Tracts Anatomy
Association fibers commissural fibers and projection fibers. They are responsible for the voluntary control of the musculature of the body and face.
 Pyramidal And Extrapyramidal Tracts
Pyramidal And Extrapyramidal Tracts
Pyramidal tracts these tracts originate in the cerebral cortex carrying motor fibres to the spinal cord and brain stem.
Tracts anatomy. In human anatomy the intestine bowel or gut. Extrapyramidal tracts these tracts originate in the brain stem carrying motor fibres to the spinal cord. See aerodigestive tract biliary tract gastrointestinal tract olfactory tract respiratory tract serpiginous tract urogenital.
The main nerve tracts in the central nervous system are of three types. A bundle of nerve fibers in the cns. A bundle of nerve fibers having a common origin and destination.
Functionally the ascending tracts can be divided into the type of information they transmit conscious or unconscious. A tube through which a substance or gas flows. Anatomy a bundle of nerve fibres having the same function origin and termination.
They are responsible for the involuntary and automatic control of all musculature such as muscle tone balance posture and locomotion. The vertebrate system are organized in bundles called tracts or fasciculi. It is composed of four tracts.
An extended area as of land. The lower gastrointestinal tract includes most of the small intestine and all of the large intestine. Anatomy anatomy a system of organs glands or other tissues that has a particular function.
Unconscious tracts comprised of the spinocerebellar tracts. Ascending tracts carry impulses along the spinal cord toward the brain and descending tracts carry them from the brain or higher regions in the spinal cord to lower regions. Choose from 500 different sets of tracts anatomy flashcards on quizlet.
Learn tracts anatomy with free interactive flashcards. A definite region or area of the body especially a group series or system of related parts or organs. A tract may also be referred to as a commissure fasciculus or decussation.
éntera is the segment of the gastrointestinal tract extending from the pyloric sphincter of the stomach to the anus and as in other mammals consists of two segments the small intestine and the large intestine. Conscious tracts comprised of the dorsal column medial lemniscal pathway and the anterolateral system.
 Spinal Cord Neurology Medbullets Step 1
Spinal Cord Neurology Medbullets Step 1
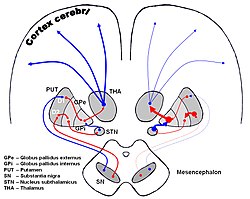
 Pallidothalamic Tracts Wikipedia
Pallidothalamic Tracts Wikipedia
 Corticospinal Tract Function Anatomy Study Com
Corticospinal Tract Function Anatomy Study Com
 Ascending Tracts Of The Spinal Cord Anatomy Kenhub
Ascending Tracts Of The Spinal Cord Anatomy Kenhub
 Lower Cervical Spine Authors Added Material Ao Surgery
Lower Cervical Spine Authors Added Material Ao Surgery
 The Spinal Cord Anatomy Revision Medicinemoggy
The Spinal Cord Anatomy Revision Medicinemoggy
 Anatomy Of Long Tracts Of Spinal Cord
Anatomy Of Long Tracts Of Spinal Cord
 Spinal Cord Anatomy Parts And Spinal Cord Functions
Spinal Cord Anatomy Parts And Spinal Cord Functions
 Easy Notes On Tracts Of The Spinal Cord Learn In Just 3
Easy Notes On Tracts Of The Spinal Cord Learn In Just 3
 Spinal Cord Tracts And Anatomy Biology Flashcards Quizlet
Spinal Cord Tracts And Anatomy Biology Flashcards Quizlet
 The Human Vocal Tract Anatomy Function Development And
The Human Vocal Tract Anatomy Function Development And
 Spinothalamic Tract Nervous System Anatomyzone
Spinothalamic Tract Nervous System Anatomyzone
 Tom Prophet Hsiung Anatomy Motor Pathways
Tom Prophet Hsiung Anatomy Motor Pathways
 Spinal Cord Anatomy The Anterior Spinothalamic Tracts Are
Spinal Cord Anatomy The Anterior Spinothalamic Tracts Are
 Neurologic Exam Adult Sensory Exam Anatomy Location Of
Neurologic Exam Adult Sensory Exam Anatomy Location Of
 Brainstem I The Medulla Organization Of The Central
Brainstem I The Medulla Organization Of The Central
 The Nervous System Sensory And Motor Tracts Of The Spinal Cord
The Nervous System Sensory And Motor Tracts Of The Spinal Cord
 Spinal Cord Associated Tracts Anatomy
Spinal Cord Associated Tracts Anatomy
 Corticospinal Tract Spinal Cord Google Search Nerve
Corticospinal Tract Spinal Cord Google Search Nerve
 Spinal Cord Anatomy And Physiology I
Spinal Cord Anatomy And Physiology I
 Corticobulbar Tract An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Corticobulbar Tract An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
 Spinal Cord Anatomy Structure Function Tracts
Spinal Cord Anatomy Structure Function Tracts
 Anatomical Foundations Of Neuroscience
Anatomical Foundations Of Neuroscience

Belum ada Komentar untuk "Tracts Anatomy"
Posting Komentar