Anatomy Neck Muscles
The motion of the muscles of the neck are divided into four categories. The muscles of the neck can be divided.
Rotation describes the action of moving the head from side to side lateral motion brings the ear to the shoulder flexion moves the chin to the chest as in looking down.

Anatomy neck muscles. The superficial muscle of the neck the platysma muscle also assists with depression of the mandible against resistance1 the primary muscles of mastication chewing food are the temporalis medial pterygoid lateral pterygoid and masseter muscles. Longus colli begins between the third and sixth cervical vertebrae. Rectus capitis lateralis originates from the first.
Bilateral both sides contraction of the muscle produces flexion of the neck. Unilateral or one sided contraction of the sternocleidomastoid muscle produces lateral rotation of the head. Rectus capitis posterior major and rectus capitis posterior minor attach the inferior nuchal line of the occiput to the c2 and c1 vertebrae respectively.
Rotation lateral flexion flexion and hyperextension. With one on each side of the neck these help flex the neck and rotate the head upward and side to. Longus capitis begins between the third and sixth cervical vertebrae.
The neck also contains the thyroid and parathyroid glands the esophagus larynx and trachea and also a number of lymph glands. Muscles of the neck. Located underneath the platysma on the sides of the neck are the sternocleidomastoid muscles.
Rectus capitis anterior begins at the first cervical vertebrae. The neck is the region between the head and the rest of the body which is built of different tissue and organs including many skeletal muscles. They move the head in every direction pulling the skull and jaw towards the shoulders spine and scapula.
It is innervated by the accessory nerve the 11th cranial nerve. The muscles of the neck are a hot topic within anatomy circles. The muscles of the neck are present in four main groups.
