Extensor Tendon Anatomy Hand
Zone i disruption of terminal extensor tendon distal to or at the dip joint of the fingers and ip joint of the thumb epl mallet finger. A flexor tendon injury can cause loss of flexion.
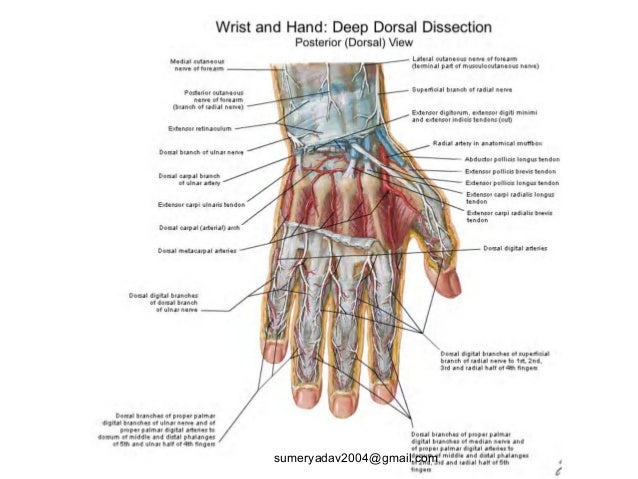 Extensor Tendons Injury And Deformity
Extensor Tendons Injury And Deformity
Understanding of and familiarity with the extensor anatomy of the hand and fingers by the radiologist is crucial for better assessment of pathologic conditions with mr imaging and optimization of this mo dality as a diagnostic tool.

