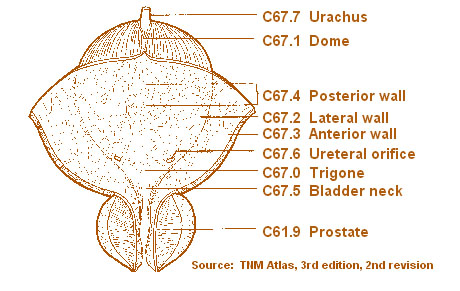 Seer Training Anatomy Of The Bladder
Seer Training Anatomy Of The Bladder
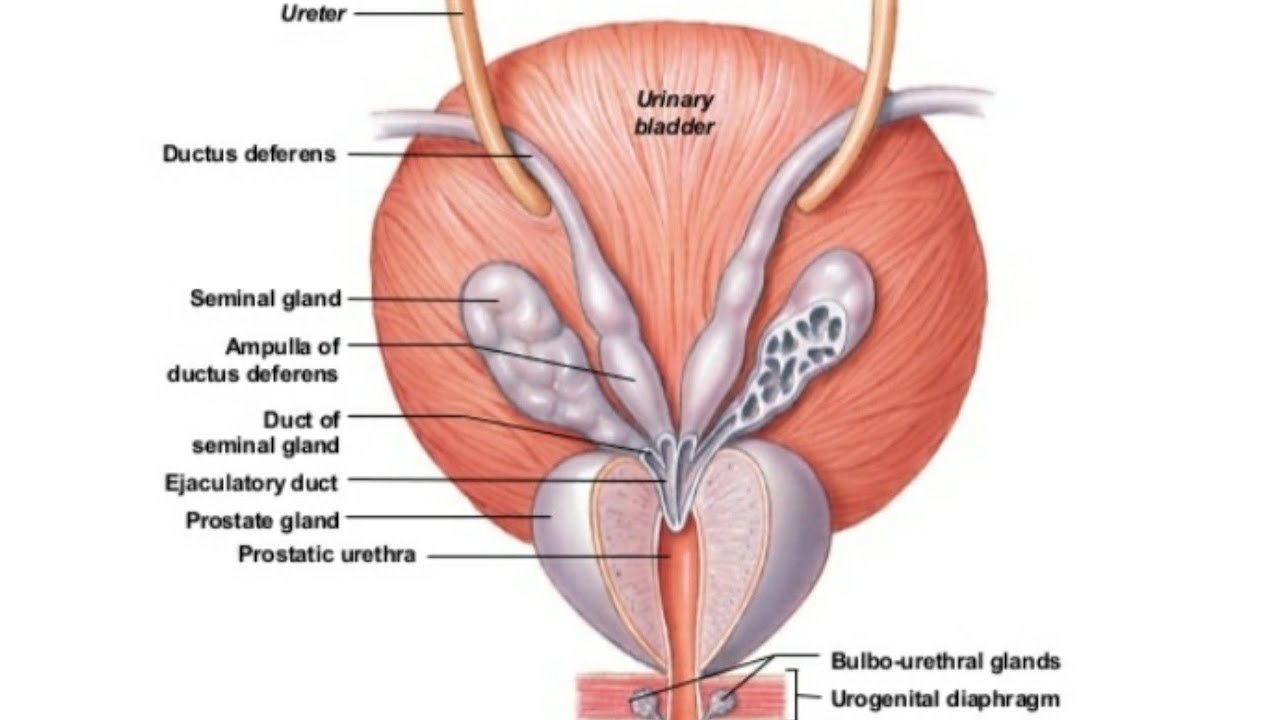 Anatomy Of Urinary Bladder External And Internal Features By Dr Abhishek Kumar
Anatomy Of Urinary Bladder External And Internal Features By Dr Abhishek Kumar
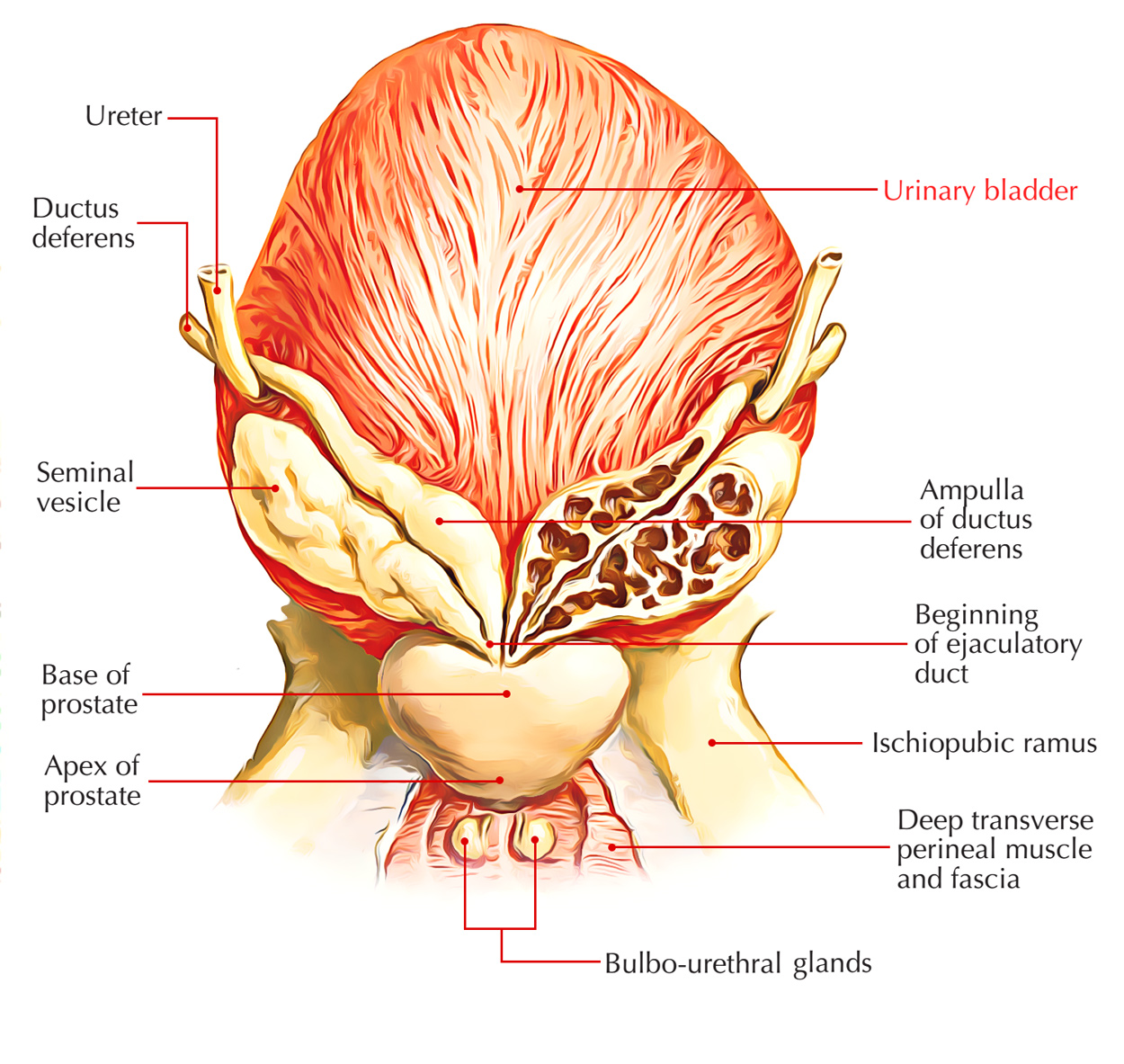
 Amazon Com Human Male Urinary Bladder With Prostate
Amazon Com Human Male Urinary Bladder With Prostate
