Anatomy Of The Glenohumeral Joint
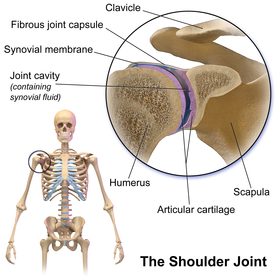
The glenohumeral joint is a ball and socket joint formed between the articulation of the rounded head of the humerus the upper arm bone and the cup like depression of the scapula called the glenoid fossa. The humeral head lies within the glenoid fossa a cavity that is lined by the glenoid labrum.
Middle glenohumeral ligament anterior glenoid cavity lesser tubercle of humerus stabilise the glenohumeral joint limit lateral rotation and extension of joint.

Anatomy of the glenohumeral joint. Bony anatomy of the shoulder. Ligaments glenohumeral ligaments superior middle and inferior the joint capsule is formed by this group. The glenohumeral gh joint is a true synovial ball and socket style diarthroidal joint that is responsible for connecting the upper extremity to the trunk.
Muscles and tendons of the shoulder. Abduction abduction requires external rotation to clear the greater tuberosity from impinging on the acromion. This joint is formed from the combination of the humeral head and the glenoid fossa of the scapula.
As mentioned previously the tendons of the rotator cuff muscles as they near their. Therefore if someone has an internal rotation contracture they can not abduct 120. The relative weakness of the capsule itself coupled with the bony structure of the glenohumeral joint means that the rotator cuff muscles are largely.
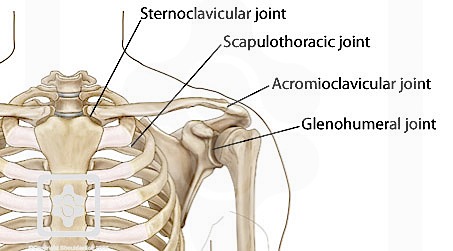
It is one of four joints that comprise the shoulder complex. Injury to the shoulder. Coracohumeral ligament attaches the base of the coracoid process to the greater tubercle.
Glenohumeral joint anatomy stabilizer and biomechanics. Reinforcement of the joint capsule. The active and passive soft tissue and bony stabilizers work together to provide glenohumeral stability.
Transverse humeral ligament spans the distance between the two tubercles of the humerus. Inferior glenohumeral ligament inferior part of blenoid labrum inferomedial part of humeral neck stabilise the glenohumeral. The glenohumeral joint motion is a result of a complex interplay between the passive and active stabilizers that require intricate balance and synchronicity.
Reference scapular plane is 30 degrees anterior to coronal plane. The glenohumeral joint consists of an articulation between the scapula and humerus. Shoulder ligaments labrum bursae and the joint capsule.
Anatomy of the shoulder glenohumeral jointscapulo thoracic joint an introduction to the anatomy of the shoulder. The shallow nature of the glenoid fossa lends the glenohumeral joint an increased range of motion while providing little stability. Limit lateral rotation and extension of joint.
