Pelvic Organ Anatomy
This can cause one or more of these organs to press down on. They also include the vagina which is the entryway to the uterus.
 Pelvic Organ Prolapse Star Clinic
Pelvic Organ Prolapse Star Clinic
It is designed to keep the pelvic organs bladder uterus and rectum in place and support spinal and pelvic stability.
Pelvic organ anatomy. The fibers from both sides also fuse to form a raphe and contribute to the anococcygeal ligament. Viscera is the plural form. Functional anatomy and prolapse the pelvic organ support system is multifaceted and includes the endopelvic fascia the perineal membrane and the levator ani muscles which are controlled by the central and peripheral nervous system.
There are many organs that sit in the pelvis including much of the urinary system and lots of the male or female reproductive systems. Posteriorly it attaches to the last 2 segments of the coccyx. A hollow organ is an internal organ that forms a hollow tube or pouch such as the stomach intestine or bladder.
The female pelvic floor is made of muscles and connective tissue that form a sling or hammock across the base of the pelvis fig 1. Pelvic organ prolapse occurs when the muscles in the pelvis can no longer support its organs such as the bladder uterus or rectum. In the study of anatomy the term viscus refers to an internal organ.
This median raphe between the anus and the coccyx is called the levator plate and is the shelf on which the pelvic organs rest. The diaphragm forms the upper surface of the abdomen. The skin tissues and organs in the pelvis are supplied by the vasculature of the pelvis and innervated by many nerves of the pelvis including the pudendal nerve.
Seventy nine organs have been identified in the human body. The female pelvic organs include the egg producing ovaries and the uterine tubes that carry the eggs into the uterus for potential fertilization by male sperm. At the level of the pelvic bones the abdomen ends and the pelvis begins.
The abdomen contains all the digestive organs including the stomach small and large intestines pancreas liver and gallbladder.
 Arteries And Veins Of Pelvic Organs Female Blood Supply Of
Arteries And Veins Of Pelvic Organs Female Blood Supply Of
 Pelvic Inflammatory Disease Wikipedia
Pelvic Inflammatory Disease Wikipedia
 1940s Pelvic Organs Of The Male Male Anatomy Internal Anatomy Original Book Illustration Mature
1940s Pelvic Organs Of The Male Male Anatomy Internal Anatomy Original Book Illustration Mature
 Pelvis And Perineum Anatomy Vessels Nerves Kenhub
Pelvis And Perineum Anatomy Vessels Nerves Kenhub
 Functional Anatomy Of Pelvic Organs Springerlink
Functional Anatomy Of Pelvic Organs Springerlink
 Female Pelvic Floor 1 Anatomy And Pathophysiology Nursing
Female Pelvic Floor 1 Anatomy And Pathophysiology Nursing
 Pelvic Organ Prolapse Pop Affects 50 Of Women Globally
Pelvic Organ Prolapse Pop Affects 50 Of Women Globally
 Female Pelvic Floor 1 Anatomy And Pathophysiology Nursing
Female Pelvic Floor 1 Anatomy And Pathophysiology Nursing
 Physiotherapy First For Pelvic Floor Dysfunction Urology News
Physiotherapy First For Pelvic Floor Dysfunction Urology News
 Pelvic Rehab Therapy Help For Uncomfortable Postpartum
Pelvic Rehab Therapy Help For Uncomfortable Postpartum
 Chapter 12 Pelvis And Perineum The Big Picture Gross
Chapter 12 Pelvis And Perineum The Big Picture Gross
 The Muscles That Control The Pelvic Floor Pericoach
The Muscles That Control The Pelvic Floor Pericoach
 Abdomen Anatomy Definition Function Muscles Biology
Abdomen Anatomy Definition Function Muscles Biology
 5 Facts About The Anatomy Of The Pelvic Cavity
5 Facts About The Anatomy Of The Pelvic Cavity
 Pelvic Cavity Anatomy Www Urology Textbook Com
Pelvic Cavity Anatomy Www Urology Textbook Com
 Female Pelvic Applied Anatomy By Dr Shashwat Jani
Female Pelvic Applied Anatomy By Dr Shashwat Jani
 Pelvic Floor What You Need To Know By Perifit Team
Pelvic Floor What You Need To Know By Perifit Team
 Muscles Of The Pelvic Floor Anatomy And Function Kenhub
Muscles Of The Pelvic Floor Anatomy And Function Kenhub
 Pelvic Organ Prolapse What Is Pelvic Organ Prolapse Best
Pelvic Organ Prolapse What Is Pelvic Organ Prolapse Best
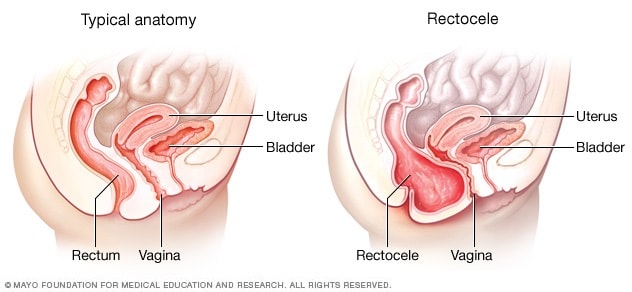
 Posterior Vaginal Prolapse Rectocele Symptoms And Causes
Posterior Vaginal Prolapse Rectocele Symptoms And Causes
 Organs Of The Pelvis Teachmeanatomy
Organs Of The Pelvis Teachmeanatomy
 Pelvic Organ Prolapse And Pessary Fitting Motion Works
Pelvic Organ Prolapse And Pessary Fitting Motion Works
 Pelvic Organ Prolapse Crash Medical Review Series
Pelvic Organ Prolapse Crash Medical Review Series
 Endometrial Mesenchymal Stem Cells As A Cell Based Therapy
Endometrial Mesenchymal Stem Cells As A Cell Based Therapy
 Functional Anatomy Of Pelvic Organs Springerlink
Functional Anatomy Of Pelvic Organs Springerlink

Belum ada Komentar untuk "Pelvic Organ Anatomy"
Posting Komentar