The Eye Anatomy And Physiology
Last week we discussed vision from a historical perspective in order to understand how johannes kepler rené descartes and bishop berkeley discovered the importance of the mind in effecting vision. Development anatomy and physiology of the eye the word perspective comes from the latin per through and specere look at.
 The Special Senses Ross And Wilson Anatomy And Physiology
The Special Senses Ross And Wilson Anatomy And Physiology
In a normal eyeball after exiting the back of the lens the light rays pass through the vitreous a clear jelly like substance that fills the globe of the eyeball.
The eye anatomy and physiology. Physiology of the eye 1. It is muscular pigmented and opaque diaphragm which hangs in the eye ball in front of lens. The vitreous humor helps the eye hold its spherical shape.
Finally the light rays land and come to a sharp focusing point on the retina. The human eye is an organ that reacts to light and has several purposesthe eye is a complex structure with layers lens muscles receptors that is surrounded by many boneswatch various parts. The eye is made up of a outer fibrous layer a middle vascular layer and an inner retinal layer where sensory.
Circular and radial muscle. By bahaa halwany department of ophthalmology medicals international 2. The eye is surrounded by the orbital bones and is cushioned by pads of fat within the orbital socket.
The eye is the organ of the visual system and responsible for processing visual detail. It has two types of muscles. They have more rods.
Interior of the ball 1 anterior cavity 2 vitreous chamber 3 lens b. Anatomy and physiology of the ear. It is a complex optical system which collects light and converts it to electrochemical impulses in neurons.
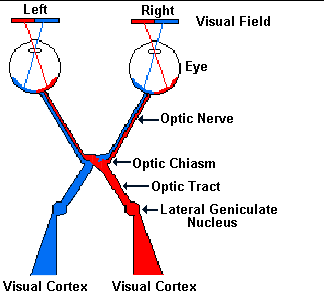
Nerve signals that contain visual information are transmitted through the optic nerve to the brain. Anatomy of the eye. Anatomy physiology pathology of the human eye included are descriptions functions and problems of the major structures of the human eye.
Anatomy and physiology of the eye 1. Conjunctiva cornea iris lens macula retina optic nerve vitreous and extraocular muscles. Extraocular muscles help move the eye in different directions.
It has small circular opening called pupil. Anatomy of the eye. Eye ball structures 1 fibrous tunic 2 vascular tunic 3 nervous tunic 3.
A tapetum is a mirror type membrane that is reflective on the back of the eye activating the rod gives better night vision vitreous humor posterior portion of eye filled with jelly like substance.
 Basic Anatomy And Physiology Of The Eye Springerlink
Basic Anatomy And Physiology Of The Eye Springerlink
 Amazon Com Semtomn Gaming Mouse Pad Blue Components Of
Amazon Com Semtomn Gaming Mouse Pad Blue Components Of
 Neuroscience For Kids The Eye And Its Connections
Neuroscience For Kids The Eye And Its Connections
 Worksheet With Answer For Structure Of Human Eye Eye
Worksheet With Answer For Structure Of Human Eye Eye
 Special Senses Anatomy And Physiology Nurseslabs
Special Senses Anatomy And Physiology Nurseslabs
 Anatomy And Physiology Of The Human Eye Effects Of
Anatomy And Physiology Of The Human Eye Effects Of
 Visual Pathway Human Anatomy Physiology Eye Anatomy
Visual Pathway Human Anatomy Physiology Eye Anatomy
 Special Senses Anatomy And Physiology Nurseslabs
Special Senses Anatomy And Physiology Nurseslabs
 The Clinical Anatomy And Physiology Of The Eye Rila
The Clinical Anatomy And Physiology Of The Eye Rila
 Biology Diagrams Images Pictures Of Human Anatomy And
Biology Diagrams Images Pictures Of Human Anatomy And
 Anatomy Of The Eye American Association For Pediatric
Anatomy Of The Eye American Association For Pediatric
 Equine Eye Anatomy And Physiology The Horse
Equine Eye Anatomy And Physiology The Horse
 Special Senses Vision Anatomy And Physiology I
Special Senses Vision Anatomy And Physiology I
 Iknow Interactive Anatomy And Physiology Of The Human Eye
Iknow Interactive Anatomy And Physiology Of The Human Eye
 Human Eye Ball Anatomy Physiology Diagram
Human Eye Ball Anatomy Physiology Diagram
 Pdf Anatomy And Physiology Of The Human Eye Effects Of
Pdf Anatomy And Physiology Of The Human Eye Effects Of
 Vision Anatomy And Physiology I
Vision Anatomy And Physiology I
 Human Eye Ball Anatomy Physiology Diagram
Human Eye Ball Anatomy Physiology Diagram
 Archive File Anatomy Of The Eye Jpg Comparative
Archive File Anatomy Of The Eye Jpg Comparative
 How The Eye Works Animation How Do We See Video Nearsighted Farsighted Human Eye Anatomy
How The Eye Works Animation How Do We See Video Nearsighted Farsighted Human Eye Anatomy
 Eye Anatomy A Closer Look At The Parts Of The Eye
Eye Anatomy A Closer Look At The Parts Of The Eye
 Anatomy Physiology 1 Final Exam
Anatomy Physiology 1 Final Exam
 Anatomy And Physiology Sensory System The Eye
Anatomy And Physiology Sensory System The Eye
 The Special Senses Ross And Wilson Anatomy And Physiology
The Special Senses Ross And Wilson Anatomy And Physiology

Belum ada Komentar untuk "The Eye Anatomy And Physiology"
Posting Komentar