Shin Anatomy
The epidermis the outermost layer of skin provides a waterproof barrier and creates our skin tone. Treatment and prevention description.
 Medial Tibial Stress Syndrome Shin Splints Run Waterloo
Medial Tibial Stress Syndrome Shin Splints Run Waterloo
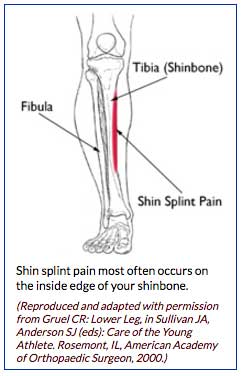
Pain typically occurs along the inner border of the tibia where muscles attach to the bone.
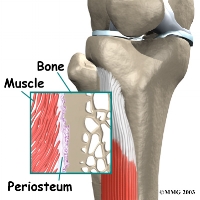
Shin anatomy. Shin splint pain most often occurs on the inside edge of your tibia shinbone. Shin splint anatomy and treatment mark charrette dc april 18 2019 shin splints or medial tibial stress syndrome has become a household word as more people pursue exercise for recreation and better health. Shin muscles such as the tibialis anterior and extensor digitorum longus dorsiflex the foot and extend the toes.
The fibula also called the calf bone is significantly smaller and is. It is situated on the lateral side of the tibia. The tibia ˈ t ɪ b i ə plural tibiae ˈ t ɪ b i i or tibias also known as the shinbone or shankbone is the larger stronger and anterior frontal of the two bones in the leg below the knee in vertebrates the other being the fibula behind and to the outside of the tibia and it connects the knee with the ankle bones.
The most common symptom of shin splints is pain. Anatomy the front edge of the tibia. Shin splints medial tibial stress syndrome is an inflammation of the muscles.
The lateral compartment is along the outside of the lower leg. Anatomy of shin splints. It is thick and fleshy above tendinous below.
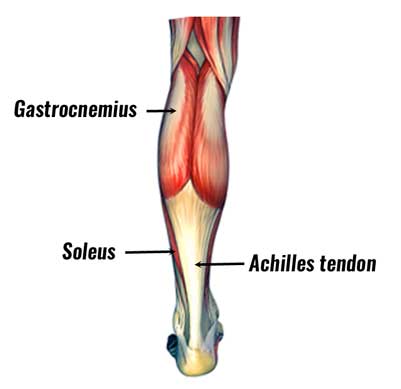
The posterior compartment holds the large muscles that we know as the calf muscles. The tibia also called the shinbone is located near the midline of the leg and is the thicker and stronger of the two bones. This muscle is mostly located near the shin.
Anatomy the front part of the lower leg. The dermis beneath the epidermis contains tough connective tissue hair follicles and sweat. The deep posterior compartment.
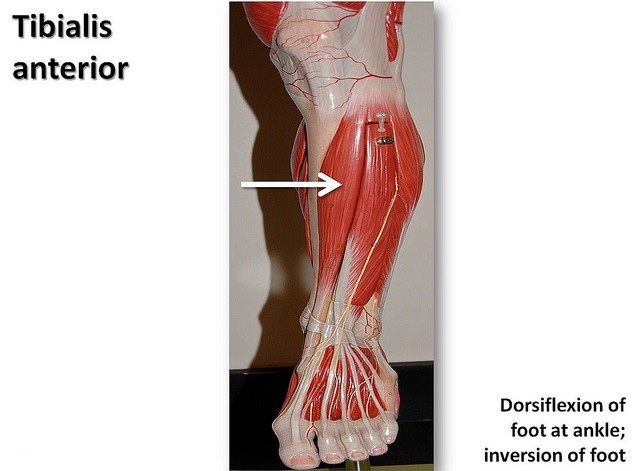
It acts to dorsiflex and invert the foot. The tibialis anterior overlaps the anterior tibial vessels and deep peroneal nerve in the upper part of the leg. Cookery chiefly brit a cut of beef the lower foreleg.
In general shin splints develop when the muscle and bone tissue periosteum. The muscles of the lower leg the anterior compartment in the front of the shin holds the tibialis anterior. The muscles of the calf also work subtly to stabilize the ankle joint and foot and to maintain the bodys balance.
The tibialis anterior is a muscle in humans that originates in the upper two thirds of the lateral surface of the tibia and inserts into the medial cuneiform and first metatarsal bones of the foot. Shin splints medial tibial stress syndrome is an inflammation of the muscles tendons and bone tissue around your tibia.
