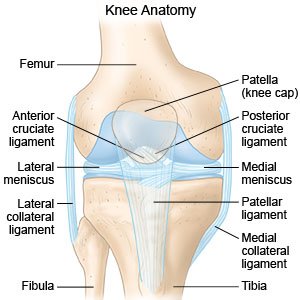
Knee Anatomy Ligaments
It consists of bones meniscus ligaments and tendons. In knee joint anatomy they are the main stabilising structures of the knee acl pcl mcl and lcl preventing excessive movements and instability.
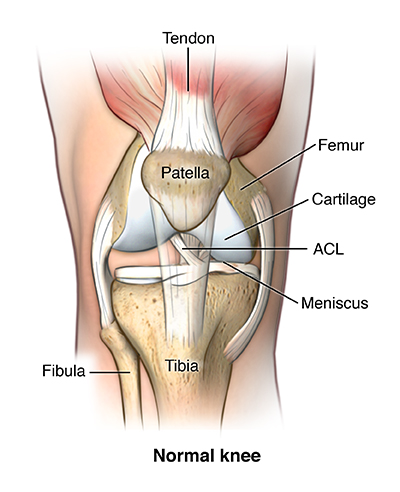
Another bone the patella kneecap is at the center of the knee.
Knee anatomy ligaments. The anterior cruciate ligament and posterior cruciate ligament provide front and back anterior and. Knee ligament sprains or tears are a common sports injury. Ligaments are tough fibrous connective tissues which link bone to bone made of collagen.
The knee is a hinge joint that is responsible for weight bearing and movement. The knee includes four important ligaments all of which connect the femur to the tibia. The medial collateral ligament on the inner side and the lateral collateral ligament on the outer side.
There are four knee ligaments thick bands of tough tissue that serve to maintain the stability of the knee joint. Your knee ligaments connect your thighbone to your lower leg bones. Ligaments are strong tough bands that are not particularly flexible.
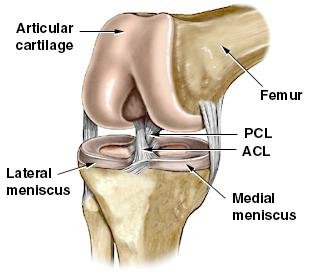
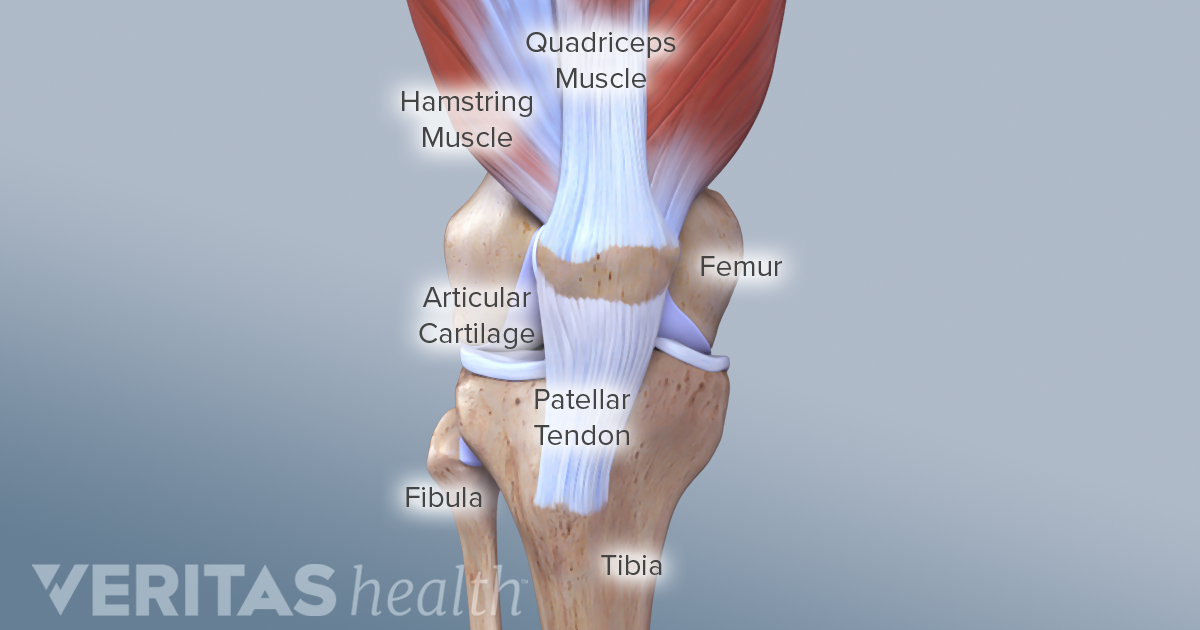
One ligament is on each side of the knee joint. Two concave pads of cartilage strong flexible tissue called menisci minimize the friction created at the meeting of the ends of the tibia and femur. Tendons connect the knee bones to the leg muscles that move the knee joint.
