Anatomy Of A Clam
Phylum mollusca class bivalvia. Clam anatomy is shockingly not unlike human anatomy.
 Game Statistics Clam Anatomy Purposegames
Game Statistics Clam Anatomy Purposegames
Anatomy of a clam and describe the function of important external features.
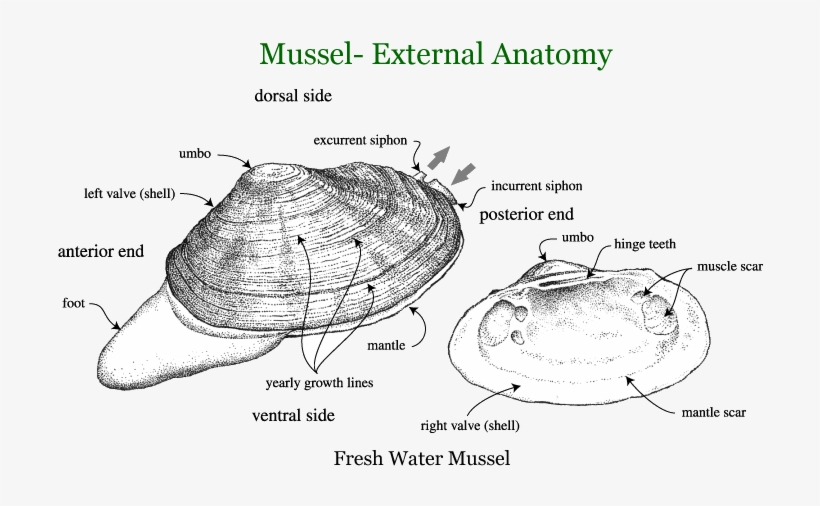
Anatomy of a clam. Some species such as the hard shelled clam here have siphons for directing water flow in and out. Owing to its sessile nature the moment the giant clam chooses a spot as its home it fastens itself to the same. Many have a siphon.
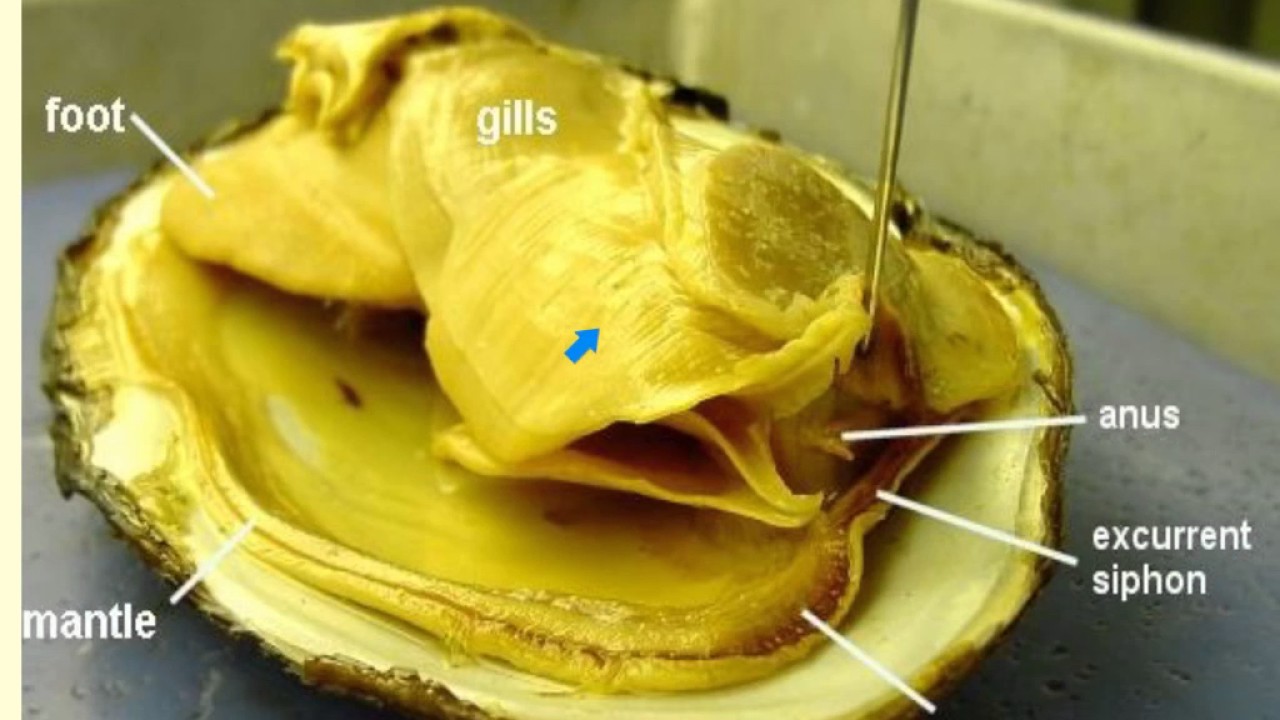
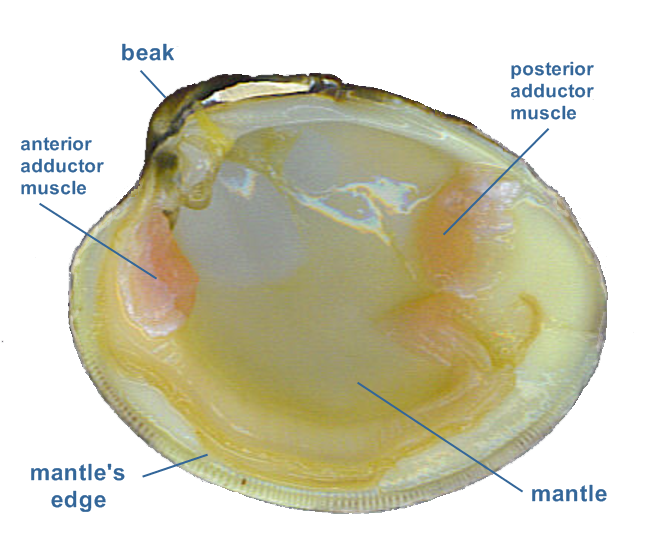
The soft body inside of the shell includes a muscular foot gills or ctenidia used for respiration and feeding muscles a digestive system nerves a three chambered heart and an open circulatory system with sinuses. If youre talking about a whole freshly shucked clam the dark part that sticks up is called the neck. Like all mollusks a clam has a mantle which surrounds its soft body.
It also has a muscular foot which enables the clam to burrow itself in mud or sand. Clams also have kidneys a heart a mouth a stomach a nervous system and an anus. If you hold a clam by the neck after the belly has been removed theres a strip that hangs from it.
External and internal anatomy of a freshwater mussel. A hinged joint and a ligament connect two elongated calcium based shell halves. They filter water as they.
Clams are marine mollusks with two valves or shells. The ligament provides tension to bring the valves apart while one or two adductor muscles can contract to close the valves. The soft tissue above the foot is called the visceral mass and contains the clams body organs.
Sessility refers to the inability of certain animals to move around. Males and females release sperm and eggs respectively and these combine as they free float in the wild to form zygotes. Internal clam anatomy remove mantle to observe thickened region ati mantle gonadal tissue reproductive system anterior adductor posterior y adductor palps and digestive system kidney and anus gills palps adductor excretory system gills respiratory sstem gills system foot mantle.
Pacific razor clams are bivalves. In zygotic form clams drift while gradually developing a shell. Clams are sexual animals and reproduce through spermatozoic means.
Bivalves are easily distinguished from other molluscs by the presence of two shells or valves. A clam in its lifecycle may be male female or hermaphroditic. Giant clams are huge sessile creatures that inhabit the shallow areas of the marine coral reefs.
A pacific razor clam has a mouth a heart kidneys gills and an anus. Anatomy of a pacific razor clam razor clam shells. They will be able to identify the major internal organs o f a clam and their functions.
