Knee Xray Anatomy
There may also be obliteration of the caudal portion of hoffas fat pad secondary to infrapatellar bursitis. Click on a link to get t1 coronal view t2 fatsat axial view t2 fatsat coronal view t2 fatsat sagittal view.
Use the mouse to scroll.
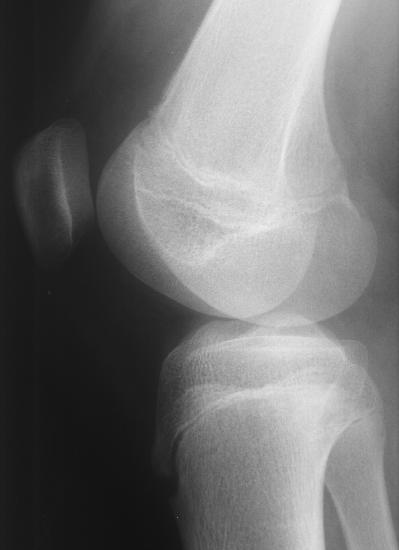
Knee xray anatomy. It is the largest synovial joint in the body and allows flexion and extension of the leg as well as some rotation in the flexed position. Normal radiographic anatomy of the knee. Atlas of knee mri anatomy.
Anteroposterior and lateral views of the knee are most common knee x rays done. An x ray is one of the most common imaging tests used to diagnose a knee problem. This is the insall salvatti ratio and should ideally me measure with the knee flexed at 30 degrees.
If its too long then think of a patellar tendon rupture. Its length should be the same as the patellar length 20. Check for errors and try again.
This is a front to back view of the knee joint also called the ap view. Stanford bone tumor bayesian network issssr msk lectures for residents ocad msk cases from around the world stanford msk mri atlas has served almost 800000 pages to users in over 100 countries. The knee is an important load bearing joint of the lower limb.
A knee x ray may appear entirely normal. Knee normal ap. Ap stands for anteroposterior meaning the image is directed from the front to the back of the knee joint.
This allows effusions to be visualised in the suprapatellar pouch. The classical radiologic picture of osgood schlatter disease is fragmentation of the tibial tubercle and local soft tissue swelling fig. In the context of trauma the lateral view is acquired with the patient lying supine and with a horizontal x ray beam.
Skyline view is typically used to assess patellofemoral joint and patella condylar alignment. This webpage presents the anatomical structures found on knee mri. The knee joint is a modified hinge joint between the femur tibia and patella.
Knee x rays are done to assess the knee joint pathology. The patellar tendon goes from the inferior pole of the patella to the tibial tuberosity. Unable to process the form.
 An Incidental Finding On A Knee Radiograph The Bmj
An Incidental Finding On A Knee Radiograph The Bmj
 Full Text Radiofrequency Techniques To Treat Chronic Knee
Full Text Radiofrequency Techniques To Treat Chronic Knee
 Radiological Anatomy Of The Lower Limb
Radiological Anatomy Of The Lower Limb
 Figure 3 From Normal Magnetic Resonance Imaging Anatomy Of
Figure 3 From Normal Magnetic Resonance Imaging Anatomy Of
 Baker Cyst Imaging Overview Radiography Computed Tomography
Baker Cyst Imaging Overview Radiography Computed Tomography
 Film Critique Of The Lower Extremity Part 2
Film Critique Of The Lower Extremity Part 2
 Radiography Knee Injury And Prevention
Radiography Knee Injury And Prevention
 Understanding The Role Of Cartilage In The Knee
Understanding The Role Of Cartilage In The Knee
 Full Text Radiofrequency Techniques To Treat Chronic Knee
Full Text Radiofrequency Techniques To Treat Chronic Knee
 Diagnosing Knee Arthritis Mu Health Care
Diagnosing Knee Arthritis Mu Health Care
 Novel Ai Approach Can Help Radiologists Improve
Novel Ai Approach Can Help Radiologists Improve
 Clinical Anatomy Radiology Lateral Knee
Clinical Anatomy Radiology Lateral Knee
 Knee Trauma Radiographic Anatomy Wikiradiography
Knee Trauma Radiographic Anatomy Wikiradiography
 Presentation1 Pptx Radiological Anatomy Of The Knee Joint
Presentation1 Pptx Radiological Anatomy Of The Knee Joint
 Simultaneous Bilateral Knee Varus Stress Radiographic
Simultaneous Bilateral Knee Varus Stress Radiographic
 Take A Knee Brown Emergency Medicine
Take A Knee Brown Emergency Medicine
 Osteonecrosis Of The Knee Orthoinfo Aaos
Osteonecrosis Of The Knee Orthoinfo Aaos
 Lateral Knee Positioning Radiology Case Radiopaedia Org
Lateral Knee Positioning Radiology Case Radiopaedia Org
 Canine Cruciate Ligament Injury
Canine Cruciate Ligament Injury
 Vector Illustration Anatomy Of A Healthy Knee Joint Front X Ray
Vector Illustration Anatomy Of A Healthy Knee Joint Front X Ray
 Radiology In Ped Emerg Med Vol 6 Case 8
Radiology In Ped Emerg Med Vol 6 Case 8
 Knee Xray Century City Los Angeles Ca Millstein Orthopedics
Knee Xray Century City Los Angeles Ca Millstein Orthopedics
 Radiology In Ped Emerg Med Vol 6 Case 8
Radiology In Ped Emerg Med Vol 6 Case 8



Belum ada Komentar untuk "Knee Xray Anatomy"
Posting Komentar