Extensor tendon anatomy hand. Zone ii disruption of tendon over middle phalanx or proximal phalanx of thumb epl zone iii. Rheumatoid arthritis ra is the most common underlying etiology of tendon rupture in the hand and wrist. Ten years later he described the process of attritional rupture of the digital extensor tendons in the rheumatoid hand with which his name has become associated.
Extensor denotes their action which is to extend or open flat joints in the hand. Extensor tendons are just under the skin. Thank you for rating.
Zones of extensor tendon injuries. Extensor tendon injuries and tenosynovitis represent clinical situations in which knowledge of this anatomy is use. They can be injured by a minor cut or jamming a finger which may cause the thin tendons to rip from their attachment to bone.
Extrinsic denotes their location outside the hand. Please vote below and help us build the most advanced adaptive learning platform in medicine. Extensor tendons are thin tendons located on the back of the hand just under the skin.
The ability to flex the fingers consists of a system of flexor muscles in the forearm and their tendons are inserted into the bones of the fingers. If not treated it may be hard to straighten one or more joints. These particular tendons allow you to straighten your fingers and thumb and can be injured by a simple cut or jammed finger.
The extensor tendon compartments of the wrist are six tunnels which transmit the long extensor tendons from the forearm into the hand. The 6 extensor compartments of the wrist and intrinsic muscles of the hand comprise 23 musculotendinous units. They lie next to the bone on the back of the hands and fingers and straighten the wrist fingers and thumb figure 1.
Each tunnel is lined internally by a synovial sheath and separated from one another by fibrous septa. The extrinsic extensor muscles of the hand are located in the back of the forearm and have long tendons connecting them to bones in the hand where they exert their action. They are located on the posterior aspect of the wrist.
The extensor tendon system of the wrist hand and fingers is more complex than the flexor tendon system.
 Lumbrical Muscles Of The Hand Anatomy Everything You Need To Know Dr Nabil Ebraheim
Lumbrical Muscles Of The Hand Anatomy Everything You Need To Know Dr Nabil Ebraheim
 De Quervain S Tenosynovitis Hand Orthobullets
De Quervain S Tenosynovitis Hand Orthobullets
 Extensor Indicis Proprius Extensor Tendons At Wrist
Extensor Indicis Proprius Extensor Tendons At Wrist
 Sagittal Band Rupture Hand Orthobullets
Sagittal Band Rupture Hand Orthobullets
 Extensor Tendon Exam Hand Surgery Source
Extensor Tendon Exam Hand Surgery Source
 Extensor Tendon Injuries Overview Hand Arm
Extensor Tendon Injuries Overview Hand Arm
 Racgp Hands Fingers Thumbs Assessment And Management
Racgp Hands Fingers Thumbs Assessment And Management
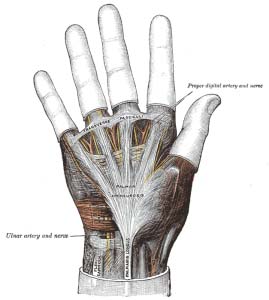 Structures Of The Hand Tendons Ligaments Teachmeanatomy
Structures Of The Hand Tendons Ligaments Teachmeanatomy
 Finger Amputation An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Finger Amputation An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
 Extensor Tendon Injury At The Pip Joint
Extensor Tendon Injury At The Pip Joint
 Extensor Muscle Anatomy Britannica
Extensor Muscle Anatomy Britannica
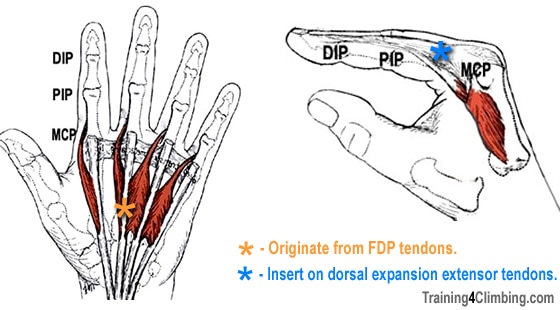 Lumbrical Muscle Training Injury Treatment Training For
Lumbrical Muscle Training Injury Treatment Training For
Anatomy 101 Thumb Tendons The Handcare Blog
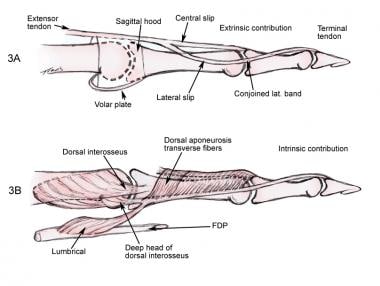 Extensor Tendon Lacerations Background History Of The
Extensor Tendon Lacerations Background History Of The
 Extensor Tendon Injuries Hand Orthobullets
Extensor Tendon Injuries Hand Orthobullets
 Figure 1 From Extensor Tendon Injuries Acute Management And
Figure 1 From Extensor Tendon Injuries Acute Management And
Extensor Tendon Injuries Www Hand Surgery Eu
 Extensor Tendon Injuries Of The Hand Emergency Department
Extensor Tendon Injuries Of The Hand Emergency Department
Patient Education Concord Orthopaedics
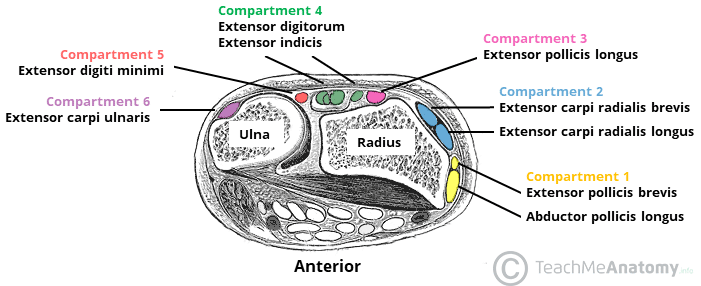 The Extensor Compartments Of The Wrist De Quervain S
The Extensor Compartments Of The Wrist De Quervain S

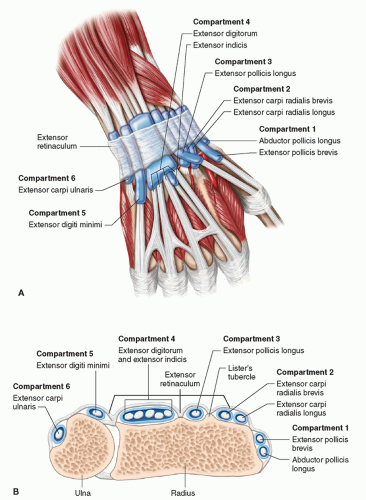


Belum ada Komentar untuk "Extensor Tendon Anatomy Hand"
Posting Komentar