Joint Anatomy
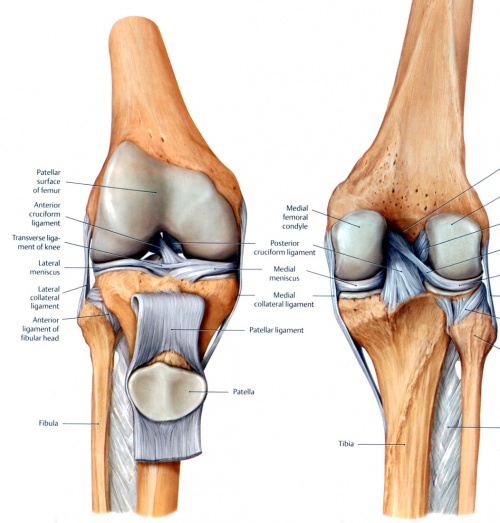
They are constructed to allow for different degrees and types of movement. The knee joins the thigh bone femur to the shin bone tibia.
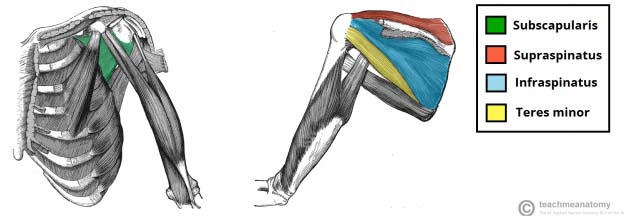
 The Shoulder Joint Structure Movement Teachmeanatomy
The Shoulder Joint Structure Movement Teachmeanatomy
The stability of the hip is increased by the strong ligaments that encircle the hip.

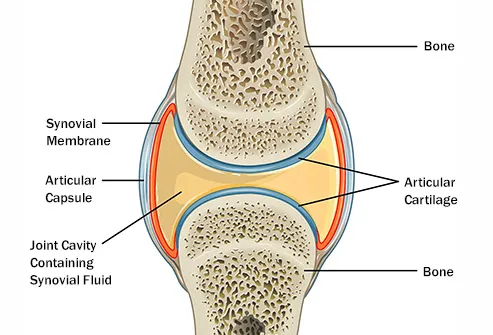
Joint anatomy. Joints consist of the following. Some joints such as the knee elbow and shoulder are self lubricating almost frictionless. This is a type of tissue that covers the surface of a bone at a joint.
Strong ligaments tough elastic bands of connective tissue surround. Joints between skeletal elements exhibit a great variety of form and function and are classified into three general morphologic types. A joint also called an articulation is any place where adjacent bones or bone and cartilage come together articulate with each other to form a connection.
The muscles of the thigh and lower back work together to keep the hip stable. Muscles of the hip. A joint or articulation or articular surface is the connection made between bones in the body which link the skeletal system into a functional whole.
Anatomy of the hip the hip joint. The hip joint is one of the most important joints in the human body. There are 6 types of synovial joints.
Joints are classified both structurally and functionally. The most common ligament injuries are acl tears mcl tears pcl tears and knee sprains which occur when the ligaments are overstretched. The hip joint is a ball and socket type joint.
It allows us to walk run and jump. Lets go through each joint. Yet the hip joint is also one of our most flexible joints and allows a greater range of motion than all other joints in the body except for the shoulder.
Anatomy the place of union usually more or less movable between two or more rigid skeletal components bones cartilage or parts of a single bone. 2 a symphysis consists of a compressable fibrocartilaginous pad that connects two bones. They have varying shapes but the important thing about them is the movement they allow.
In knee joint anatomy they are the main stabilising structures of the knee acl pcl mcl and lcl preventing excessive movements and instability. Joints can be grouped by their structure into fibrous cartilaginous and synovial joints 1 a synchrondosis is an immovable cartilaginous joint. A tissue called the synovial membrane lines the joint.
The smaller bone that runs alongside the tibia fibula and the kneecap patella are the other bones that make the knee joint. It bears our bodys weight and the force of the strong muscles of the hip and leg.
