Jejunum Anatomy
Proteins cholesterol fats and also the vitamins soluble in fats a d e and k. The jejunum lies coiled in the upper part of peritoneal cavity below the left of the transverse mesocolon while the ileum is found in the lower part of the peritoneal cavity and in the pelvis.
Anatomy of the small intestine the jejunum.
Jejunum anatomy. The jejunum by definition is the first 40 of the small intestine beyond the duodenum. This produces species variation see species differences. Digestion of nutrients like protein by proteinase starch by amylase etc.
It is suspended by the mesentery mesojejunum. The jejunum has wider bore thicker walls and is redder in color. Jejunum name refers to the fact that early anatomists typically found it to be empty.
Jejunum anatomy circular folds. The duodenum jejunum and ileum. As their name implies microvilli are even smaller than villi.
The jejunums main function is to absorb micro and macro nutrients contained within the ingested foods and to move the foods and liquids further through the digestive tube in order to complete the digestion process. The anatomy of the jejunum is best explained with its main function in focus. An acute angle called the duodenojejunal flexure is formed by the.
Some of the most important functions of jejunum are. It lies on the abdominal floor separated from the parietal peritoneum by the greater omentum. This induces an osmotic gradient leading to a.
It extends from the pylorus of the stomach to the iloececal junction where it meets the large intestine. The jejunum has the typical histological pattern as the entire small intestine. Small intestine in small intestine the second region the jejunum in the central section of the abdomen comprises about two fifths of the remaining tract.
