Anatomy And Physiology Of Cell
The cell is structural and functional unit of all living things. Composed of flattened mamebranous sacs that are stacked on each other.
 Pin By Gazznotes On Anatomy Tissues Physiology Human
Pin By Gazznotes On Anatomy Tissues Physiology Human
There are two types of er.
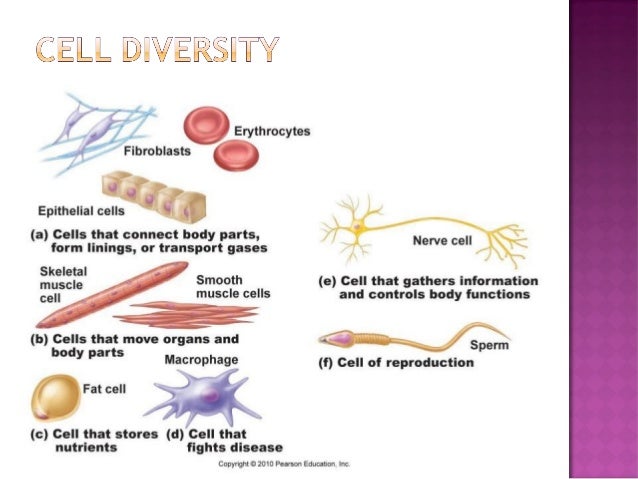
Anatomy and physiology of cell. What that said to me was that when you got right down to it there wasnt a whole lot of difference between a cell and a galaxy. This practice test for the cell function and structure for anatomy physiology is designed to help you for your exam by concentrating on the important facts you may see again on an exam. Various molecules are made in the er and transported around the cell in its channels.
A somatic cell is a general term for a body cell and all human cells except for the cells that produce eggs and sperm which are referred to as germ cells are somatic cells. Parts of a human cell. The major parts of a cell are the nucleus cytoplasm and cell membrane.
A cell membrane which surrounds and protects the cell. The cell was its own worldbut instead of stars gases and dark matter there was mitochondria a nucleus and cytoplasm. Somatic cells contain two copies of each of their chromosomes one copy received from each parent for a total of 46 23 pairs.
Smooth er and rough er. The nucleus contains a nucleolus and is separated from the cytoplasm by the nuclear envelope. Cytology is the branch of microscopic anatomy that studies the cells and histology is the branch of microscopic anatomy that studies tissues.
Functions include odification packaging and distribution of proteins and lipids for secretion or internal use. From the smallest to the largest part of the human anatomy in that sequential order are the. The endoplasmic reticulum er is a network of membranes that form channels throughout the cytoplasm from the nucleus to the plasma membrane.
The human body is made up of 50 to 100 trillion cells and each cell is designed to perform a variety of functions to keep your body is functioning shape. Anatomy and physiology chapter 3. Cell theory in the late 1600s an english scientist named robert hook was the first to observe plant cells with a crude microscope.
Then almost a century and a half later in the 1830s two german scientists proposed that all living things are composed of cells their names were mathias schleiden and theodor schwann. Within the body cells represent a level of organization between organelles and tissues. The cytoplasm which is the watery interior of the cell which contains ions proteins and organelles.
The nucleus contains the cells dna a type of nucleic acid. Organelles which carry out all activities necessary for the cell to live grow and reproduce.
 Anatomy And Physiology Cell Organelles
Anatomy And Physiology Cell Organelles
 Medical Physiology Cellular Physiology Cell Structure And
Medical Physiology Cellular Physiology Cell Structure And
 Cell Structure Anatomy Physiology 141 With Folwer At
Cell Structure Anatomy Physiology 141 With Folwer At
 Chapter 3 Cell Structure Function Pictures From Essentials
Chapter 3 Cell Structure Function Pictures From Essentials
 Erythrocytes Anatomy And Physiology Openstax
Erythrocytes Anatomy And Physiology Openstax
 Biochemistry In Anatomy And Physiology Cell Structure Dna
Biochemistry In Anatomy And Physiology Cell Structure Dna
 Anatomy And Physiology Cell Organelles
Anatomy And Physiology Cell Organelles
 The Cells Tissues And Organisation Of The Body Ross And
The Cells Tissues And Organisation Of The Body Ross And
 Solved Correctly Label The Indicated Structures On The Cell
Solved Correctly Label The Indicated Structures On The Cell
 Anatomy Physiology Lecture Notes Ch 3 Cells Part 1
Anatomy Physiology Lecture Notes Ch 3 Cells Part 1
 Ppt Chapter 10 Plant Anatomy Physiology Michael G
Ppt Chapter 10 Plant Anatomy Physiology Michael G
 Anatomy And Physiology Of Animals The Cell Wikibooks Open
Anatomy And Physiology Of Animals The Cell Wikibooks Open
 Coloring Book Awesome Anatomy Physiology Coloring Workbook
Coloring Book Awesome Anatomy Physiology Coloring Workbook
 Introduction To Anatomy And Physiology Poultry Hub
Introduction To Anatomy And Physiology Poultry Hub
 The Cell Outlines Of General Anatomy And Physiology Cells
The Cell Outlines Of General Anatomy And Physiology Cells
 Ap Exam 1 Study Guide Biol 114 Studocu
Ap Exam 1 Study Guide Biol 114 Studocu
 Test Bank For Human Anatomy And Physiology 10th Edition By
Test Bank For Human Anatomy And Physiology 10th Edition By
 Vcc Lc Worksheets Anatomy Physiology
Vcc Lc Worksheets Anatomy Physiology
 Anatomy And Physiology Curriculum Map
Anatomy And Physiology Curriculum Map
 Anatomy And Physiology Cell Organelles
Anatomy And Physiology Cell Organelles
 3 2 The Cytoplasm And Cellular Organelles Anatomy And
3 2 The Cytoplasm And Cellular Organelles Anatomy And
 Anatomy And Physiology Cells Nursing Crib
Anatomy And Physiology Cells Nursing Crib

Belum ada Komentar untuk "Anatomy And Physiology Of Cell"
Posting Komentar