Anatomy Of Plants
Anatomy of plants plants are the primary producers in earths ecosystem. Collenchyma are characterized by the presence of.
Parenchyma para beside enchyma in poured parenchyma is the fundamental tissue of the plant body.
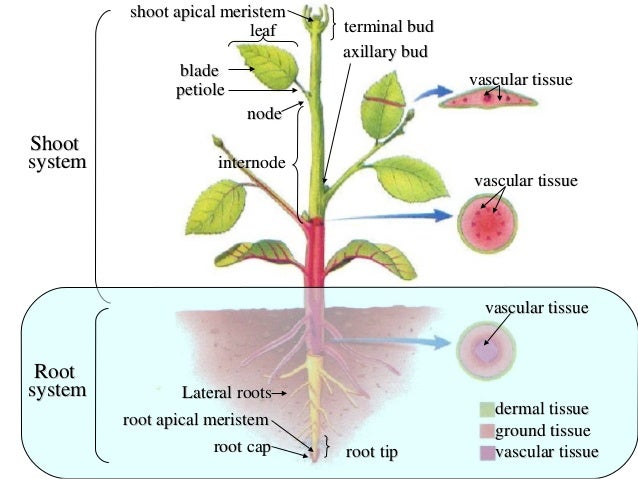
Anatomy of plants. The following is a diagram of the external anatomy of a typical flowering plant. Arise in stems and leaves and are use support the leaves flowers and fruits of plants conduct movem vascular bundle made up of xylem phloem and cambium fibrous roots thin roots. Anatomy of flowering plants study of internal structure of plants is called anatomy.
B isodiametric cells with deposits of cellulose and pectin at the corners. Understanding plant function is the key to enhancing crop production preserving plant biodiversity producing medicines and much more. Multiple choice questions on plant anatomy.
Anatomy is the study of internal structure of organism. These studies are very important because they lead to a better understanding of how to care for plants and fight plant diseases. It is found in every part of the plant body like pith and cortex of stem and root mesophyll of leaves flesh of fruits floral parts and even in xylem and phloem.
Plants have cells as the basic unit cells are organised into tissues and in turn the tissues are organised into organs. A elongated cells with deposits of cellulose and pectin all over the wall. Plant anatomy plant anatomy is the study of plant tissues and cells in order to learn more about the way these organisms are constructed and how they work.
Study of plant anatomy includes histology study of organization and structure of tissues. Plant cells have a supportive cellulose cell wall unlike animal cells which lack cellulose. Originally it included plant morphology the description of the physical form and external structure of plants but since the mid 20th century plant anatomy has been considered a separate field referring only to internal plant structure.
Anatomy helps in knowing the structural peculiarities of different group of plants and indicates the structural adaptation to diverse environments. C elongated cells with thickening at the corners. Plants are autotrophic meaning that they produce their own food via photosynthesis and as a result ultimately produce food for the ecosystems consumers such as humans.
Plant anatomy is now frequently investigated at the cellular level and often involves the sectioning of tissues and microscopy. Plant anatomy or phytotomy is the general term for the study of the internal structure of plants. Cells have thin primary walls and polyhedral shapes.
Plants are autotrophic meaning that they produce their own food via photosynthesis and as a result ultimately produce food for the ecosystem s consumers such as humans. Axil the angle between the upper side of the stem and a leaf branch or petiole. Made up of xylem phloem and cambium thin roots that collects water and nutrients close to the soil form from shoot tissues.
 Comparative Anatomy And Embryology Advanced Ck 12 Foundation
Comparative Anatomy And Embryology Advanced Ck 12 Foundation
 An Introduction To The Structure And Reproduction Of Plants
An Introduction To The Structure And Reproduction Of Plants
 The Gorgeous Anatomy Of Plants By Nehemiah Grew Aleph
The Gorgeous Anatomy Of Plants By Nehemiah Grew Aleph
 Plants Structure Homeostasis Lessons Tes Teach
Plants Structure Homeostasis Lessons Tes Teach
 Anatomy Of Flowering Plants Excellup
Anatomy Of Flowering Plants Excellup
 Plant Anatomy Plants 2 Diagram Quizlet
Plant Anatomy Plants 2 Diagram Quizlet
 The Anatomy Of Plants With An Idea Of A Philosophical
The Anatomy Of Plants With An Idea Of A Philosophical
 Aspects Of Plant Anatomy Relevant To Phloem Transport A
Aspects Of Plant Anatomy Relevant To Phloem Transport A
 Flower Anatomy In The Garden Flower Anatomy Anatomy
Flower Anatomy In The Garden Flower Anatomy Anatomy
 The Gorgeous Anatomy Of Plants By Nehemiah Grew Aleph
The Gorgeous Anatomy Of Plants By Nehemiah Grew Aleph
 Anatomy Of Dicotyledonous Plants Support And Transport
Anatomy Of Dicotyledonous Plants Support And Transport
 Root Plant Anatomy Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock
Root Plant Anatomy Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock
 Anatomy Of Flowering Plants Jipmer Chapters Important
Anatomy Of Flowering Plants Jipmer Chapters Important
 Plant Anatomy Plant Biology 306 598
Plant Anatomy Plant Biology 306 598
 Development Of Kranz Anatomy Langdale Lab
Development Of Kranz Anatomy Langdale Lab
 Anatomy Of Seed Plants Katherine Esau Wiley New York
Anatomy Of Seed Plants Katherine Esau Wiley New York
 Plant Anatomy And Leaf Morphology In Plum Overexpressing
Plant Anatomy And Leaf Morphology In Plum Overexpressing
 Biology Anatomy Of Flowering Plants Part 1 Introduction Cbse Class 11 Xi
Biology Anatomy Of Flowering Plants Part 1 Introduction Cbse Class 11 Xi

Belum ada Komentar untuk "Anatomy Of Plants"
Posting Komentar