Knee Ligaments Anatomy
One ligament is on each side of the knee joint. The knee is a hinge joint that is responsible for weight bearing and movement.
 Ligaments Of The Knee Knee Sports Orthobullets
Ligaments Of The Knee Knee Sports Orthobullets
Knee anatomy share on pinterest the knee is the most complex joint in the human body.
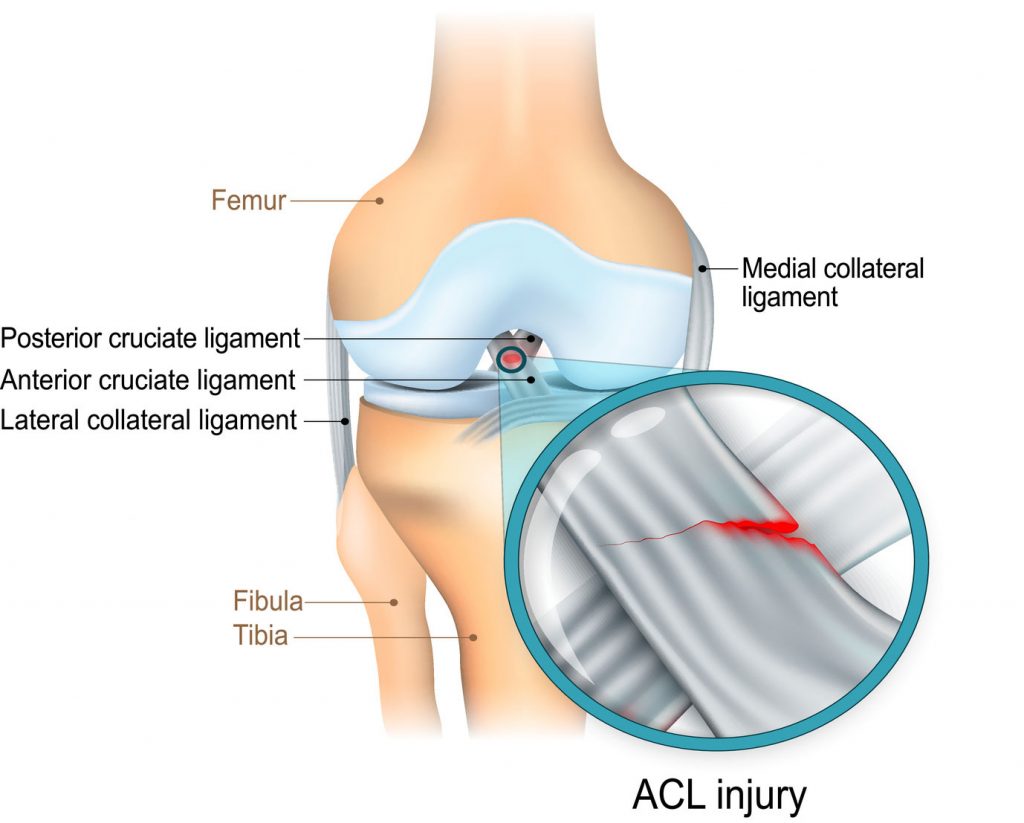
Knee ligaments anatomy. Ligaments are tough fibrous connective tissues which link bone to bone made of collagen. The anterior cruciate ligament and posterior cruciate ligament provide front and back anterior and. The anterior cruciate ligament prevents the femur from sliding backward on the tibia or the tibia sliding forward on the femur.
These two prevent sideways sliding of the knee joint ad also brace it against unusual movement. Ligaments in the knee. Ligaments of the knee.
The function of ligaments is to attach bones to bones and give strength and stability to the knee as the knee has very little stability. The bones are held together by a joint capsule which consists of two distinct layers an outer layer of dense connective tissue and an inner membrane called the synovium which secretes a fluid to lubricate the joint. There are four knee ligaments thick bands of tough tissue that serve to maintain the stability of the knee joint.
