External Eye Anatomy
The outer fibrous or sclera 2. Lacrimal system tear drainage system the lacrimal system is crucial for tear production and management which includes distribution of tears and draining excess tears.
 External Eye Anatomy Archives Stock Eye Images
External Eye Anatomy Archives Stock Eye Images
The structure of the human eye is made of three layers.
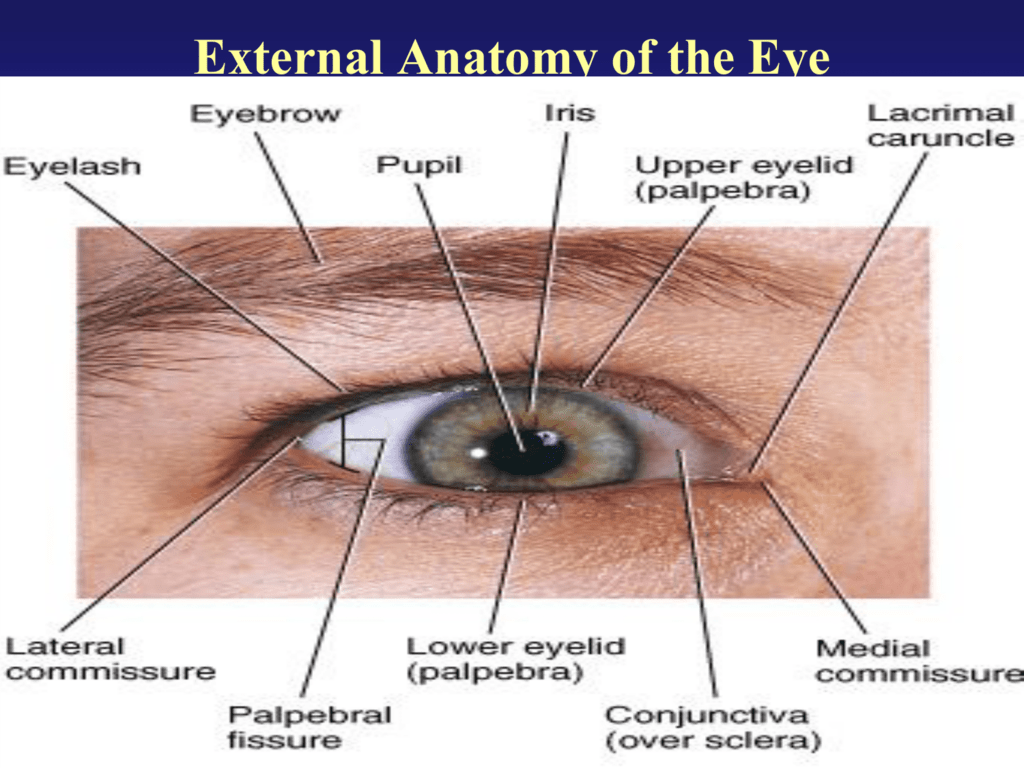
External eye anatomy. The eye sits in a protective bony socket called the orbit. Malfunction in any part of the system can cause serious complications. Nerve signals that contain visual information are transmitted through the optic nerve to the brain.
As light passes through the eye the iris changes shape by expanding and letting more light through or constricting and letting less light through to change pupil size. Low to high sort by price. The iris is the colored part of the eye that controls the amount of light that enters into the eye.
Learn vocabulary terms and more with flashcards games and other study tools. The eye is surrounded by the orbital bones and is cushioned by pads of fat within the orbital socket. Much less important than the lower punctum.
The lens then changes shape to allow the accurate focusing of light on the retina. Oval opening in the upper lid margin where tears enter to flow to the lacrimal sac. It is the most visible part of the eye.
Six muscles attach to the outer surface of the eye and produce mucous membrane that lines the eyelids and outer surface of th two movableshades that further protect the eye from injury st modified sebaceous glands lubricates eye. The cornea allows light to enter the eye. The extraocular muscles are attached to the white part of the eye called the sclera.
