Anatomy Of Cervical Muscles
The top section of the spine is the cervical section which contains nerves that innervate muscles of the head neck and thoracic cavity as well as transmit sensory information to the cns. These muscles are innervated by the posterior rami of various cervical spinal nerves.
The neck muscles including the sternocleidomastoid and the trapezius are responsible for the gross motor movement in the muscular system of the head and neck.
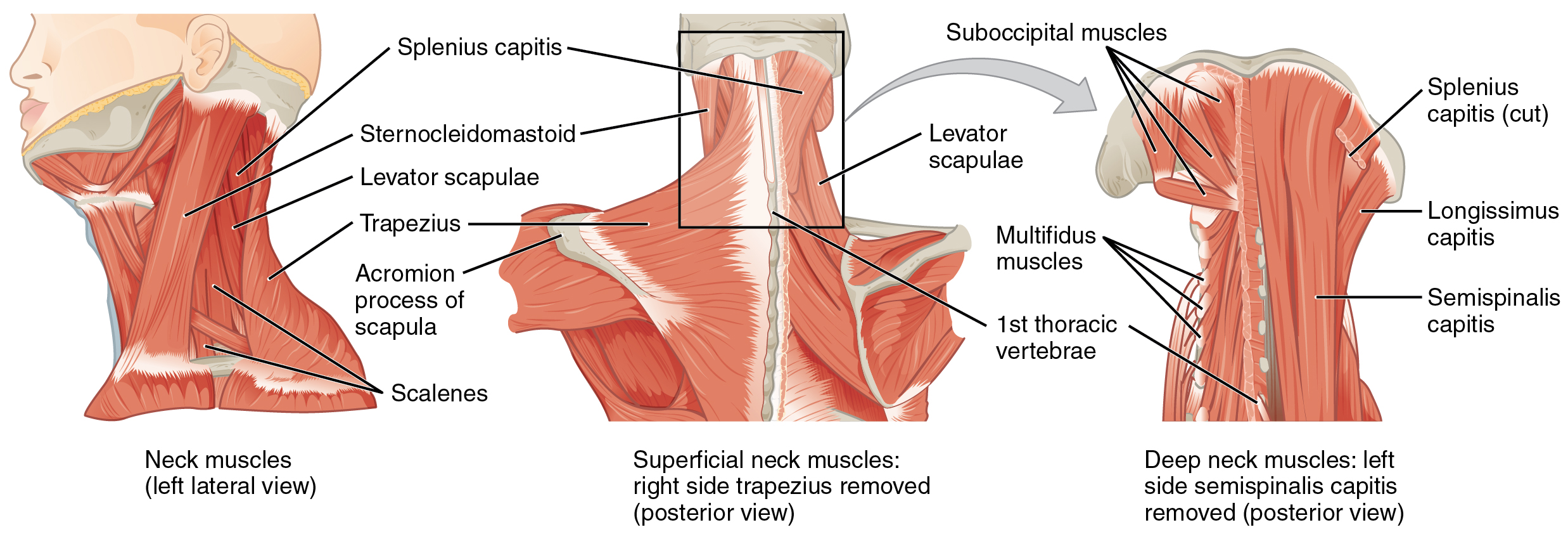
Anatomy of cervical muscles. Rectus capitis anterior begins at the first cervical vertebrae. Cervical spine anatomy there are seven vertebrae in the cervical spine neck area which surround the spinal canal and the spinal cord. The musculature of the neck is comprised of a number of different muscle groups.
They can also be recruited as accessory muscles of respiration. They move the head in every direction pulling the skull and jaw towards the shoulders spine and scapula. Rectus capitis lateralis originates from the first.
The cervical spine section contains seven vertebrae c 1 through c 7 and eight nerve pairs c 1 through c 8. The musculature of the neck is comprised of a number of different muscle groups. Longus capitis begins between the third and sixth cervical vertebrae.
The cervical spine bends directly forward with the chin tilting down. Head and neck motions typically involve one or more of the following movements of the cervical spine. The posterior scalene also originates from the cervical spine but attaches instead to the second rib.
These muscles give the sides of the neck their. Muscles of the neck. Together the scalenes act to flex the neck.
Longus colli begins between the third and sixth cervical vertebrae. Discs made up of gelatinous material act as cushioning between these vertebra with nerves passing out of the spinal canal between the disc and vertebra. Therefore for this articles purposes the neck muscles may be divided into four major structural groups each in its own quadrant.
