Nasal Passage Anatomy
Projecting out of the lateral walls of the nasal cavity are curved shelves of bone. The flow of air from outside of the body to the lungs begins with the nose which is divided into the left and right nasal passages.
 Nose Useful Notes On Human Nose And Para Nasal Sinuses
Nose Useful Notes On Human Nose And Para Nasal Sinuses
Just beneath each concha is a passage known as the meatus named for the adjacent turbinate.
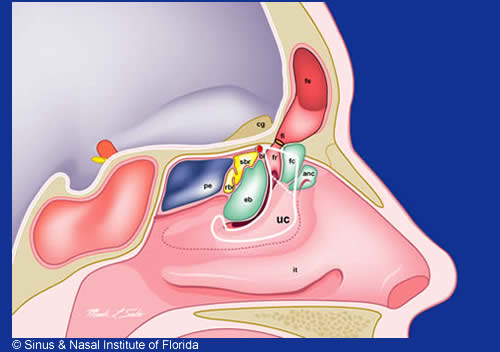
Nasal passage anatomy. Beyond the nasal valve the nasal passages are lined mostly by membranes more like the lining of the lungs called respiratory epithelium which is thin and rich in blood vessels. The sinuses are part of your nose and respiratory system. Openings into the nasal cavity.
The lateral nasal wall consists of inferior and middle turbinates and occasionally a superior or supreme turbinate bone. The turbinates consist of three ridges of thin shell like bone known as the nasal conchae. The nasal passages are lined with a membrane composed primarily of one layer of flat closely packed cells called epithelial cells.
Superior middle and inferior meatus. The nasal cavity extends from the external opening the nostrils. The nasal cavity is surrounded by a.
In bones behind your nose are your sphenoid sinuses. Anatomy of the nasal cavity. This region is divided into a labyrinth of slit like passages by multiple bony proturbances that fill the nose and act as shelves.
The exhaled air travels in the reverse path and leaves the body through the nasal cavity. The superior the middle and the inferior turbinates. Theyre lined with soft pink tissue called mucosa.
Role as a passage for inhaled air. Normally the sinuses are empty except for a thin layer of mucus. The ridges are named for their position.
The nasal cavity divisions. As you breathe in air through your nose and. Anatomy of the nasal passages.
Internally the nasal septum divides the nasal cavity into a right and left side. They connect to your nasal passages in a complex network of air flow and drainage passages. One of the functions of the nose is to drain a variety.
During inhalation air enters through the nostrils and passes via the nasal cavity into the pharynx and larynx the next sections in the respiratory tract to eventually reach the lungs. Anatomy and physiology of the nasal cavity inner nose and mucosa introduction. Anatomy of the nose.
The external nose consists of paired nasal bones and upper and lower lateral cartilages. The nasal cavity refers to the interior of the nose. The nasal cavity is the most superior part of the respiratory tract.
Anatomy of the nose.
 Nasal And Sinus Conditions Of Childhood Michael Rothschild Md
Nasal And Sinus Conditions Of Childhood Michael Rothschild Md
 Easy Notes On Nasal Cavity Learn In Just 4 Minutes
Easy Notes On Nasal Cavity Learn In Just 4 Minutes
 Nasal Cavity Definition Anatomy Functions Diagrams
Nasal Cavity Definition Anatomy Functions Diagrams
 The Nasal Cavity Structure Vasculature Innervation
The Nasal Cavity Structure Vasculature Innervation
 Nasal Cavity Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock
Nasal Cavity Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock
 Sinus Infection Sinusitis Symptoms Signs Treatment
Sinus Infection Sinusitis Symptoms Signs Treatment
 Anatomy And The Human Blockhead Anatomy Of The Nasal
Anatomy And The Human Blockhead Anatomy Of The Nasal
 Easy Notes On Nasal Cavity Learn In Just 4 Minutes
Easy Notes On Nasal Cavity Learn In Just 4 Minutes
 Lining Of The Nasal Cavity Acland S Video Atlas Of Human
Lining Of The Nasal Cavity Acland S Video Atlas Of Human
 Nasal Sinus Program Davis Ear Nose Throat Sleep Center
Nasal Sinus Program Davis Ear Nose Throat Sleep Center
 Anatomical Structure Of The Nasal Cavity Through A Vertical
Anatomical Structure Of The Nasal Cavity Through A Vertical
 Nasal Cavity Definition Anatomy Functions Diagrams
Nasal Cavity Definition Anatomy Functions Diagrams
 Nasal Cavity Nose Atlas Of Anatomy
Nasal Cavity Nose Atlas Of Anatomy
 Chapter 23 Nasal Cavity The Big Picture Gross Anatomy
Chapter 23 Nasal Cavity The Big Picture Gross Anatomy
 World S Best Nasal Cavity Stock Pictures Photos And Images
World S Best Nasal Cavity Stock Pictures Photos And Images
 Nasal Physiology Overview Anatomy Of The Nose Nasal Airflow
Nasal Physiology Overview Anatomy Of The Nose Nasal Airflow
 Sinus Nasal Institute Of Florida
Sinus Nasal Institute Of Florida
 Seer Training Nose Nasal Cavities Paranasal Sinuses
Seer Training Nose Nasal Cavities Paranasal Sinuses
 Human Body Anatomy Nasal Passage Way
Human Body Anatomy Nasal Passage Way
 Supportive Bones And Cartilages Of The Nasal Cavity
Supportive Bones And Cartilages Of The Nasal Cavity
 The Anatomy Of Your Sinusitis Pain And How To Cure It
The Anatomy Of Your Sinusitis Pain And How To Cure It
 The Nasal Cavity Structure Vasculature Innervation
The Nasal Cavity Structure Vasculature Innervation


Belum ada Komentar untuk "Nasal Passage Anatomy"
Posting Komentar