Frozen Shoulder Adhesive Capsulitis Cleveland Clinic
 Shoulder Glenohumeral Joint Human Anatomy Vector Diagram
Shoulder Glenohumeral Joint Human Anatomy Vector Diagram
 2 Shoulder Joint Its Applied Anatomy 07 1
2 Shoulder Joint Its Applied Anatomy 07 1
:watermark(/images/watermark_5000_10percent.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/atlas_overview_image/771/PoKFfwUGXrJ4sytwNutLA_upper-arm-nerves-vessels_english.jpg) Shoulder Joint Anatomy Muscles Ligaments And Movements
Shoulder Joint Anatomy Muscles Ligaments And Movements
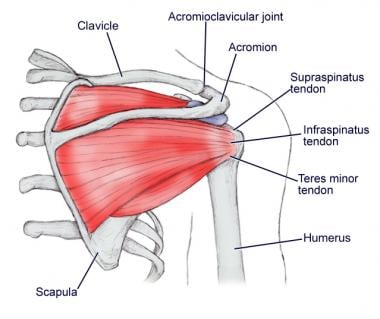 Shoulder Joint Anatomy Overview Gross Anatomy Microscopic
Shoulder Joint Anatomy Overview Gross Anatomy Microscopic
 Shoulder Joint Anatomy Skeletal System Cartilages Ligaments
Shoulder Joint Anatomy Skeletal System Cartilages Ligaments
 Shoulder Anatomy Shoulder Injuries Chicago Westchester
Shoulder Anatomy Shoulder Injuries Chicago Westchester
 Anatomy Of The Shoulder Region Ppt Video Online Download
Anatomy Of The Shoulder Region Ppt Video Online Download
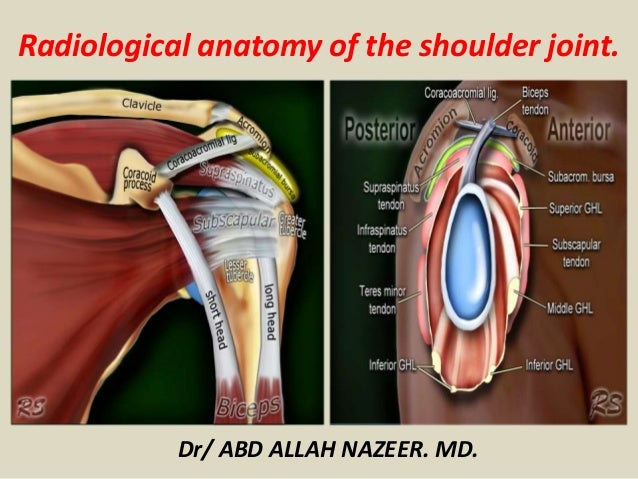 Presentation1 Pptx Radiological Anatomy Of The Shoulder Joint
