Knee Anatomy Meniscus
They are attached to the small depressions fossae. As a vital part of the joint it acts to prevent the deterioration and degeneration of articular cartilage and the onset and development of osteoarthritis.
A meniscus injury is one of the most common knee injuries.
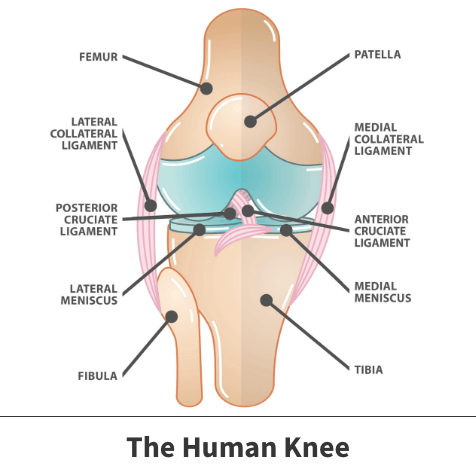
Knee anatomy meniscus. Meniscus anatomy the menisci of the knee are two pads of fibrocartilaginous tissue which serve to disperse friction in the knee joint between the lower leg tibia and the thigh femur. Tendons are often overlooked as part of knee joint anatomy. Bursitis often occurs from overuse or injury.
Each of your knees has two c shaped pieces of cartilage that act like a cushion between your shinbone and your thighbone menisci. In most of our joints including the knee there is a layer of articular cartilage which is made of collagen and chondroitin. A torn meniscus is one of the most common knee injuries.
The knee cap actually sits inside the patellar tendon. Pain swelling and warmth in any of the bursae of the knee. They are they soft tissues found at the end of muscles which link the muscle to bone.
Collection of fluid in the back of the knee. The medial meniscus is often injured when the knee is twisted or sprained with sudden force. Any activity that causes you to forcefully twist or rotate your knee especially when putting your full weight on it can lead to a torn meniscus.
When people talk about torn cartilage in the knee they are usually referring to a torn meniscus. It provides a smooth surface over the bones. They are concave on the top and flat on the bottom articulating with the tibia.
However anyone at any age can tear a meniscus. Athletes particularly those who play contact sports are at risk for meniscus tears. Meniscus tears are among the most common knee injuries.
The main tendon found at the knee is the patellar tendon which links the quads muscles to the shin bone. Extensive scientific investigations in recent decades have established the anatomical biomechanical and functional importance that the meniscus holds within the knee joint. Tendons at the knee.
Menisci tend to get injured during movements that forcefully twist your knee while bearing weight this is very prevalent in younger populations or they tend to grow weaker with age and tear as a result of minor injuries or movements. External rotation rotating the knee outward puts the most strain on the meniscus while inward internal rotation is the least strenuous. The knee meniscus is a special layer of extra cartilage that lines the knee joint.
Its job is to cushion the joint and transfer forces between the tibia and femur bones. It is less mobile than the lateral meniscus because it is firmly attached to the tibial collateral ligament.
 An Overview Of Knee Anatomy Meniscus Tear Treatment
An Overview Of Knee Anatomy Meniscus Tear Treatment
 Anatomy Knee Restoration Center Of Indiana
Anatomy Knee Restoration Center Of Indiana
 Beantown Physio Pt Tip Of The Month Archive Meniscal Tears
Beantown Physio Pt Tip Of The Month Archive Meniscal Tears
 Knee Human Anatomy Function Parts Conditions Treatments
Knee Human Anatomy Function Parts Conditions Treatments
 Torn Meniscus Symptoms Treatment Mri Test Recovery Time
Torn Meniscus Symptoms Treatment Mri Test Recovery Time
 Meniscus Vs Cartilage Tear Of The Knee
Meniscus Vs Cartilage Tear Of The Knee
 Understanding The Role Of Cartilage In The Knee
Understanding The Role Of Cartilage In The Knee
 Anatomy Of The Knee Baxter Regional Medical Center
Anatomy Of The Knee Baxter Regional Medical Center
 Knee Pain On The Inside Of Your Joint Causes Solutions
Knee Pain On The Inside Of Your Joint Causes Solutions
 Clinical Anatomy Knee Mensicus And Knee Joint
Clinical Anatomy Knee Mensicus And Knee Joint
 Coronary Ligament Of The Knee Wikipedia
Coronary Ligament Of The Knee Wikipedia
 Meniscus Tears Florida Orthopaedic Institute
Meniscus Tears Florida Orthopaedic Institute
 Discoid Meniscus Orthoinfo Aaos
Discoid Meniscus Orthoinfo Aaos
 Torn Meniscus Johns Hopkins Medicine
Torn Meniscus Johns Hopkins Medicine
 Menicus Injuries United States The Orthopedic Center
Menicus Injuries United States The Orthopedic Center
 Meniscus Knees Knee Legs Skeleton Leg Thigh Joints
Meniscus Knees Knee Legs Skeleton Leg Thigh Joints
 Meniscus Repair In Los Angeles Meniscectomy In Beverly Hills
Meniscus Repair In Los Angeles Meniscectomy In Beverly Hills
 012b Knee Joint Anatomy Flashcards Memorang
012b Knee Joint Anatomy Flashcards Memorang


Belum ada Komentar untuk "Knee Anatomy Meniscus"
Posting Komentar