Posterior cruciate ligament pcl which is located in the center of the knee and prevents excessive backward shifting of the knee. The function of ligaments is to attach bones to bones and to help keep them stable. Two groups of muscles support the knee.
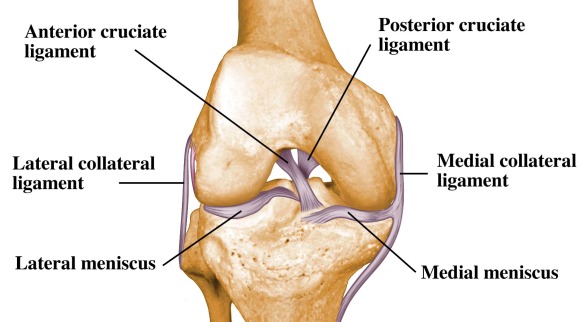
In the knee they give stability and strength to the knee joint as the bones and cartilage of the knee have very little stability on their own. Knee ligament impose limitations on the movement of the knee allowing it to concentrate forces of the muscles on extension and flexion. These are called the cruciate ligaments and consist of the anterior cruciate ligament and the posterior cruciate ligament.
There are also several key ligaments a type of fibrous connective tissue that connect these bones. Ligaments join the knee bones and provide stability to the knee. Anterior cruciate ligament acl which is located in the center of the knee and prevents excessive forward movement of the tibia.