The muscles in the neck are responsible for the movement of the head in the cervical region in all directions. The fan shaped trapezius muscles extend from the back of the skull down to the middle of the back along the spine and fan over into the shoulders. The cervical spine straightens or moves directly backward with the chin tilting up.
 Trapezius Muscle An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Trapezius Muscle An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
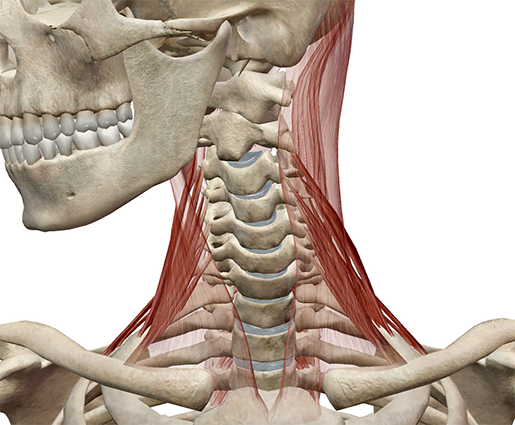 Learn Muscle Anatomy Scalene Muscles
Learn Muscle Anatomy Scalene Muscles
Heads Up Assessing And Activating Cervical Spine Core Muscles
A B The Neck Head Musculoskeletal Anatomy Showing The 216
 Neck Muscles Anatomy Posterior Triangle Prevertebral And Lateral Muscles
Neck Muscles Anatomy Posterior Triangle Prevertebral And Lateral Muscles
 Muscle Anatomy Of The Neck Everything You Need To Know Dr Nabil Ebraheim