In knee joint anatomy knee ligaments are the main stabilising structures of the knee preventing excessive movements and instability. The medial meniscus situated on the inside of the knee. The knee includes four important ligaments all of which connect the femur to the tibia.
Ligaments join the knee bones and provide stability to the knee. Knee ligament impose limitations on the movement of the knee allowing it to concentrate forces of the muscles on extension and flexion. Once stretched they tend to stay stretched and if stretched too far they snap.
The medial collateral ligament on the inner side and the lateral collateral ligament on the outer side. These are called the cruciate ligaments and consist of the anterior cruciate ligament and the posterior cruciate ligament. Tendons connect the knee bones to the leg muscles that move the knee joint.
On the sides of the knee are the medial collateral ligament mcl and the lateral collateral ligament lcl. Ligaments are strong tough bands that are not particularly flexible.
 Amazon Com Kouber Anatomical Medical Knee Joint With
Amazon Com Kouber Anatomical Medical Knee Joint With
 Anatomy Of The Knee Central Coast Orthopedic Medical Group
Anatomy Of The Knee Central Coast Orthopedic Medical Group
 Care Of Your Knee Following Anterior Cruciate Ligament Acl
Care Of Your Knee Following Anterior Cruciate Ligament Acl
 Knee Ligament Repair Johns Hopkins Medicine
Knee Ligament Repair Johns Hopkins Medicine
 Anatomical Drawing Of The Ligaments In The Knee Download
Anatomical Drawing Of The Ligaments In The Knee Download
 Collateral Ligaments Of The Knee Joint Patellar Tendon
Collateral Ligaments Of The Knee Joint Patellar Tendon
 Preventing Acl Injury Through Strengthening Exercises
Preventing Acl Injury Through Strengthening Exercises
 The Knee Resource Posterolateral Corner Injury
The Knee Resource Posterolateral Corner Injury
 Knee Joint Picture Image On Medicinenet Com
Knee Joint Picture Image On Medicinenet Com
 Acl Injury Symptoms And Causes Mayo Clinic
Acl Injury Symptoms And Causes Mayo Clinic
 Anterior Cruciate Ligament Acl Injuries Core Em
Anterior Cruciate Ligament Acl Injuries Core Em
 Ligaments Of The Knee Knee Sports Orthobullets
Ligaments Of The Knee Knee Sports Orthobullets
 Anatomy Knee Joint Klinik Am Ring
Anatomy Knee Joint Klinik Am Ring
 Knee Joint Anatomy Bones Ligaments Muscles Tendons Function
Knee Joint Anatomy Bones Ligaments Muscles Tendons Function
 Anatomy Of The Knee Baxter Regional Medical Center
Anatomy Of The Knee Baxter Regional Medical Center
 Ligaments Of The Knee Knee Sports Orthobullets
Ligaments Of The Knee Knee Sports Orthobullets
 Types Of Knee Ligaments Stanford Health Care
Types Of Knee Ligaments Stanford Health Care
 Inner Knee Pain Why Does The Inside Of My Knee Hurt
Inner Knee Pain Why Does The Inside Of My Knee Hurt
 Torn Knee Ligaments Ligament Knee Tear Acl Acl Injury
Torn Knee Ligaments Ligament Knee Tear Acl Acl Injury
 Posterior Cruciate Ligament An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Posterior Cruciate Ligament An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
 Knee Ligaments Cruciates Collaterals Knee Pain Explained
Knee Ligaments Cruciates Collaterals Knee Pain Explained
 Matthew Boyle Orthopaedic Surgeon Knee Anatomy Knee
Matthew Boyle Orthopaedic Surgeon Knee Anatomy Knee
 Classification Of Knee Ligament Injuries Musculoskeletal Key
Classification Of Knee Ligament Injuries Musculoskeletal Key




Belum ada Komentar untuk "Knee Ligaments Anatomy"
Posting Komentar