Femoral Neck Anatomy
Abstract paediatric femoral neck fractures are uncommon injuries and are usually caused by high energy trauma. At the ends of the femur are areas of compact bone which is solid and does not contain marrow.
 Two Little Runners A Diagnosis Femoral Neck Stress Reaction
Two Little Runners A Diagnosis Femoral Neck Stress Reaction
Femoral neck fractures are a subset of proximal femoral fractures.

Femoral neck anatomy. A fractured neck of femur is classified as either intracapsular or extracapsular. The femoral neck is the weakest part of the femur. Surgical options can vary based on age delbet classification and displacement of the fracture.
The neck and head of the femur contain spongy bone. There were no immediate post operative complications and she was progressed to full weight bearing three months after surgical fixation. Since disruption of blood supply to the femoral head is dependent on the type of fracture and causes significant morbidity diagnosis and classification of these fractures is important.
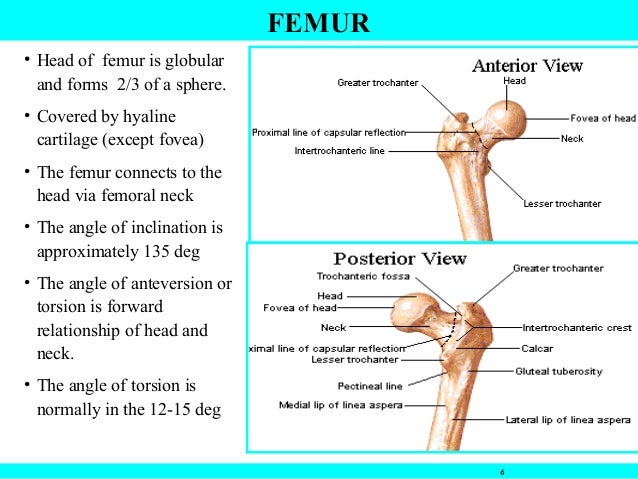
The femoral neck the femoral neck usually sits at a 120 135 degree angle with some variation. The classical clinical finding is that of an externally rotated shortened leg. The femur neck femoral neck or neck of the femur is a flattened pyramidal process of bone connecting the femoral head with the femoral shaft and forming with the latter a wide angle opening medialward.