Muscle Anatomy Of The Neck Everything You Need To Know Dr Nabil Ebraheim
 The Lateral Cervical Muscles Human Anatomy
The Lateral Cervical Muscles Human Anatomy
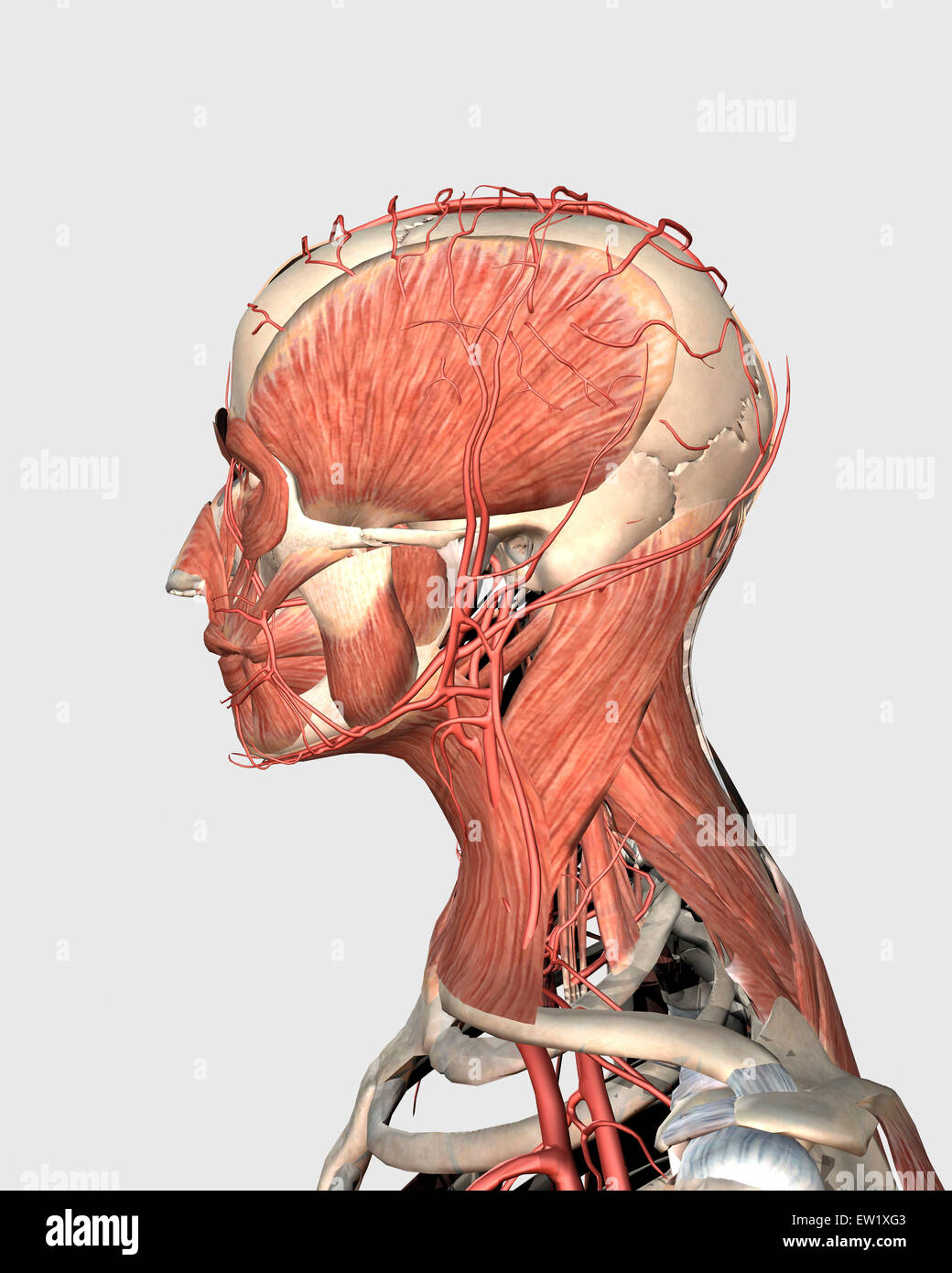 Medical Illustration Showing Human Head And Neck Muscles
Medical Illustration Showing Human Head And Neck Muscles
Penetrating Neck Injuries Rebel Em Emergency Medicine Blog
 Yoga Anatomy Yoga For Neck Pain And Neck Tension Yoga Journal
Yoga Anatomy Yoga For Neck Pain And Neck Tension Yoga Journal
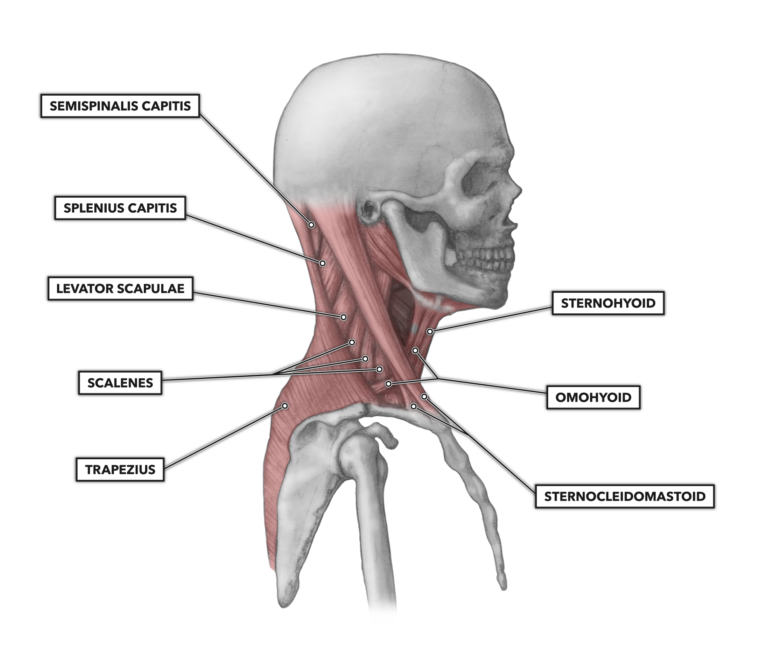 Crossfit Cervical Muscles Part 1
Crossfit Cervical Muscles Part 1
 Head And Neck Muscles Boundless Anatomy And Physiology
Head And Neck Muscles Boundless Anatomy And Physiology
 Muscular Anatomy And Soft Tissue Headandcervicalspine
Muscular Anatomy And Soft Tissue Headandcervicalspine
 Neck Muscle Anatomy Health Medicine And Anatomy Reference
Neck Muscle Anatomy Health Medicine And Anatomy Reference
 Neck Muscles Anatomy Art Watercolor Splash
