Paranasal Sinuses Anatomy
The maxillary sinus the largest of the sinuses. Rudimentary sphenoid sinuses are there at birth forming pneumatizing completely by the age of 5 years 6.
Ethmoid air cells sinuses.
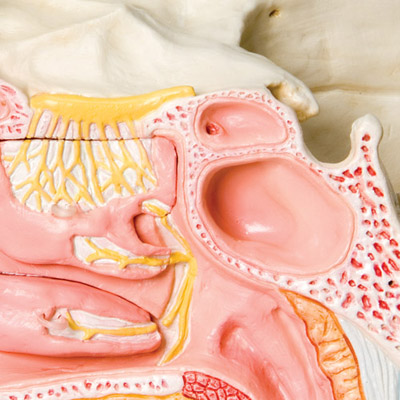
Paranasal sinuses anatomy. 42 18 52 2 and 53 4. Nose hairs at the entrance to the nose trap large inhaled particles. The frontal sinuses superior to the eyes in the frontal bone.
Sphenoidal sinus see figs. The maxillary sinuses the largest of the paranasal sinuses are under the eyes. Paranasal sinuses frontal sinuses.
Frontal sinus see figs. Where are the paranasal sinuses situated. 52 6 maxillary sinus see fig.
What are the paranasal sinuses a formation from. Infection of the sinuses causes inflammation particularly pain and swelling of the mucosa and is known as sinusitis. The superior border of this sinus is the bony orbit the inferior is the maxillary alveolar bone and corresponding tooth roots.
They have thin walls which are often penetrated by the long roots of the posterior maxillary teeth. Others are much smaller. They further develop over the first few years of life 11.
If more than one sinus is affected it is called pansinusitis. Your cheekbones hold your maxillary sinuses the. In the frontal ethmoid and sphenoid of the cranium and the maxillary bones of the face.
These sinuses which have the same names as the bones in which they are located surround the nasal cavity and open into it. As the paranasal sinuses are continuous with the nasal cavity an upper respiratory tract infection can spread to the sinuses. The sinuses are a connected system of hollow cavities in the skull.
42 4 42 5 and 53 4. Humans possess four paired paranasal sinuses divided into subgroups that are named according to the bones within which the sinuses lie. Anatomy of the paranasal sinuses development.
The frontal sinus the rostral maxillary sinus the caudal maxillary sinus the sphenopalatine sinus the dorsal conchal sinus the ventral conchal sinus and the ethmoidal sinus also known as the middle conchal sinus. The largest sinus cavities are about an inch across. The maxillary and ethmoid sinuses are present at birth starting to form around the 3rd or 4th month of gestational development 10.
Paranasal sinuses are air filled cavities in the frontal maxilae ethmoid and sphenoid bones. My interpretation of the anatomy and literature leads me to recognise seven paired paranasal sinuses. The maxillary sinuses are the largest of the all the paranasal sinuses.
From the nasal mucosa and their continued communication with the nasal fossae.
 Section Of Head Model Sagital Section Of Head
Section Of Head Model Sagital Section Of Head
 Ct Anatomy Of Para Nasal Sinuses
Ct Anatomy Of Para Nasal Sinuses
 Science Source Paranasal Sinuses Illustration
Science Source Paranasal Sinuses Illustration
 Nose Useful Notes On Human Nose And Para Nasal Sinuses
Nose Useful Notes On Human Nose And Para Nasal Sinuses
 The Hidden Anatomy Of Paranasal Sinuses Reveals
The Hidden Anatomy Of Paranasal Sinuses Reveals
 Anatomy Nasal Cavity Paranasal Sinuses Nasopharynx
Anatomy Nasal Cavity Paranasal Sinuses Nasopharynx
 Amazon Com Emvency Wall Tapestry Sinuses Of Nose Human
Amazon Com Emvency Wall Tapestry Sinuses Of Nose Human
 Human Nose Model With Paranasal Sinuses 5 Part 3b Smart
Human Nose Model With Paranasal Sinuses 5 Part 3b Smart
 Anatomy Paranasal Sinuses Side Views Frontal Stock Vector
Anatomy Paranasal Sinuses Side Views Frontal Stock Vector
 The Paranasal Sinuses Stock Photos The Paranasal Sinuses
The Paranasal Sinuses Stock Photos The Paranasal Sinuses
 Seer Training Nose Nasal Cavities Paranasal Sinuses
Seer Training Nose Nasal Cavities Paranasal Sinuses
 Anatomical Representation Paranasal Sinuses Their Names
Anatomical Representation Paranasal Sinuses Their Names
 Paranasal Sinuses Acrylic Print
Paranasal Sinuses Acrylic Print
 Chapter 23 Nasal Cavity The Big Picture Gross Anatomy
Chapter 23 Nasal Cavity The Big Picture Gross Anatomy
 Human Nose Model With Paranasal Sinuses 5 Part 3b Smart Anatomy
Human Nose Model With Paranasal Sinuses 5 Part 3b Smart Anatomy
 Paranasal Sinuses Radiology Key
Paranasal Sinuses Radiology Key
 Paranasal Sinus Anatomy Overview Gross Anatomy
Paranasal Sinus Anatomy Overview Gross Anatomy
 Paranasal Sinuses Anatomy And Clinical Aspects Kenhub
Paranasal Sinuses Anatomy And Clinical Aspects Kenhub
 Nose Anatomy And Histology Of The Human Nose Medical Library
Nose Anatomy And Histology Of The Human Nose Medical Library
 The Radiology Assistant Paranasal Sinuses Mri
The Radiology Assistant Paranasal Sinuses Mri
 Sinus Cavities Paranasal Sinuses Location Anatomy
Sinus Cavities Paranasal Sinuses Location Anatomy
 Basic Ct Anatomy Of Paranasal Sinuses
Basic Ct Anatomy Of Paranasal Sinuses


Belum ada Komentar untuk "Paranasal Sinuses Anatomy"
Posting Komentar