 General Anatomy Of The Bull And The Cow Illustrated Atlas
General Anatomy Of The Bull And The Cow Illustrated Atlas
 General Anatomy Of The Bull And The Cow Illustrated Atlas
General Anatomy Of The Bull And The Cow Illustrated Atlas
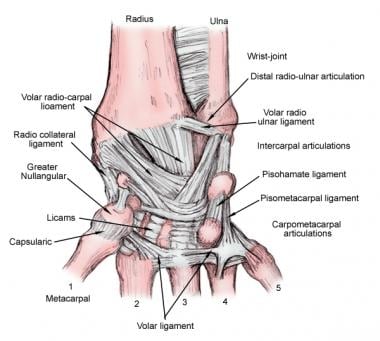 Wrist Joint Anatomy Overview Gross Anatomy Natural Variants
Wrist Joint Anatomy Overview Gross Anatomy Natural Variants
 Joint Definition Anatomy Movement Types Britannica
Joint Definition Anatomy Movement Types Britannica
 Total Joint Anatomy Lakeshore Orthopaedics
Total Joint Anatomy Lakeshore Orthopaedics
 Knee Joint Picture Image On Medicinenet Com
Knee Joint Picture Image On Medicinenet Com
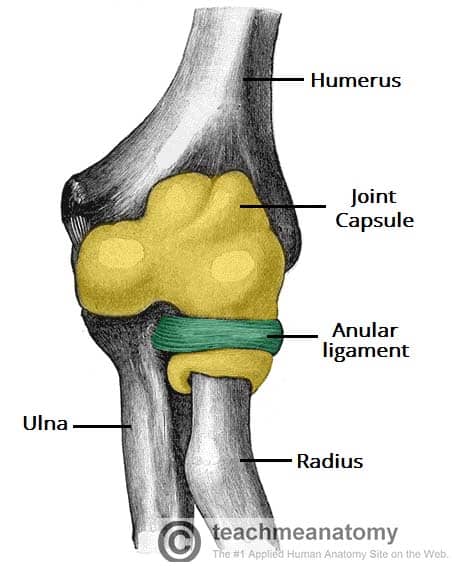 The Radioulnar Joints Teachmeanatomy
The Radioulnar Joints Teachmeanatomy
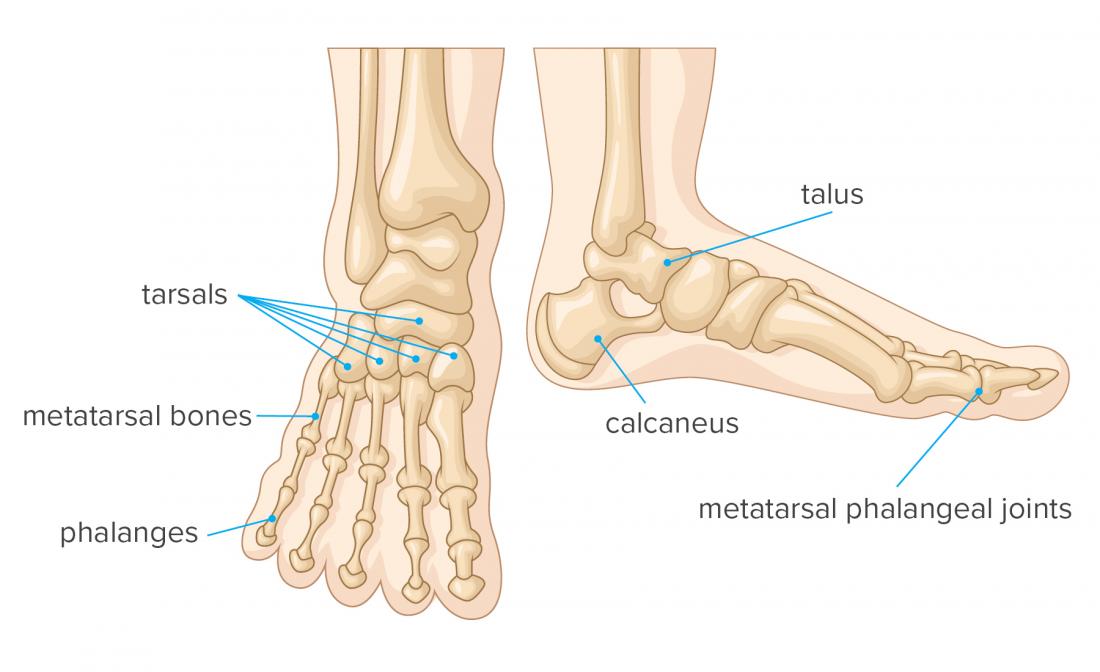 Foot Bones Anatomy Conditions And More
Foot Bones Anatomy Conditions And More
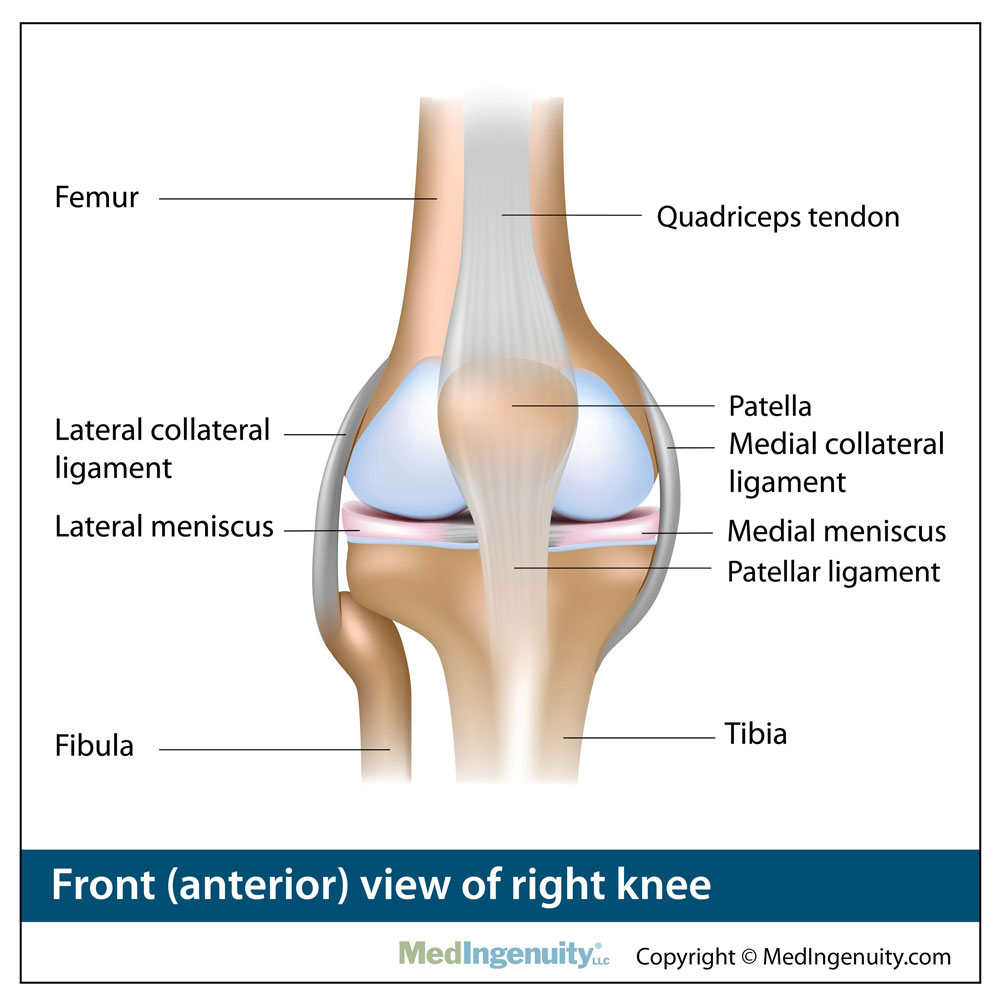 Anatomy Library Fort Worth Bone Joint Clinic
Anatomy Library Fort Worth Bone Joint Clinic
 Anatomy Joint Children S Wisconsin
Anatomy Joint Children S Wisconsin
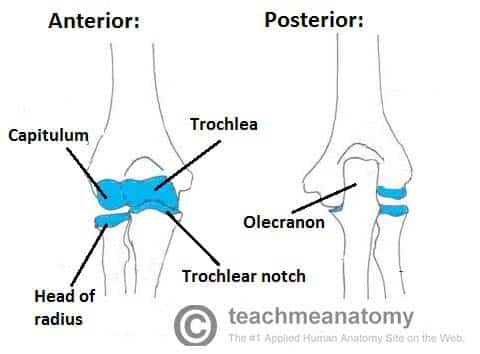 The Elbow Joint Structure Movement Teachmeanatomy
The Elbow Joint Structure Movement Teachmeanatomy
 Glenohumeral Joint Anatomy Stabilizer And Biomechanics