Neck Muscles Anatomy Art Watercolor Splash
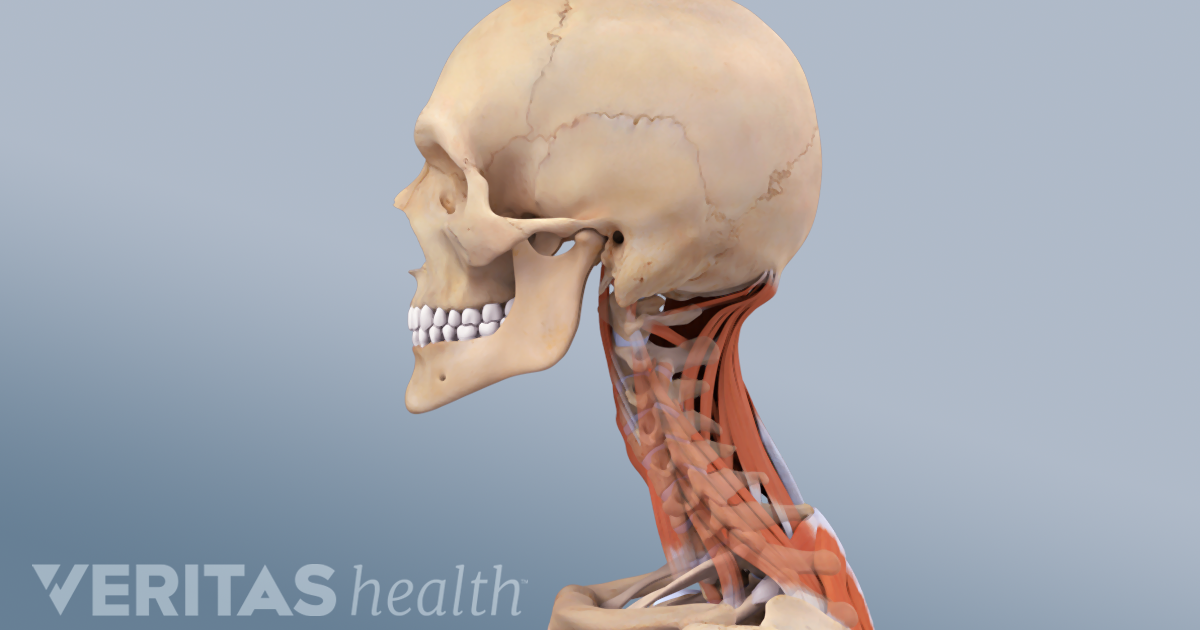 Cervicogenic Headache Causes And Risk Factors
Cervicogenic Headache Causes And Risk Factors
 11 3 Axial Muscles Of The Head Neck And Back Anatomy And
11 3 Axial Muscles Of The Head Neck And Back Anatomy And
 Anatomy 2 U1 L16 Muscles And Deep Fascia Of The Neck
Anatomy 2 U1 L16 Muscles And Deep Fascia Of The Neck
 Anatomy Of Human Face And Neck Muscles Front View Metal Print
Anatomy Of Human Face And Neck Muscles Front View Metal Print
Medical Exhibits Demonstrative Aids Illustrations And Models

 Cervical Motor Control Part 1 Clinical Anatomy Of Cervical
Cervical Motor Control Part 1 Clinical Anatomy Of Cervical
The Neck Muscles Human Anatomy
 Human Muscle System Functions Diagram Facts Britannica
Human Muscle System Functions Diagram Facts Britannica

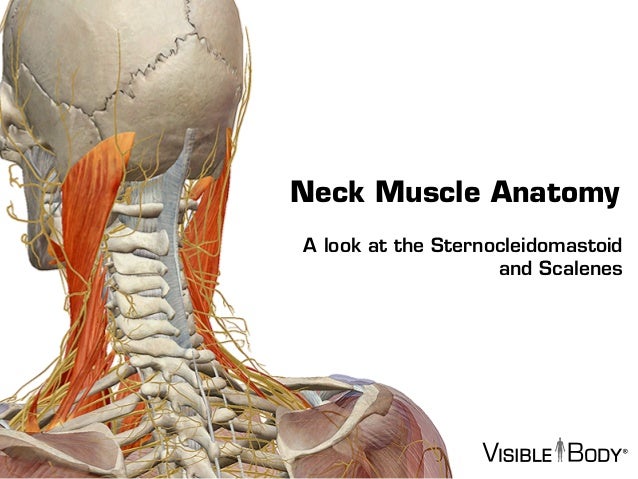
Belum ada Komentar untuk "Anatomy Of Cervical Muscles"
Posting Komentar