On the sides of the knee are the medial collateral ligament mcl and the lateral collateral ligament lcl. The anterior cruciate ligament prevents the femur from sliding backward on the tibia or the tibia sliding forward on the femur. The knee is designed to fulfill a number of functions.
The most common ligament injuries are acl tears mcl tears. Ligaments of the knee. Ligaments in the knee.
The medial collateral ligament mcl and lateral collateral ligament lcl are found on the sides of your knee. These two prevent sideways sliding of the knee joint ad also brace it against unusual movement.
 Knee Sprain How To Treat A Sprained Knee
Knee Sprain How To Treat A Sprained Knee
Knee Advanced Orthopedics Sports Medicine
 Knee Surgeon Marc Hirner Orthopaedic Surgeon
Knee Surgeon Marc Hirner Orthopaedic Surgeon
 14102 04b Tendons And Ligaments Of The Right Knee Anatomy
14102 04b Tendons And Ligaments Of The Right Knee Anatomy
 Knee Joint Anatomy Bones Ligaments Muscles Tendons Function
Knee Joint Anatomy Bones Ligaments Muscles Tendons Function
 The Knee Anatomy Injury Care And Prevention Soccer
The Knee Anatomy Injury Care And Prevention Soccer
 Knee Human Anatomy Function Parts Conditions Treatments
Knee Human Anatomy Function Parts Conditions Treatments
Fractures Of The Proximal Tibia Shinbone Orthoinfo Aaos
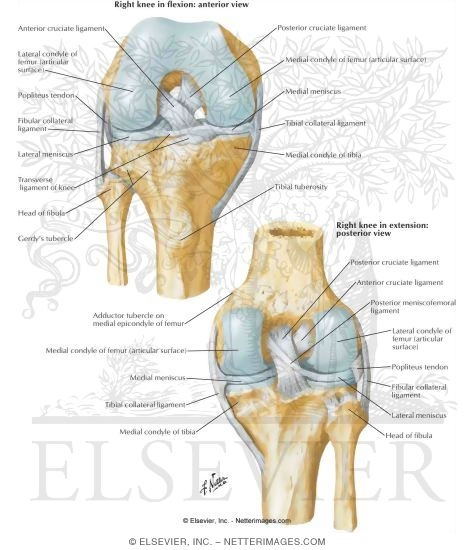 Cruciate And Collateral Ligaments Of Right Knee Joint Knee
Cruciate And Collateral Ligaments Of Right Knee Joint Knee
 Care Of Your Knee Following Anterior Cruciate Ligament Acl
Care Of Your Knee Following Anterior Cruciate Ligament Acl
 Knee Anatomy Including Ligaments Cartilage And Meniscus
Knee Anatomy Including Ligaments Cartilage And Meniscus
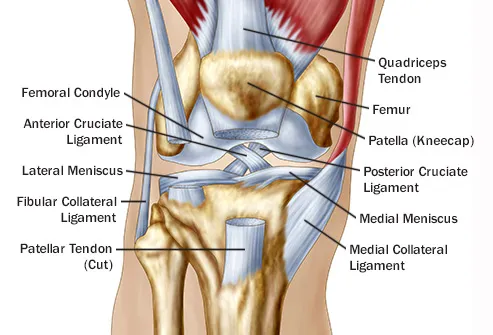 Reasons For Pain Behind In Back Of The Knee
Reasons For Pain Behind In Back Of The Knee