Glenohumeral Joint Anatomy Stabilizer And Biomechanics
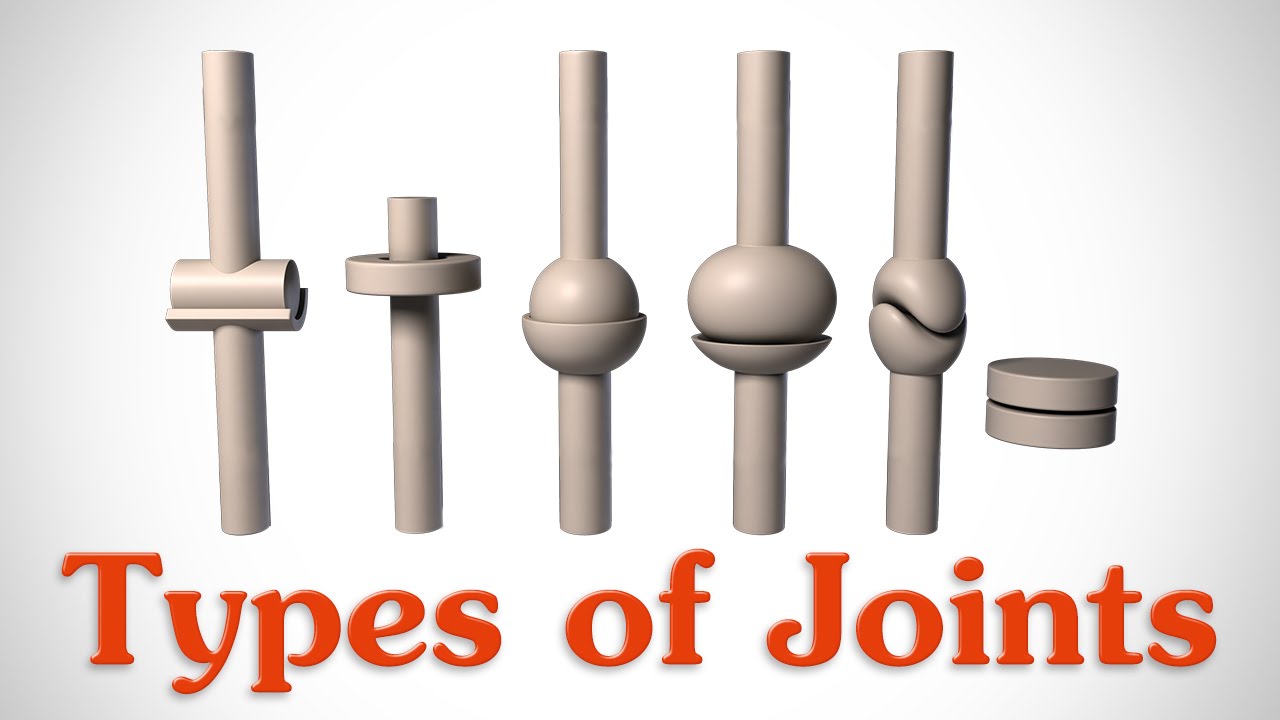 The 6 Types Of Joints Human Anatomy For Artists
The 6 Types Of Joints Human Anatomy For Artists
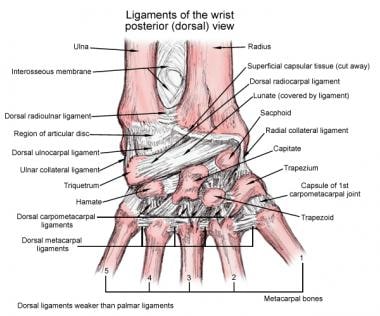 Wrist Joint Anatomy Overview Gross Anatomy Natural Variants
Wrist Joint Anatomy Overview Gross Anatomy Natural Variants

 Anatomy Of The Knee Comprehensive Orthopaedics
Anatomy Of The Knee Comprehensive Orthopaedics
Inflammatory Arthritis Of The Hip Orthoinfo Aaos
 What Is The Si Joint Si Joint Anatomy Si Bone
What Is The Si Joint Si Joint Anatomy Si Bone
 Free Anatomy Quiz The Joints Of The Body Quiz 1