Presentation1 Pptx Radiological Anatomy Of The Shoulder Joint
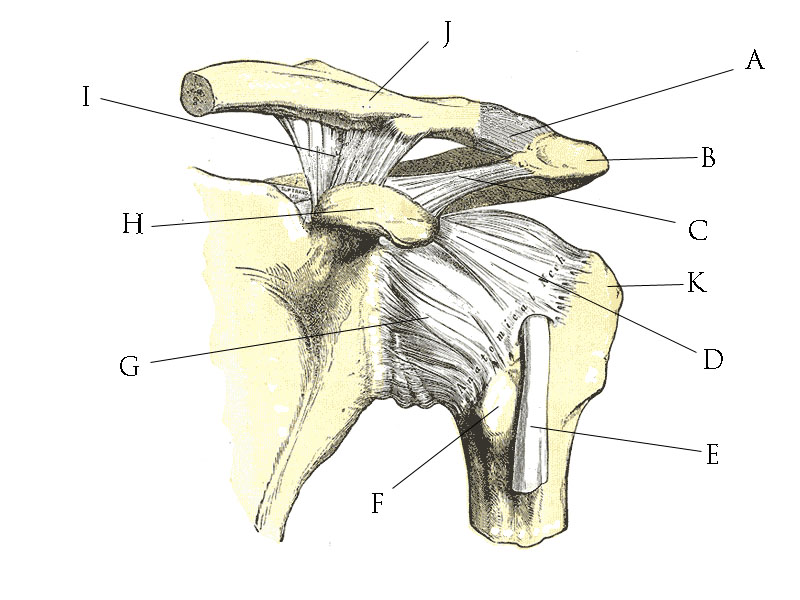 Human Anatomy Quizzes Shoulder Joint Wikiversity
Human Anatomy Quizzes Shoulder Joint Wikiversity
 Anatomical Landmark Positions For Locating The Glenohumeral
Anatomical Landmark Positions For Locating The Glenohumeral

 Pin On The Shoulder Rotator Cuff Bankart Labrum Tear Bicep
Pin On The Shoulder Rotator Cuff Bankart Labrum Tear Bicep
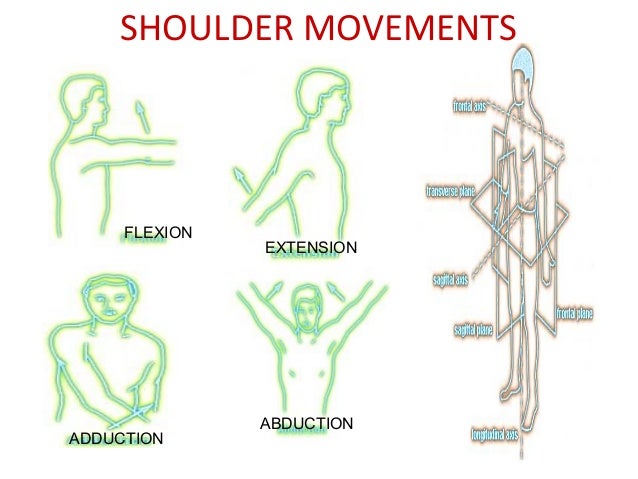 Anatomy Of Shoulder Joint Vamshi Kiran
Anatomy Of Shoulder Joint Vamshi Kiran
 Glenohumeral Joint Anatomy Britannica
Glenohumeral Joint Anatomy Britannica
Shoulder Anatomy Musculoskeletal Ultrasoundupper Extremities
 Shoulder Joint Treatment Orange County Shoulder Surgeon
Shoulder Joint Treatment Orange County Shoulder Surgeon
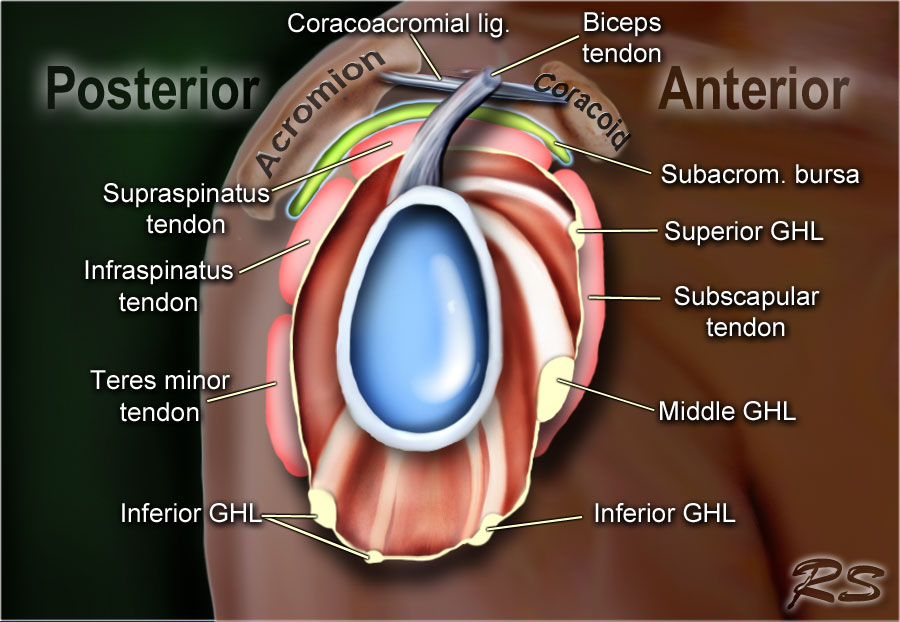 The Radiology Assistant Shoulder Mr Anatomy
The Radiology Assistant Shoulder Mr Anatomy
 Shoulder Joint Of Human Body Anatomy Infographic Diagram With
Shoulder Joint Of Human Body Anatomy Infographic Diagram With




Belum ada Komentar untuk "Anatomy Of The Glenohumeral Joint"
Posting Komentar