It lies in front of the crystalline lens and separates the anterior chamber from the posterior chamber. The iris is part of the uveal tractthe middle layer of the wall of the eye. Modified sweat glands between lashes.
This is a strong layer of tissue that covers nearly the entire surface of the eyeball. Click on a label to display the definition. These muscles move the eye up and down and side to side and rotate the eye.
The human eye ball is spherical in structure and is about 24 mm in a diameter. Start studying external eye anatomy. Anatomy of the eye.
Human eye parts 1. Extraocular muscles help move the eye in different directions. Home eye anatomy illustrations external eye anatomy showing 112 of 15 results default sorting sort by popularity sort by average rating sort by newness sort by price.
Six extraocular muscles in the orbit are attached to the eye. Tap on the image or pinch out and pinch in to resize the image.
 Vision And The Eye S Anatomy Healthengine Blog
Vision And The Eye S Anatomy Healthengine Blog
 N 295 Lecture 5 6 Eye And Ear Student Copy
N 295 Lecture 5 6 Eye And Ear Student Copy
 Parts Of The Eye American Academy Of Ophthalmology
Parts Of The Eye American Academy Of Ophthalmology
 The Eye Structure Function Ppt Video Online Download
The Eye Structure Function Ppt Video Online Download
 Parts Of The Eye American Academy Of Ophthalmology
Parts Of The Eye American Academy Of Ophthalmology
 Special Senses Vision Overview Of Special Senses
Special Senses Vision Overview Of Special Senses
 What Is The Structure And Function Of The Human Eye Quora
What Is The Structure And Function Of The Human Eye Quora
 Best Eye Anatomy Ideas And Images On Bing Find What You
Best Eye Anatomy Ideas And Images On Bing Find What You
 Structure And Function Of Human Eye It閱讀
Structure And Function Of Human Eye It閱讀
 External Anatomy Human Eye Wall Mural Wallmonkeys Com
External Anatomy Human Eye Wall Mural Wallmonkeys Com
 Eye Anatomy And Vision Course Hero
Eye Anatomy And Vision Course Hero
 External Eye Anatomy Archives Stock Eye Images
External Eye Anatomy Archives Stock Eye Images
 Anatomy Of The Human Eye In Front External View Schematic Diagram
Anatomy Of The Human Eye In Front External View Schematic Diagram
 An Exploration Of The Eye Light Is Essential For Vision
An Exploration Of The Eye Light Is Essential For Vision
 Stock Eye Anatomy Images From Jirehdesign Com Eye Illustrations
Stock Eye Anatomy Images From Jirehdesign Com Eye Illustrations
 Cornea Charleston Eye Care Charleston Carolina Eyecare
Cornea Charleston Eye Care Charleston Carolina Eyecare
 Diagram Of The Eye Lions Eye Institute
Diagram Of The Eye Lions Eye Institute
 External Eye Anatomy Eye Anatomy Eyes Problems Optometry
External Eye Anatomy Eye Anatomy Eyes Problems Optometry
 External Anatomy Of The Eye Ppt Video Online Download
External Anatomy Of The Eye Ppt Video Online Download
 Stock Eye Anatomy Images From Jirehdesign Com Eye Illustrations
Stock Eye Anatomy Images From Jirehdesign Com Eye Illustrations
 Ucsd S Practical Guide To Clinical Medicine
Ucsd S Practical Guide To Clinical Medicine
 Orbits And Eyes Anatomical Illustrations
Orbits And Eyes Anatomical Illustrations
 Min Anatomy And Physiology Of The Human Eye Eyeball And
Min Anatomy And Physiology Of The Human Eye Eyeball And
 Orbital Compartment Syndrome Curriculum
Orbital Compartment Syndrome Curriculum
 Eye Anatomy Paediatric Academy
Eye Anatomy Paediatric Academy




Belum ada Komentar untuk "External Eye Anatomy"
Posting Komentar