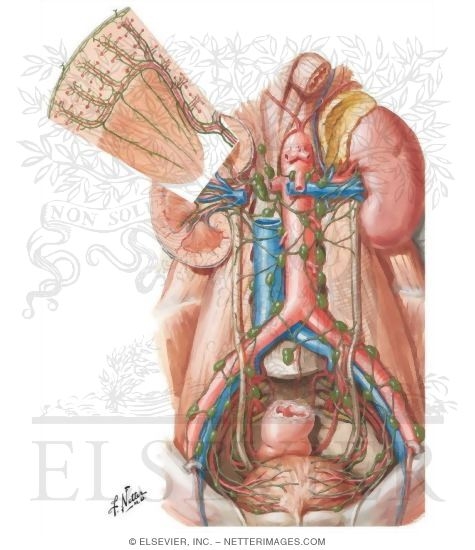
 Lymph Vessels And Nodes Of Kidneys And Urinary Bladder
Lymph Vessels And Nodes Of Kidneys And Urinary Bladder
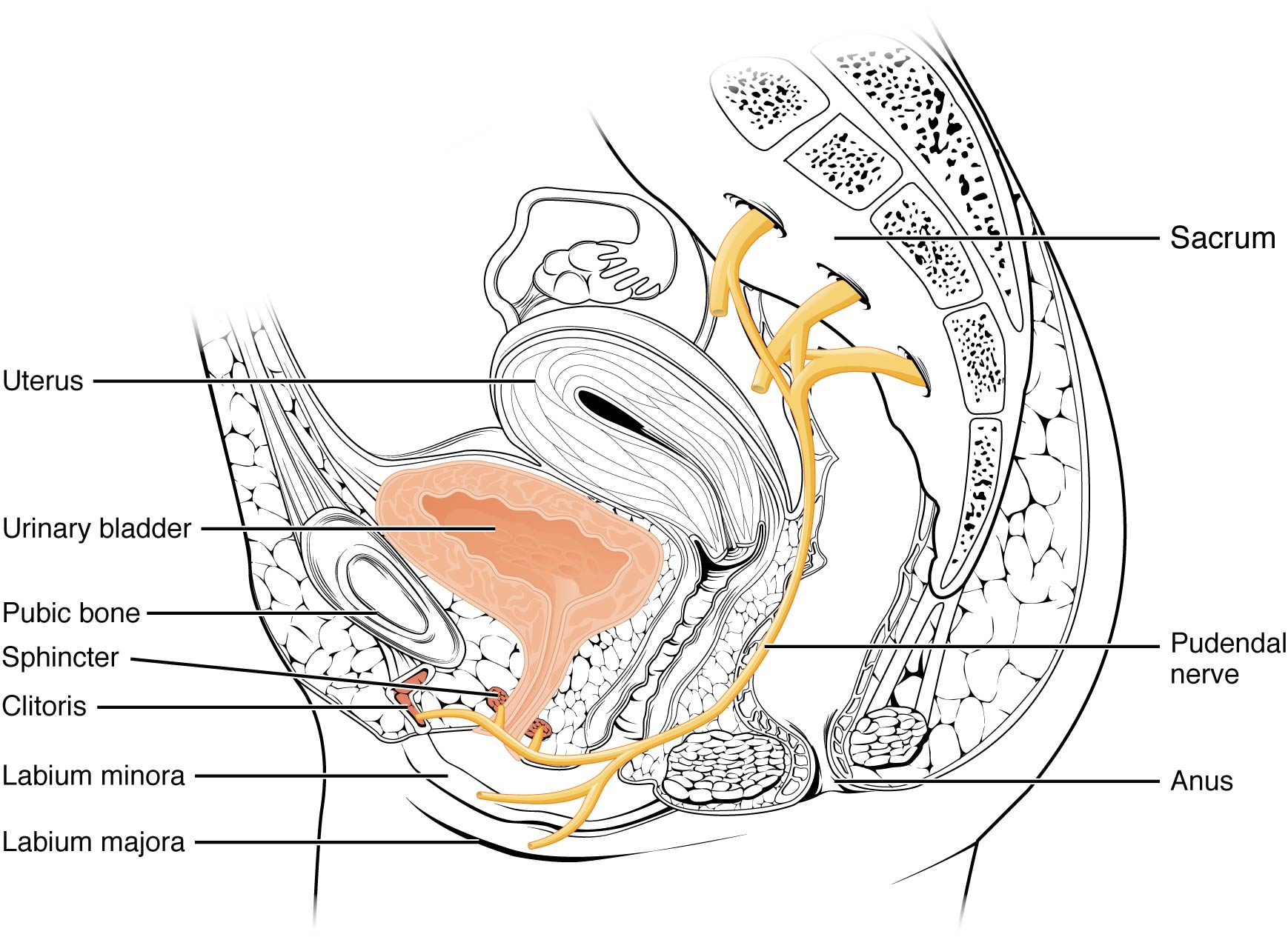
 The Urinary System Urinary Bladder And Urethra Female
The Urinary System Urinary Bladder And Urethra Female
 Anatomy Female Urinary Bladder Wall Mural
Anatomy Female Urinary Bladder Wall Mural
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/1189/Male_urinary_bladder.png) Urinary Bladder Anatomy Function And Clinical Notes Kenhub
Urinary Bladder Anatomy Function And Clinical Notes Kenhub
 Royalty Free Urinary Bladder Stock Images Photos Vectors
Royalty Free Urinary Bladder Stock Images Photos Vectors
 The Urinary Bladder Structure Function Nerves
The Urinary Bladder Structure Function Nerves




Belum ada Komentar untuk "Urinary Bladder Anatomy"
Posting Komentar