Free Anatomy Quiz The Joints Of The Body Quiz 1
 Synovial Joint Easy Pic For Patients To Understand And You
Synovial Joint Easy Pic For Patients To Understand And You
 Elbow Anatomy Elbow Pain Chicago Westchester Hinsdale Il
Elbow Anatomy Elbow Pain Chicago Westchester Hinsdale Il
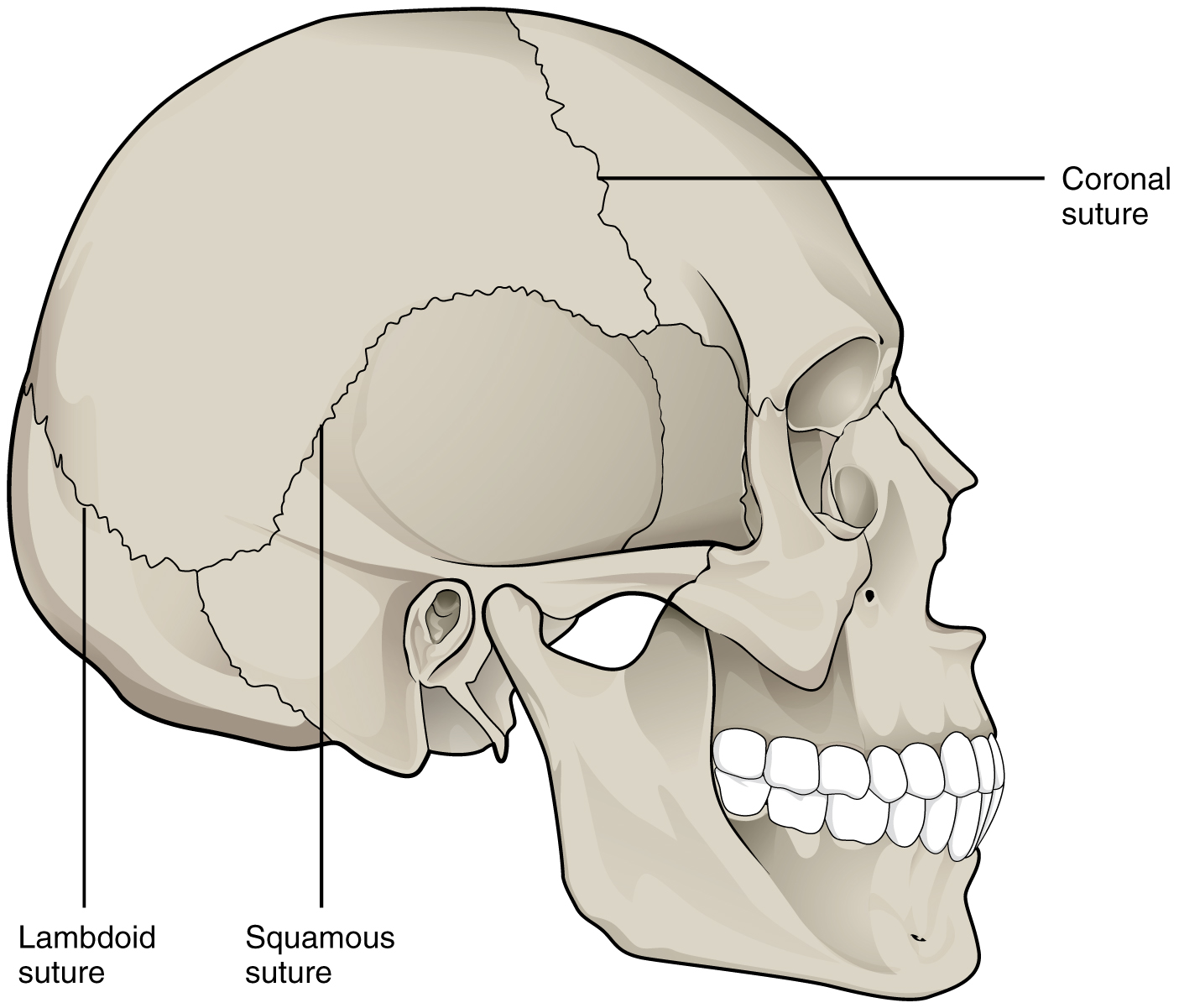 9 1 Classification Of Joints Anatomy And Physiology
9 1 Classification Of Joints Anatomy And Physiology
 2 Anatomy Of Knee Joint Adapted From 34 Download
2 Anatomy Of Knee Joint Adapted From 34 Download
 Why Are My Joints So Stiff What Can I Do
Why Are My Joints So Stiff What Can I Do


Belum ada Komentar untuk "Joint Anatomy"
Posting Komentar