The Anatomy Of The Hip Joint
The hip joint is one of the largest joints in the body and is a major weight bearing joint. The round head of the femur rests in a cavity the acetabulum that allows free rotation of the limb.
 Hip Joint Anatomy Pictures And Information
Hip Joint Anatomy Pictures And Information
Hip problems occur when any one of these components starts to degenerate or is in some way compromised or irritated.
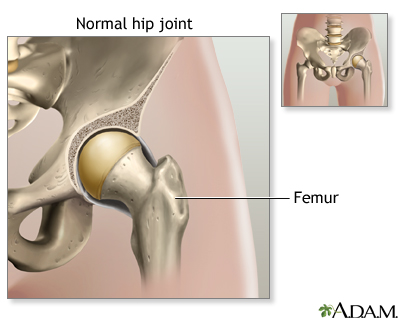
The anatomy of the hip joint. And synovial membrane and fluid which encapsulates the hip joint and lubricates it respectively. Bones of the hip joint. The hip joint consists of two main parts.
Hip ligaments and tendons tough fibrous tissues that bind bones to bones and muscles to bones. Hip anatomy function and common problems. Amphibians and reptiles have relatively weak pelvic girdles and the femur extends horizontally.
The femoral nerve innervates the flexors of the hip joint which pass anterior to the hip joint. So the anterior portion of the hip joint is innervated by the femoral nerve 2. The hip joint is one of the most important joints in the human body.
It forms a connection from the lower limb to the pelvic girdle and thus is designed for stability and weight bearing rather than a large range of movement. The hip joint is a ball and socket joint. The hip joint is a ball and socket synovial joint formed by an articulation between the pelvic acetabulum and the head of the femur.
Bands of tissue called ligaments connect the ball to the socket stabilizing the hip and forming the joint capsule. The pelvis and the femur the thighbone. It is the largest ball and socket joint in your body.
Femoral head a ball shaped piece of bone located at the top of your thigh bone or femur acetabulum a socket in your pelvis into which the femoral head fits. The hip joint is the articulation of the pelvis with the femur which connects the axial skeleton with the lower extremity. There are two other protrusions near the top of the femur known as the greater and lesser trochanters.
Yet the hip joint is also one of our most flexible joints and allows a greater range of motion than all other joints in the body except for the shoulder. Also the area adjacent to this joint. At the top of the femur is a rounded protrusion which articulates with the pelvis.
The adult os coxae or hip bone is formed by the fusion of the ilium the ischium and the pubis which occurs by the end of the teenage years. The hip joint is made up of two bones. Hip in anatomy the joint between the thighbone femur and the pelvis.
This portion is referred to as the head of the femur or femoral head. Weight bearing stresses on the hip during walking can be 5 times a persons body weight. A healthy hip can support your weight and allow you to move without pain.
It is the largest ball and socket joint in your body. It allows us to walk run and jump. It is the largest bone in the body.
It bears our bodys weight and the force of the strong muscles of the hip and leg.
 Total Hip Replacement Orthoinfo Aaos
Total Hip Replacement Orthoinfo Aaos
 Hip Anatomy Yoga Understanding The Hips For Yoga Jason
Hip Anatomy Yoga Understanding The Hips For Yoga Jason
 Hip Osteoarthritis Physiopedia
Hip Osteoarthritis Physiopedia
 Hip Anatomy Orthopedic Surgery Algonquin Il Barrington
Hip Anatomy Orthopedic Surgery Algonquin Il Barrington
 Total Hip Replacement Orthoinfo Aaos
Total Hip Replacement Orthoinfo Aaos
 Anatomy Of The Hip Joint Semantic Scholar
Anatomy Of The Hip Joint Semantic Scholar
 Hip Replacement Procedure Types Recovery Time And Risks
Hip Replacement Procedure Types Recovery Time And Risks
 International Hip Dysplasia Institute
International Hip Dysplasia Institute
 The Hip Joint Articulations Movements Teachmeanatomy
The Hip Joint Articulations Movements Teachmeanatomy
 Basics Of Hip Anatomy Mike Scaduto
Basics Of Hip Anatomy Mike Scaduto
 Yoga For Hip Stability Understanding Hypermobility
Yoga For Hip Stability Understanding Hypermobility
 3b Scientific A81 Functional Hip Joint 3b Smart Anatomy
3b Scientific A81 Functional Hip Joint 3b Smart Anatomy
 Hip And Thigh Bones Joints Muscles Kenhub
Hip And Thigh Bones Joints Muscles Kenhub
 The Gross Antomy Of The Hip Hoint And Applied Anatomy
The Gross Antomy Of The Hip Hoint And Applied Anatomy
 Ultimate Hip Joint Anatomy In One Picture Hip Anatomy
Ultimate Hip Joint Anatomy In One Picture Hip Anatomy
 Hip Anatomy Pictures Function Problems Treatment
Hip Anatomy Pictures Function Problems Treatment
 Hip Joint Replacement Series Normal Anatomy Medlineplus
Hip Joint Replacement Series Normal Anatomy Medlineplus
 Hip And Thigh Bones Joints Muscles Kenhub
Hip And Thigh Bones Joints Muscles Kenhub
 Hip And Thigh Bones Joints Muscles Kenhub
Hip And Thigh Bones Joints Muscles Kenhub
 Hip Arthritis Treatments Osteotomy Hip Replacement Hss
Hip Arthritis Treatments Osteotomy Hip Replacement Hss
 Hip Joint Anatomy Overview Gross Anatomy
Hip Joint Anatomy Overview Gross Anatomy
 Hip Joint Anatomy Hip Bones Ligaments Muscles
Hip Joint Anatomy Hip Bones Ligaments Muscles
 Hip Anatomy Recon Orthobullets
Hip Anatomy Recon Orthobullets


Belum ada Komentar untuk "The Anatomy Of The Hip Joint"
Posting Komentar