Trigeminal Nerve Anatomy
In this article we shall look at the anatomical course of the nerve and the motor sensory and parasympathetic functions of its terminal branches. Trigeminal nerve anatomy and function.
 Easy Notes On Trigeminal Nerve Learn In Just 3 Minutes
Easy Notes On Trigeminal Nerve Learn In Just 3 Minutes
The trigeminal nerve roots and ganglion like those of other cranial nerves.
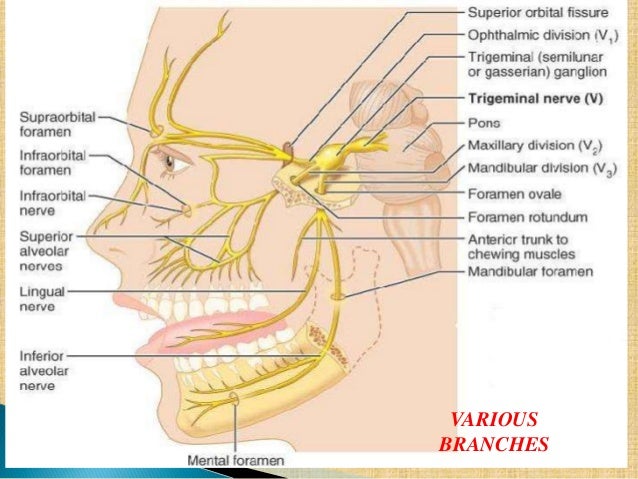
Trigeminal nerve anatomy. Ophthalmic division cn v1 or va maxillary division cn v2 or vb mandibular division cn v3 or vc. The trigeminal nerve is the largest of the 12 cranial nerves. The trigeminal nerve is a mixed cranial nerve that has both sensory and motor functions.
The frontal nerve the lacrimal nerve and the nasociliary nerves converge in. It supplies sensations to the face mucous membranes and other structures of the head. It is the largest of the cranial nerves.
Join us in this video where we discuss the trigeminal nerve cranial nerve v. There are three divisions of the trigeminal nerve. The trigeminal nerve has three different divisions.
It is both large and complicated and has multiple brainstem nuclei sensory and motor as well as many interconnections with other cranial nerves. Its main function is transmitting sensory information to the skin sinuses and mucous membranes in the face. The ophthalmic nerve passes forward in the lateral wall of the cavernous sinus.
The three sensory nerve branches of the trigeminal nervethe ophthalmic nerve. It is the motor nerve for the muscles of mastication and contains proprioceptive fibers. It also stimulates movement in the jaw muscles.
The acronym mom can be used to recall the three. We go into great detail on the origin course and structures supplied by the trigeminal nerve. The trigeminal nerve is the fifth cranial nerve and its primary role is relaying sensory information from the face and head although it does provide motor control to the muscles of mastication.
The trigeminal nerve is the largest and most complex of the 12 cranial nerves cns. The trigeminal nerve cn v is the fifth paired cranial nerve. It is also the largest cranial nerve.
The motor section of the trigeminal nerve has a nucleus point situated in the pons innervating the masticating muscles and also the tensor muscle in the tympanic membranes of the ear. The trigeminal nerve is the biggest cranial nerve and has sensory as well as motor divisions. It gains access into the orbit via the superior orbital fissure fig.
The trigeminal nerve the fifth cranial nerve or simply cn v is a nerve responsible for sensation in the face and motor functions such as biting and chewing. The trigeminal nerve trifurcates into ophthalmic maxillary and mandibular nerves distal to the trigeminal ganglion.
 Trigeminal Neuralgia What You Need To Know
Trigeminal Neuralgia What You Need To Know
 Trigeminal Neuralgia Bell S Palsy And Other Cranial Nerve
Trigeminal Neuralgia Bell S Palsy And Other Cranial Nerve
 Trigeminal Neuralgia The Ccj Dr Ernesto Fernandez Medium
Trigeminal Neuralgia The Ccj Dr Ernesto Fernandez Medium
 Anatomy Of Trigeminal Nerve Springerlink
Anatomy Of Trigeminal Nerve Springerlink
 Trigeminal Nerve Anatomical Vector Illustration Diagram With
Trigeminal Nerve Anatomical Vector Illustration Diagram With
 Nerve Blocks Of The Face Nysora
Nerve Blocks Of The Face Nysora
 Trigeminal Nerve Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock
Trigeminal Nerve Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock
 The Trigeminal Nerve Cn V Course Divisions
The Trigeminal Nerve Cn V Course Divisions
 The Trigeminal Nerve And The Social Nervous System
The Trigeminal Nerve And The Social Nervous System
 Anatomy Dermatomes Of The Face Image
Anatomy Dermatomes Of The Face Image
 Trigeminal Nerve Anatomy Illustration Stock Image C047
Trigeminal Nerve Anatomy Illustration Stock Image C047
 Neural Blockade For Trigeminal Neuralgia Radiology Key
Neural Blockade For Trigeminal Neuralgia Radiology Key
 The Trigeminal Nerve Human Anatomy
The Trigeminal Nerve Human Anatomy
 The Cranial Nerves Organization Of The Central Nervous
The Cranial Nerves Organization Of The Central Nervous
 Superficial Face Innervation Trigeminal Nerve Cnv Diagram
Superficial Face Innervation Trigeminal Nerve Cnv Diagram
 Trigeminal Nerve Cn V Anatomy Function And Branches Kenhub
Trigeminal Nerve Cn V Anatomy Function And Branches Kenhub
 Anatomy Of The Trigeminal Nerve Springerlink
Anatomy Of The Trigeminal Nerve Springerlink
 Mandibular Nerve Trigeminal Nerve Mandible Anatomy Png
Mandibular Nerve Trigeminal Nerve Mandible Anatomy Png
 Trigeminal Nerve Cn V Anatomy Function And Branches Kenhub
Trigeminal Nerve Cn V Anatomy Function And Branches Kenhub
 12129 02x Trigeminal Nerve Distribution Anatomy Exhibits
12129 02x Trigeminal Nerve Distribution Anatomy Exhibits
 Anatomical Organization Of The Trigeminal Nerve The
Anatomical Organization Of The Trigeminal Nerve The


Belum ada Komentar untuk "Trigeminal Nerve Anatomy"
Posting Komentar