 Human Anatomy Male Tibia Shin Bone 3d Illustration Buy
Human Anatomy Male Tibia Shin Bone 3d Illustration Buy
 Complete Guide To Shin Splints 2019
Complete Guide To Shin Splints 2019
 Anatomy Of The Knee For Dancers Dance Work Balance
Anatomy Of The Knee For Dancers Dance Work Balance
 Shin Splints Medial Tibial Stress Syndrome Zion Physical
Shin Splints Medial Tibial Stress Syndrome Zion Physical
 How To Prevent Shin Splints Mike Young On Shin Splint
How To Prevent Shin Splints Mike Young On Shin Splint
 Calf Strain Torn Calf Muscle Treatment Rehabilitation
Calf Strain Torn Calf Muscle Treatment Rehabilitation
The Knee Joint Mobility Health
 Shins And Calves Back In The Game Physical Therapy
Shins And Calves Back In The Game Physical Therapy
Vivian Grisogono About The Shin
Positive Health Online Article Shin Splints Compartment
 Tibial Stress Syndrome Shin Splints Knee Sports
Tibial Stress Syndrome Shin Splints Knee Sports
 Anatomy Of The Knee Howstuffworks
Anatomy Of The Knee Howstuffworks
 Shin Splints Medial Tibial Stress Syndrome Zion Physical
Shin Splints Medial Tibial Stress Syndrome Zion Physical
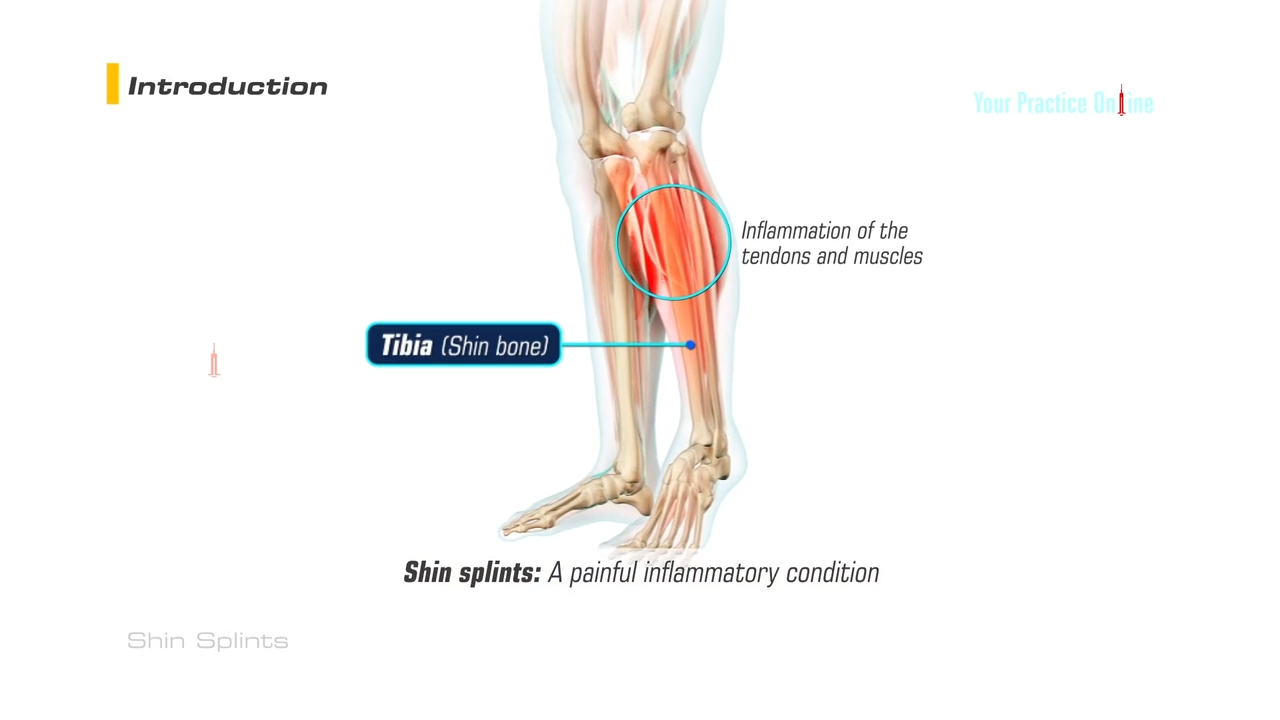
 Anatomy Of Shin Splints Treatment And Prevention
Anatomy Of Shin Splints Treatment And Prevention
 Shin Splints Thermoskin Supports And Braces For Injury
Shin Splints Thermoskin Supports And Braces For Injury
 Knee Joint Picture Image On Medicinenet Com
Knee Joint Picture Image On Medicinenet Com
Anatomy Knee Restoration Center Of Indiana




Belum ada Komentar untuk "Shin Anatomy"
Posting Komentar