This structure supports the head of the femur bone and its insertion into the hip. Low energy trauma can result in pathologic neck fractures and stress fractures of the neck due to repetitive activity. A fracture of this area is known as a hip fracture and happens during aging.
The femoral aspect of the hip is made up of the femoral head with its articular cartilage and the femoral neck which connects the head to the shaft in the region of the lesser and greater. Obq11233 a 48 year old active female runner underwent percutaneous screw fixation of a minimally displaced femoral neck fracture six months ago. Inside the body of the femur is the medullary cavity which contains bone marrow.
Fractures of the neck of femur are very common injuries which mainly occur in elderly females with osteoporotic bones. A fracture distal to this line is therefore extracapsular whereas a fracture proximal to this is intracapsular. The hip joint capsule inserts along the intertrochanteric line.
Surrounding the compact bone is spongy bone which has lots of small cavities dispersed throughout it.
 Femoral Neck Stress Fractures Knee Sports Orthobullets
Femoral Neck Stress Fractures Knee Sports Orthobullets
 Femoral Neck Fracture Hip Fracture Physioadvisor
Femoral Neck Fracture Hip Fracture Physioadvisor
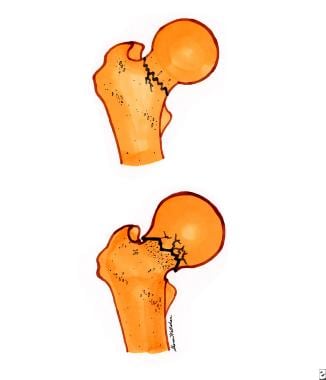 Hip Fracture In Emergency Medicine Practice Essentials
Hip Fracture In Emergency Medicine Practice Essentials
 Proximal Femur Reduction Fixation Arthroplasty
Proximal Femur Reduction Fixation Arthroplasty
Human Anatomy Normal Circulation Of The Femoral Head
 Transcervical Femoral Neck Fractures Causes Treatment Rx
Transcervical Femoral Neck Fractures Causes Treatment Rx
 Femoral Neck Fractures Presentation And Treatment Bone And
Femoral Neck Fractures Presentation And Treatment Bone And
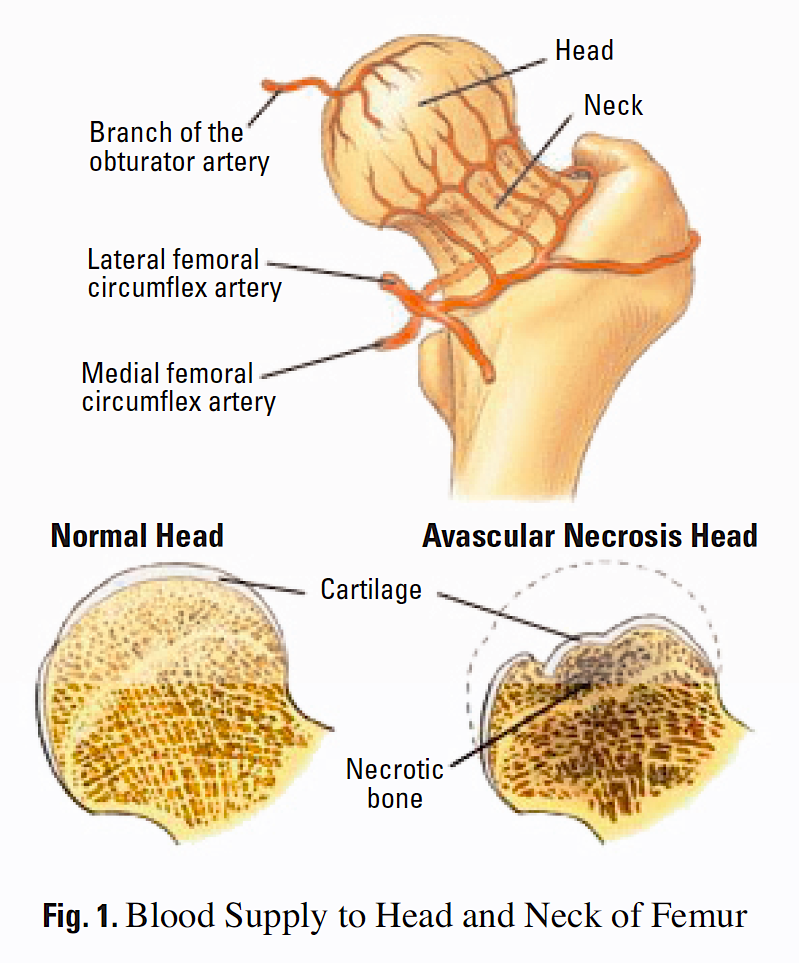 Femoral Neck Fractures Core Em
Femoral Neck Fractures Core Em
Hip Resurfacing Orthoinfo Aaos
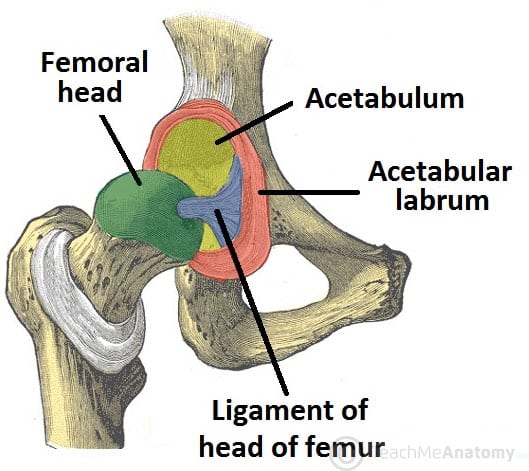 The Hip Joint Articulations Movements Teachmeanatomy
The Hip Joint Articulations Movements Teachmeanatomy
 Anatomy Of The Human Proximal Femur Upper Third Of The
Anatomy Of The Human Proximal Femur Upper Third Of The
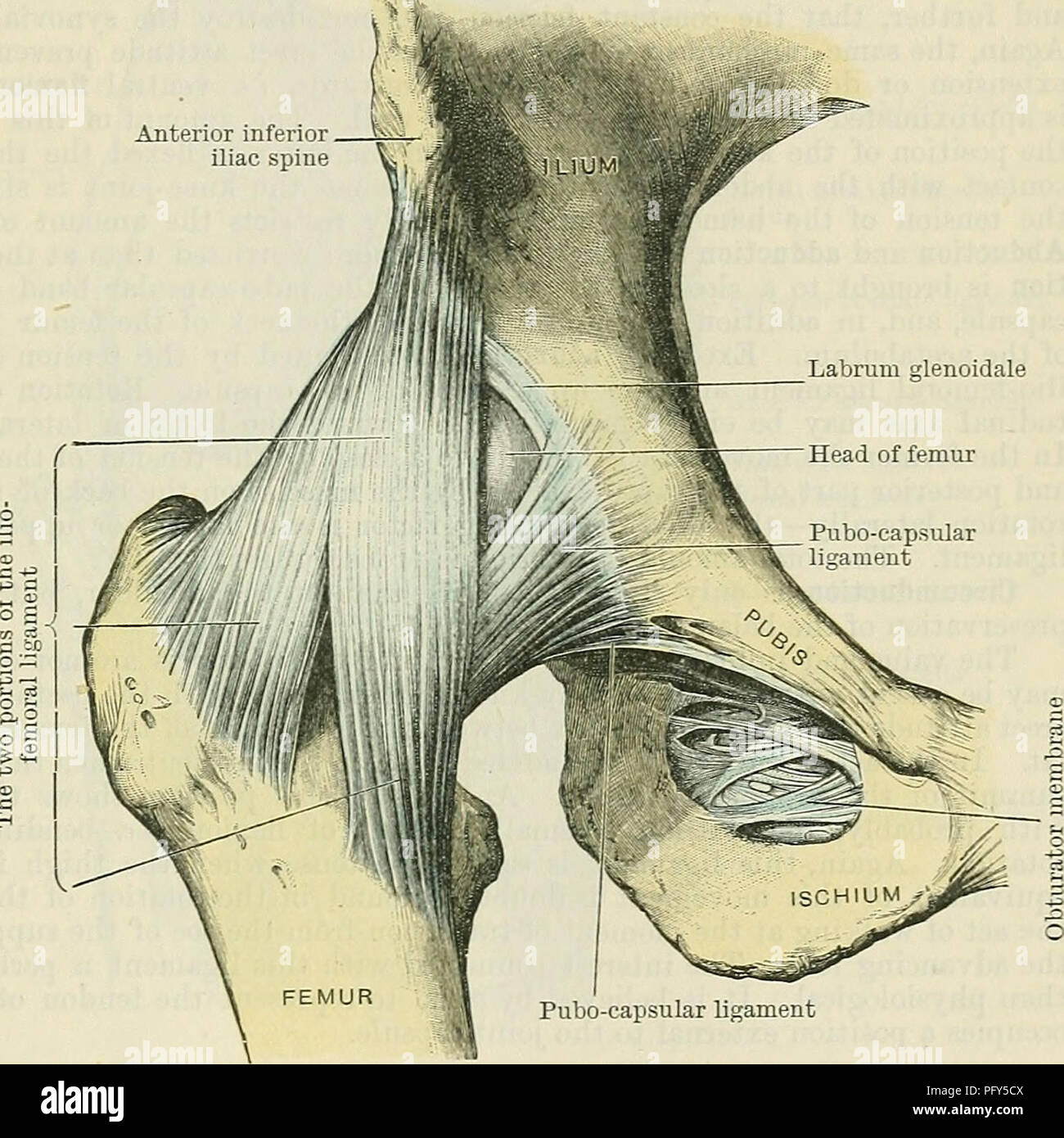 Cunningham S Text Book Of Anatomy Anatomy The Hip Joixt
Cunningham S Text Book Of Anatomy Anatomy The Hip Joixt
 Femoral Head Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock
Femoral Head Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock
Femoral Neck Fracture Fracture Of Hip

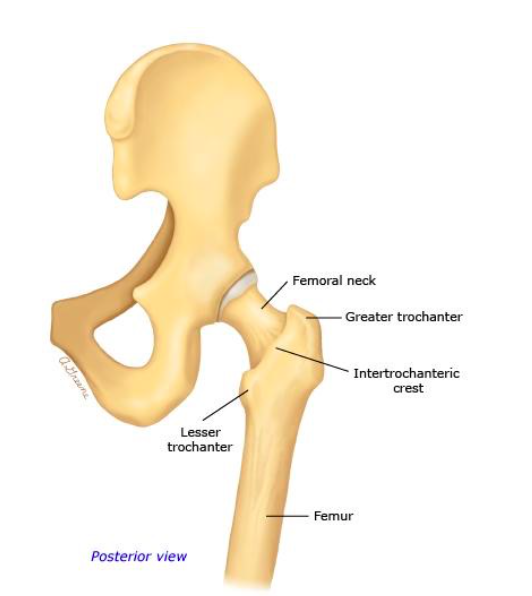 Femoral Neck Fractures Core Em