 Clam Anatomy Clam Discussion Nano Reef Community
Clam Anatomy Clam Discussion Nano Reef Community
 Parts Of A Clam Zoology 2 Lesson 9 Mollusks Anatomy
Parts Of A Clam Zoology 2 Lesson 9 Mollusks Anatomy
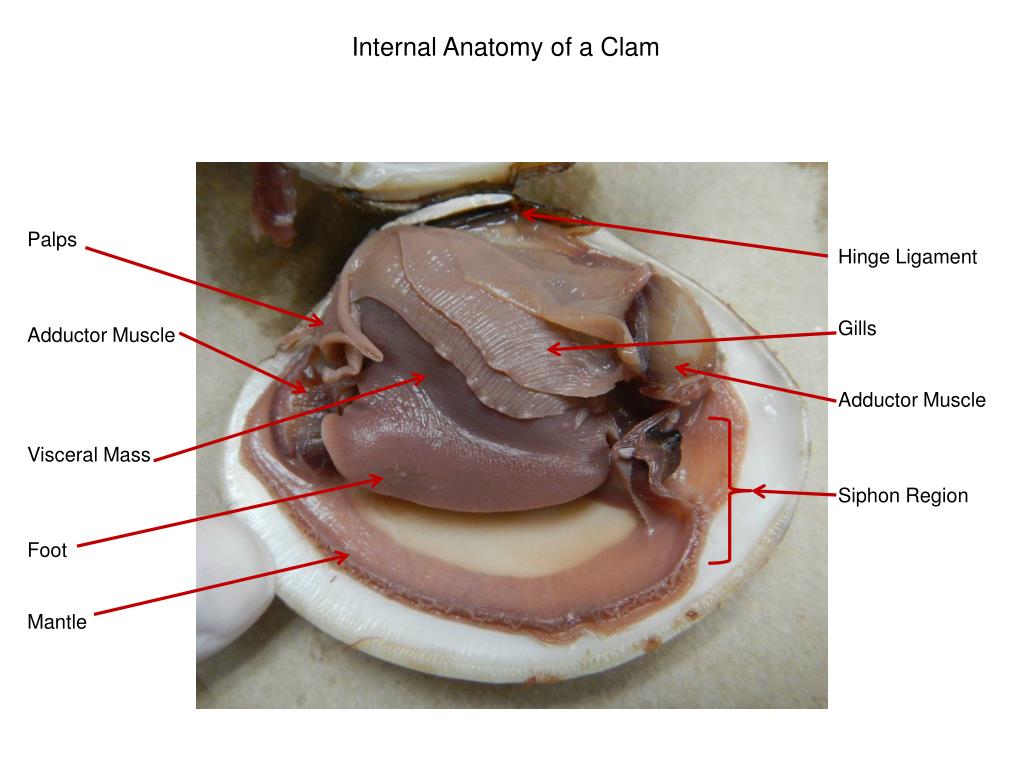 Ppt Dissection Of A Clam Powerpoint Presentation Free
Ppt Dissection Of A Clam Powerpoint Presentation Free

 Seasonal Control Of Particle Clearance By Isolated Gills
Seasonal Control Of Particle Clearance By Isolated Gills
 Principle Anatomy Of A Giant Clam A Dorsal View B
Principle Anatomy Of A Giant Clam A Dorsal View B
 Mollusks Bivalves Marine Biology New Jersey Scuba Diving
Mollusks Bivalves Marine Biology New Jersey Scuba Diving
 Clam Dissection Schoolworkhelper
Clam Dissection Schoolworkhelper
 Clam Dissection And Anatomy Of The Clam Dvd Ctvalley Bio
Clam Dissection And Anatomy Of The Clam Dvd Ctvalley Bio
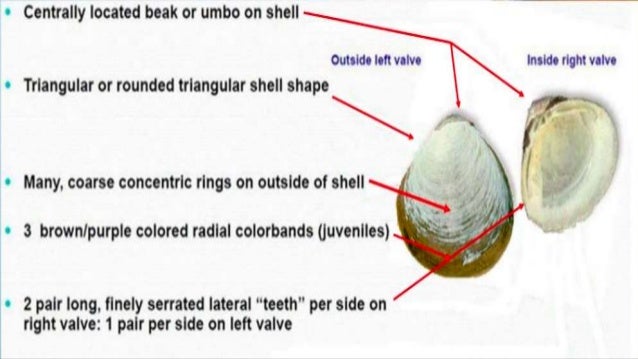 Anatomy Physiology Giant Clam Fish
Anatomy Physiology Giant Clam Fish
 Experiment Recording The Muscles Of Clams
Experiment Recording The Muscles Of Clams
 Mussels And Clams External Anatomy Of Mussels Free
Mussels And Clams External Anatomy Of Mussels Free
The Hatchery Culture Of Bivalves A Practical Manual
 Amazon Com Frey Scientific 597006 Mini Guide To Clam
Amazon Com Frey Scientific 597006 Mini Guide To Clam

 Anatomy Of A Clam Illustration Science Art Com
Anatomy Of A Clam Illustration Science Art Com
 Zoo Clam Anatomy Pt 1 Diagram Quizlet
Zoo Clam Anatomy Pt 1 Diagram Quizlet
 Clam Anatomy Lesson Plan For 6th 8th Grade Lesson Planet
Clam Anatomy Lesson Plan For 6th 8th Grade Lesson Planet
Fresh Water Mussel Collection Introduction Anatomy
 Odfw The Life History Of The Razor Clam
Odfw The Life History Of The Razor Clam

Belum ada Komentar untuk "Anatomy Of A Clam"
Posting Komentar