These are special ridges in the mucosal surface of the small intestine. The small intestine is a organ located in the gastrointestinal tract which assists in the digestion and absorption of ingested food. In human digestive system.
Most of the foods especially lipophilic nutrients are absorbed by the jejunum with the help of the microvilli. The jejunum begins in the upper left quadrant of the abdomen but lies mostly within the umbilical region. Villi are located within the circular folds and measure 1 millimeter in length.
Jejunum occupies the ventral part of the abdominal cavity filling those parts that are not occupied by other viscera. Anatomically the small bowel can be divided into three parts. The transition from the extraperitoneal ascending part of the duodenum to the intraperitoneal jejunum.
Gross And Microscopic Anatomy Of The Small Intestine
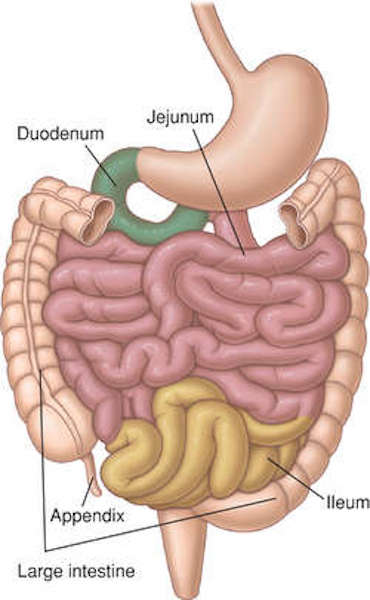 Anatomy Lesson 47 Brave Bowels Gurgly Gut Gi Tract
Anatomy Lesson 47 Brave Bowels Gurgly Gut Gi Tract
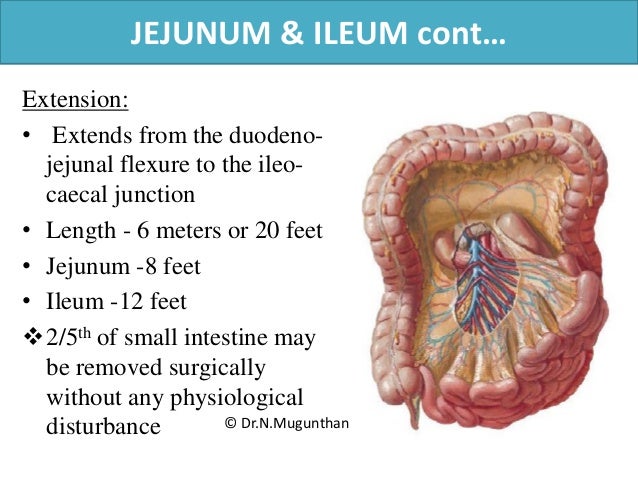 Mesentery Jejunum Ileum Superior Mesenteric Artery Pdf
Mesentery Jejunum Ileum Superior Mesenteric Artery Pdf
Difference Between Duodenum And Jejunum Definition
 Anatomy Of The Small Intestine Jejunum And Ileum
Anatomy Of The Small Intestine Jejunum And Ileum
Anatomy Of The Small Intestine
 Jejunum S Function In The Small Intestine And Digestive System
Jejunum S Function In The Small Intestine And Digestive System
 Regions Of The Small Intestine The Duodenum Is Attached To
Regions Of The Small Intestine The Duodenum Is Attached To
:watermark(/images/watermark_only.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/anatomy_term/arteriae-jejunales/GDRvwhHwcq6SsEAOfJIQ_Arteriae_jejunales_magnified.png) Jejunum Anatomy Histology Function Composition Kenhub
Jejunum Anatomy Histology Function Composition Kenhub
Difference Between Duodenum And Jejunum Definition
:watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/anatomy_term/superior-mesenteric-vein-10/bstyv5xDqPoPvRT655hQ_Superior_mesenteric_vein_2.png) Jejunum Anatomy Histology Function Composition Kenhub
Jejunum Anatomy Histology Function Composition Kenhub
 Jejunum Flap Plastic Surgery Key
Jejunum Flap Plastic Surgery Key
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/11863/the-arteries-of-the-small-intestine_english.jpg) Small Intestine Anatomy Location And Function Kenhub
Small Intestine Anatomy Location And Function Kenhub
 Small Intestine Anatomy Overview Gross Anatomy
Small Intestine Anatomy Overview Gross Anatomy
Amicus Illustration Of Amicus Anatomy Abdomen Bowel Organs
 Circular Folds An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Circular Folds An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
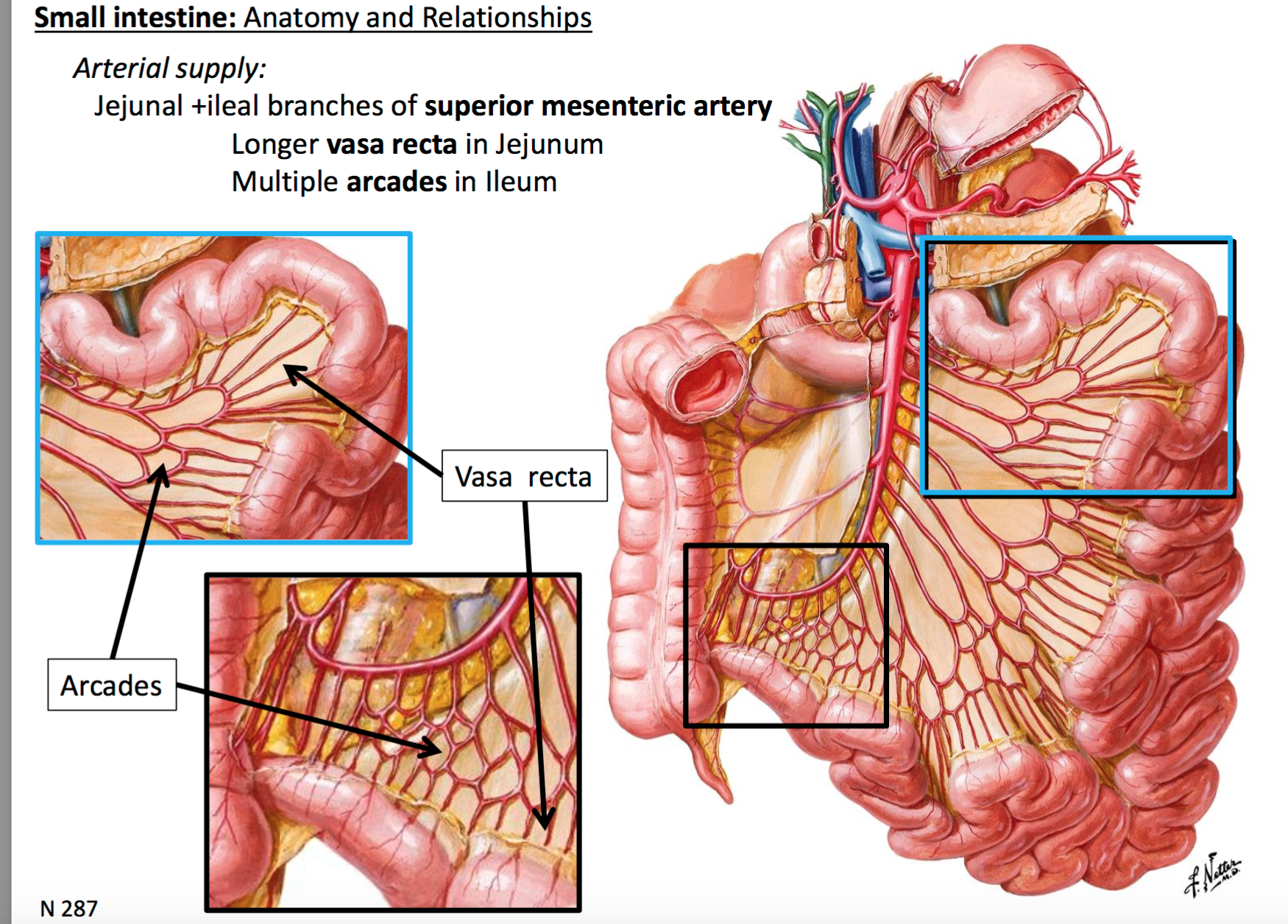
 Jejunum Anatomy Physiology Wikivet English
Jejunum Anatomy Physiology Wikivet English
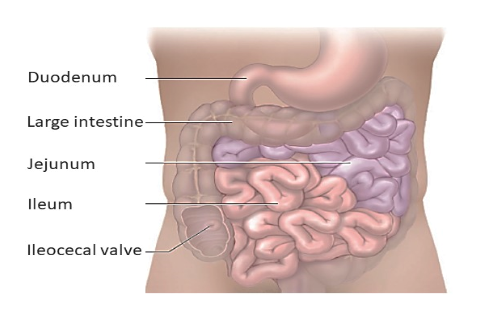 Answered The Small Intestine Can Be Divided Into Bartleby
Answered The Small Intestine Can Be Divided Into Bartleby
 Jejunal Arcades Fewer Larger Loops Than Ileal Arcades Ileal
Jejunal Arcades Fewer Larger Loops Than Ileal Arcades Ileal
 Gross Anatomy Of The Jejunum Including Blood And Nerve
Gross Anatomy Of The Jejunum Including Blood And Nerve
 Anatomy Of The Abdomen Doctor Stock
Anatomy Of The Abdomen Doctor Stock
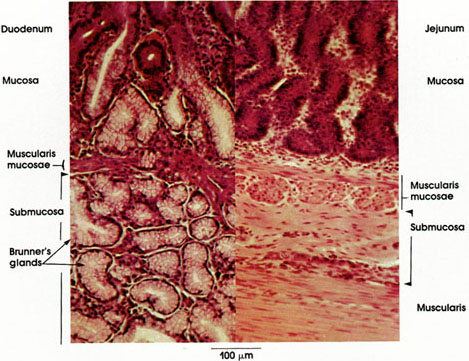 Anatomy Atlases Atlas Of Microscopic Anatomy Section 1 Cells
Anatomy Atlases Atlas Of Microscopic Anatomy Section 1 Cells
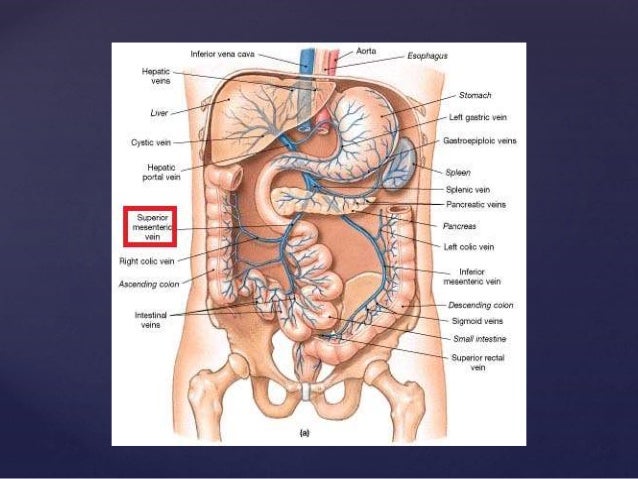 Gross Anatomy Of The Jejunum Including Blood And Nerve
Gross Anatomy Of The Jejunum Including Blood And Nerve
 The Small And Large Intestines Anatomy And Physiology Ii
The Small And Large Intestines Anatomy And Physiology Ii



Belum ada Komentar untuk "Jejunum Anatomy"
Posting Komentar