Femoral Neck Fractures Core Em
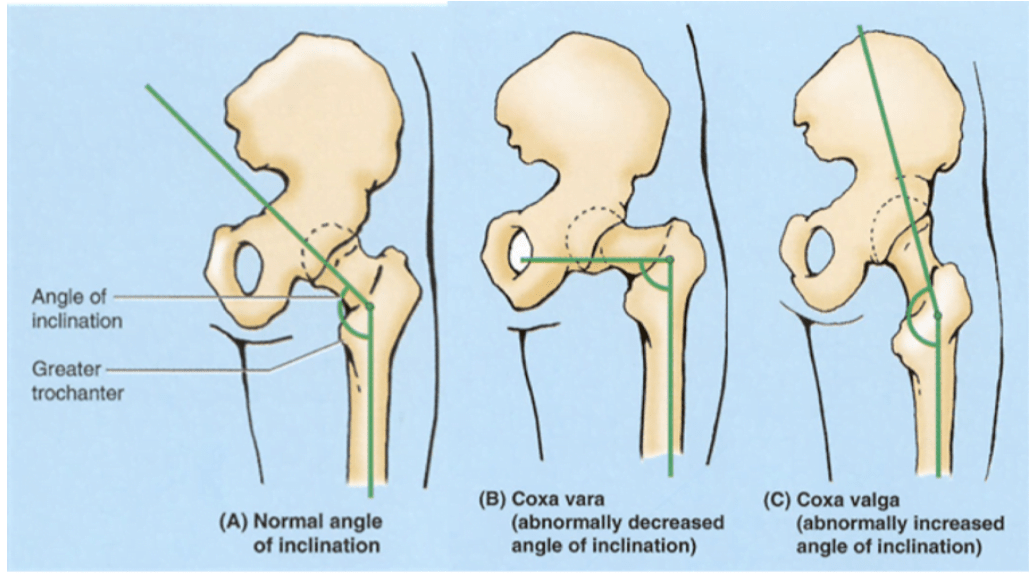 How Your Anatomy Influences Your Squat Mechanics Jc Fitness
How Your Anatomy Influences Your Squat Mechanics Jc Fitness
 Classification Of Hip Fracture According To Anatomical
Classification Of Hip Fracture According To Anatomical
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/11238/anatomy-hip-joint_english.jpg) Femur Bone Anatomy Proximal Distal And Shaft Kenhub
Femur Bone Anatomy Proximal Distal And Shaft Kenhub
 Femur Bone Anatomy Landmarks And Muscle Attachments
Femur Bone Anatomy Landmarks And Muscle Attachments
 Anatomical Teaching Models Plastic Human Joint Models
Anatomical Teaching Models Plastic Human Joint Models
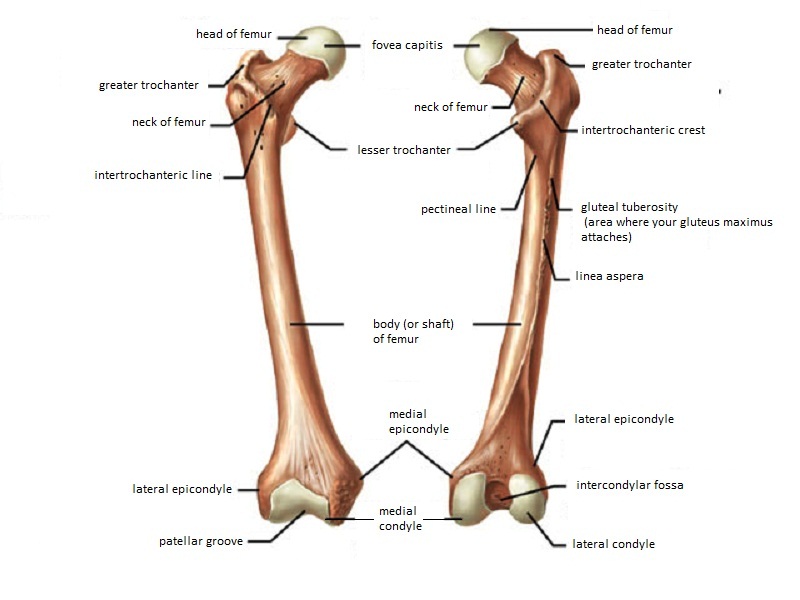 Femur Anatomy And Attachments Bone And Spine
Femur Anatomy And Attachments Bone And Spine
 Proximal Femur Approach Lateral Approach Femoral Neck
Proximal Femur Approach Lateral Approach Femoral Neck






Nice blog, Thanks for providing a valuable information
BalasHapusBhagwan Mahaveer Viklang Sahayata Samiti (BMVSS) is the world's largest organisation rehabilitating over 1.78 million amputees and polio patients by fitting / providing artificial limbs (Jaipur Foot variety), calipers, and other aids and appliances, mostly in India and also in 27 countries across the world.
prosthesis