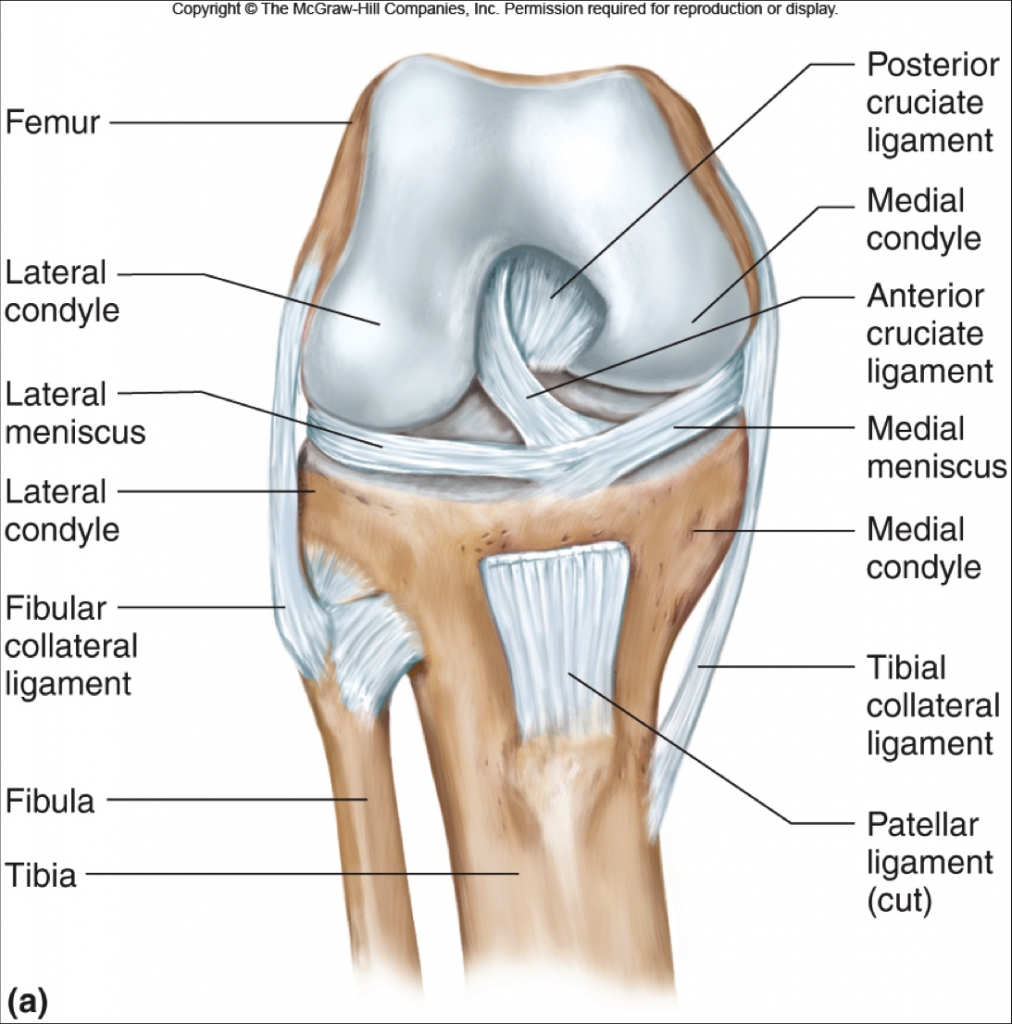 Anterior Cruciate Ligament Acl Injuries Core Em
Anterior Cruciate Ligament Acl Injuries Core Em
 The Structure Of A Joint Medlineplus Medical Encyclopedia Image
The Structure Of A Joint Medlineplus Medical Encyclopedia Image
 Anatomy Of The Knee How The Knee Works Knee Anatomy
Anatomy Of The Knee How The Knee Works Knee Anatomy
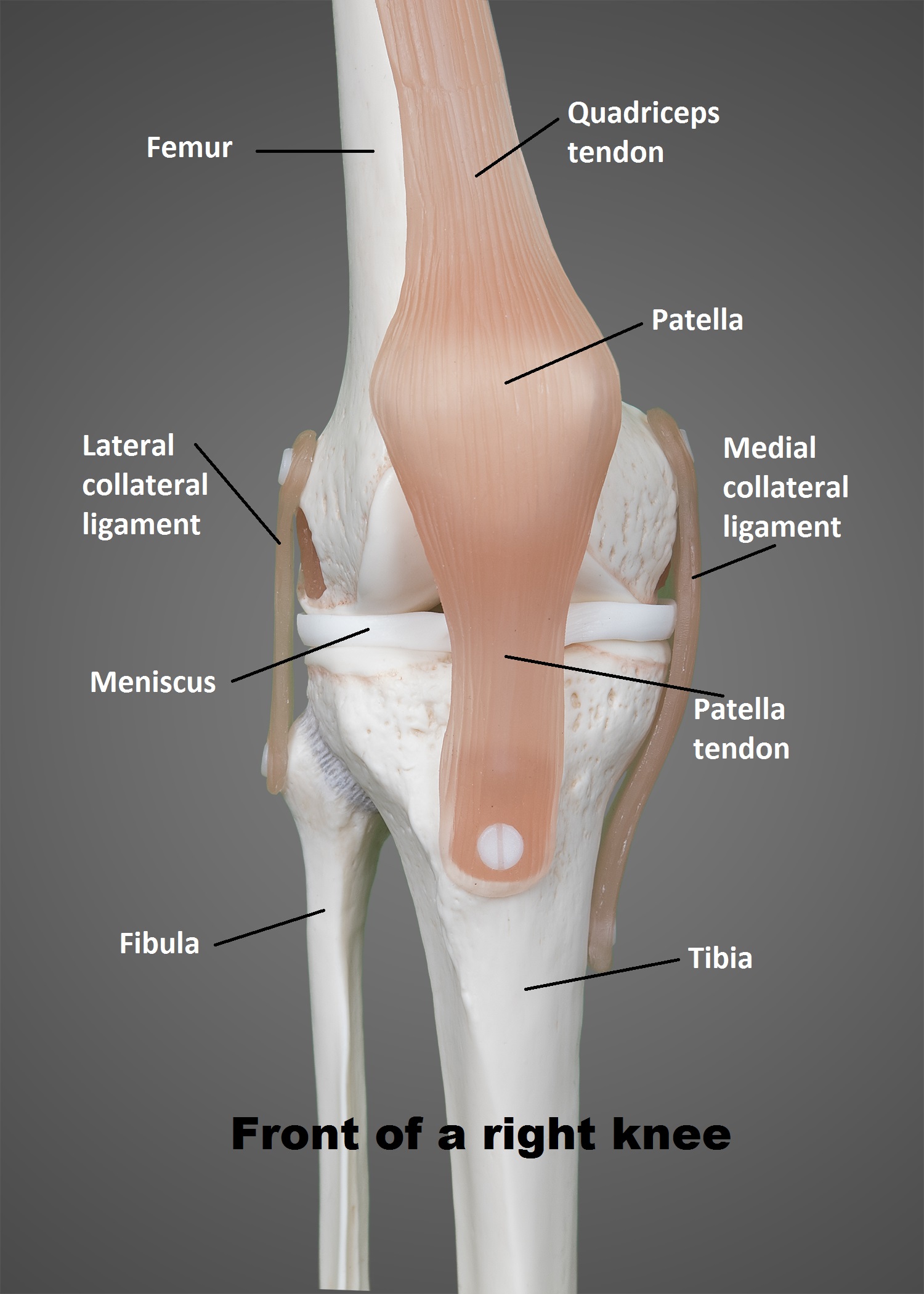 The Knee Ut Health San Antonio
The Knee Ut Health San Antonio
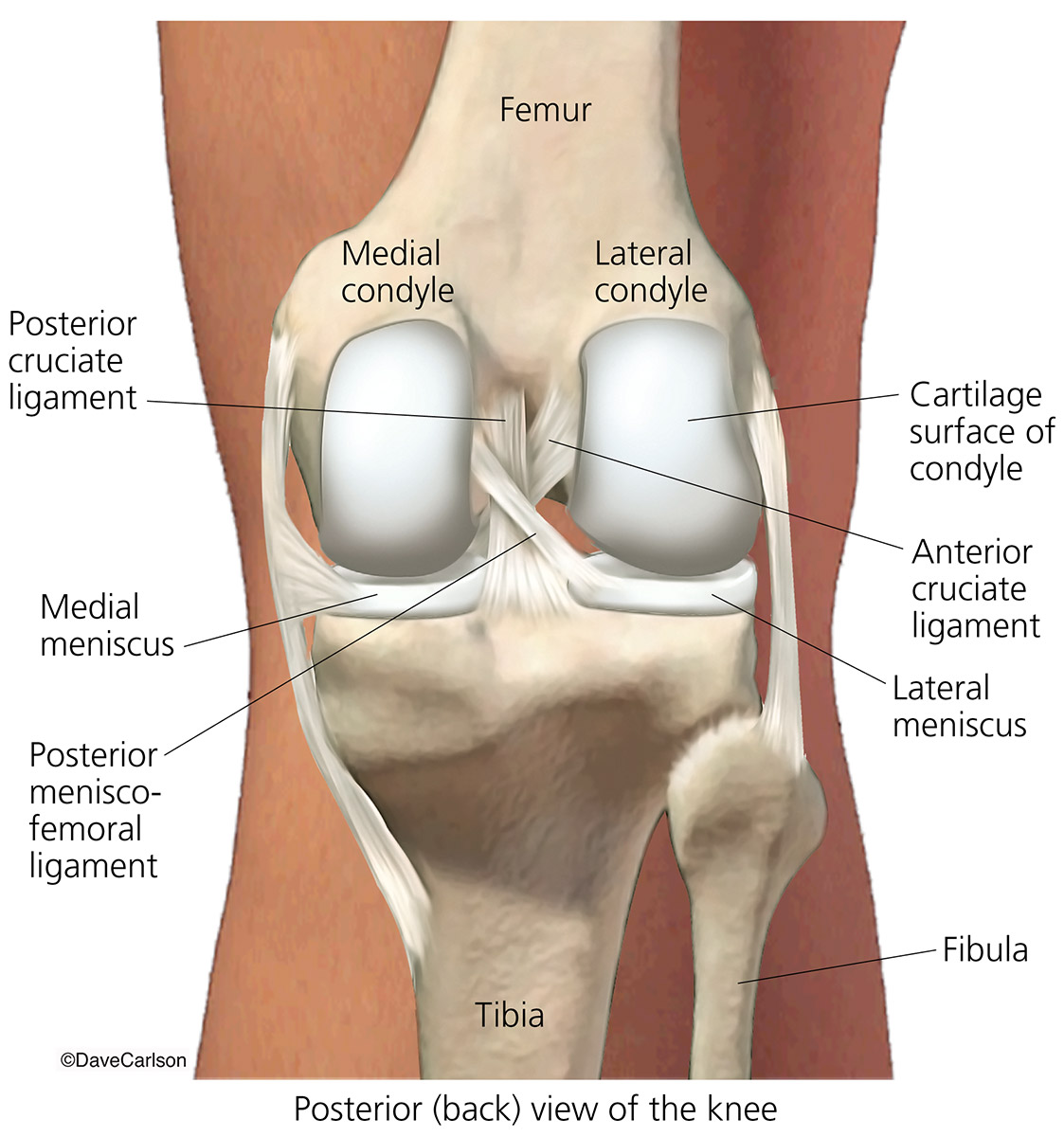
 Knee Joint Back View Carlson Stock Art
Knee Joint Back View Carlson Stock Art
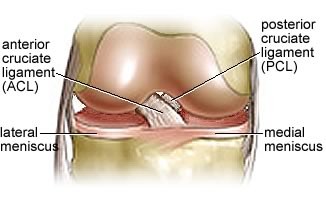 The Knee Explained Article Nzihf
The Knee Explained Article Nzihf
 Acl Solutions Acl Knee Anatomy And Diagram Images
Acl Solutions Acl Knee Anatomy And Diagram Images
 Matthew Boyle Orthopaedic Surgeon Knee Anatomy Knee
Matthew Boyle Orthopaedic Surgeon Knee Anatomy Knee



Belum ada Komentar untuk "Knee Anatomy Ligaments"
Posting Komentar