They are usually described within the triangles. The neck muscles including the sternocleidomastoid and the trapezius are responsible for the gross motor movement in the muscular system of the head and neck. The main functions of the neck muscles are to permit movements of the neck or head and to provide structural support of the head.
So there are the muscles of the anterior triangle and the muscles of the posterior triangle. The suboccipital muscles act to rotate the head and extend the neck. Anatomy of the neck the neck contains a number of overlapping muscles blood vessels nerves and myriad structures all contained in a small space and liable to damage and distress.
 Muscle Anatomy Of The Neck Everything You Need To Know Dr Nabil Ebraheim
Muscle Anatomy Of The Neck Everything You Need To Know Dr Nabil Ebraheim
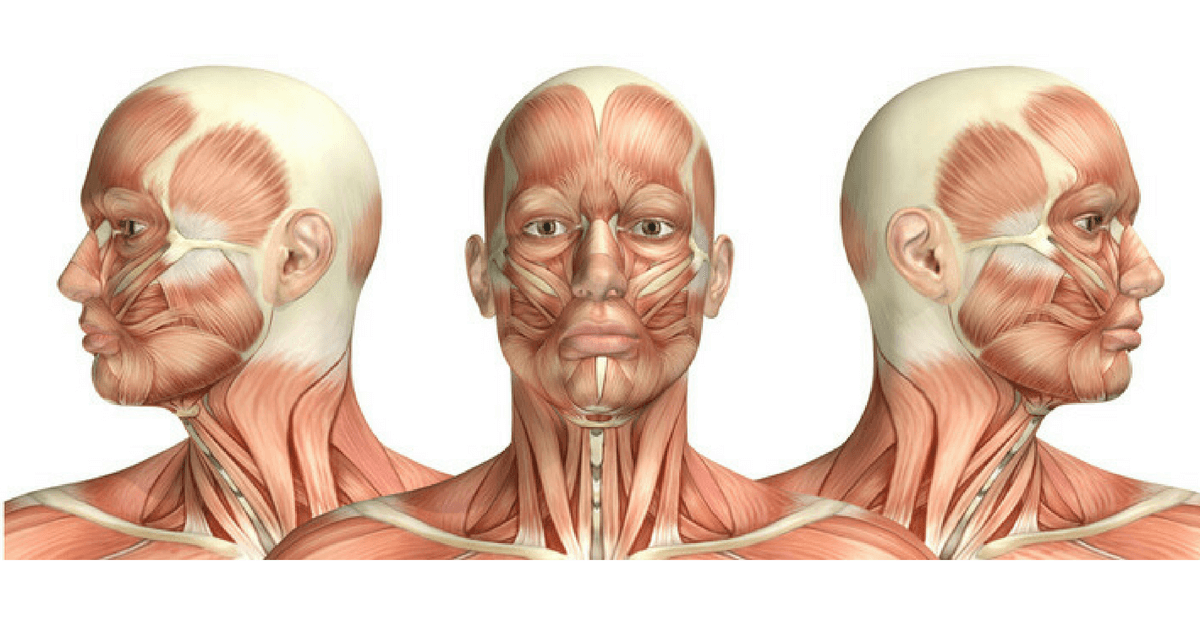 Test Your Anatomy Knowledge Head Neck Medical Exam Prep
Test Your Anatomy Knowledge Head Neck Medical Exam Prep
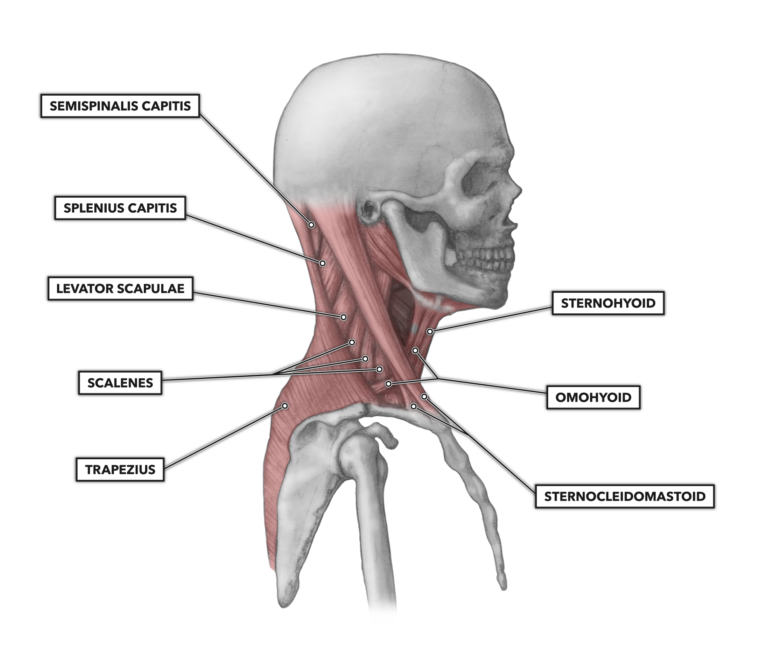 Crossfit Cervical Muscles Part 1
Crossfit Cervical Muscles Part 1
 Muscles Of The Neck Musculature Of The Cervical Spine
Muscles Of The Neck Musculature Of The Cervical Spine

Why Neck Training Should Be A Priority For Athletes
Medical Exhibits Demonstrative Aids Illustrations And Models
 Posterior Triangle Of The Neck Head And Neck Anatomy Human
Posterior Triangle Of The Neck Head And Neck Anatomy Human
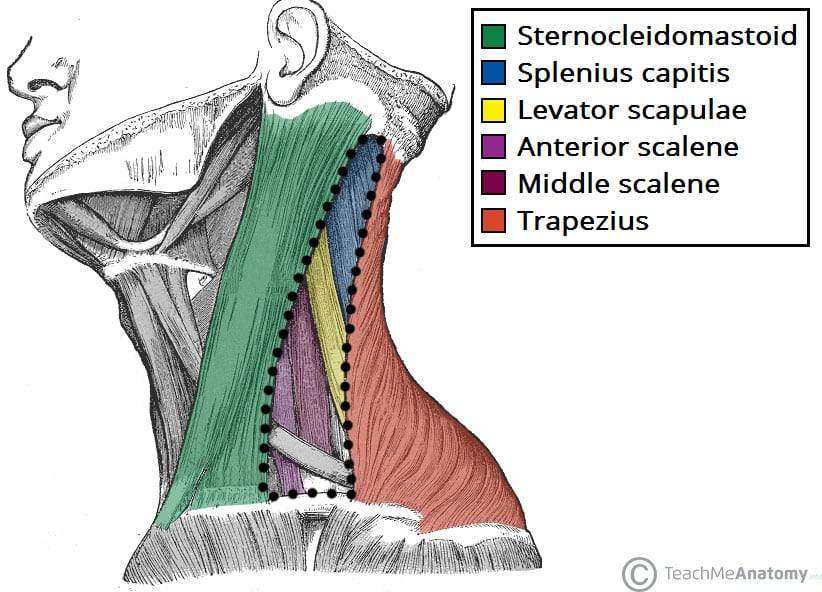 Posterior Triangle Of The Neck Subdivisions Teachmeanatomy
Posterior Triangle Of The Neck Subdivisions Teachmeanatomy
 Human Neck Anatomy And Physiology Anatomy Of The Upper Spine
Human Neck Anatomy And Physiology Anatomy Of The Upper Spine
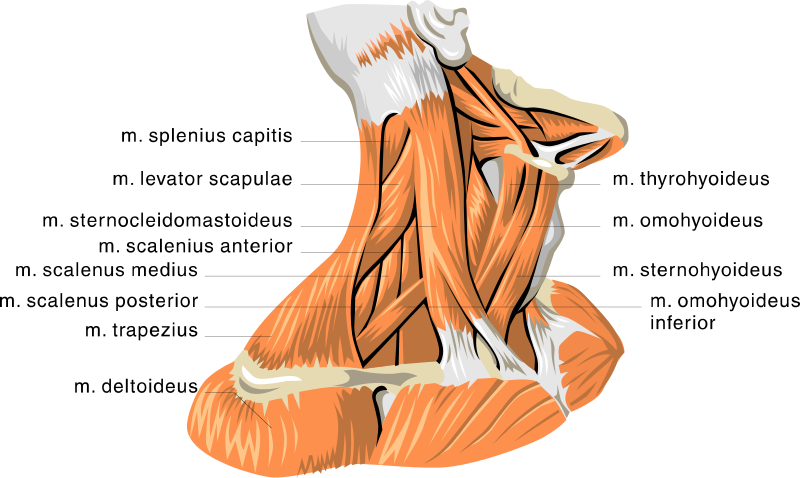 Anatomy Neck Muscles Medical Anatomy Muscle
Anatomy Neck Muscles Medical Anatomy Muscle
 Anatomy Of The Head And Neck Medical Illustrations Showing
Anatomy Of The Head And Neck Medical Illustrations Showing
 Head And Neck Anatomical Chart
Head And Neck Anatomical Chart
 Lateral Neck Muscles Download Scientific Diagram
Lateral Neck Muscles Download Scientific Diagram
 3b Scientific C05 Head And Neck Musculature 3 4 Full Size 5 Part 3b Smart Anatomy
3b Scientific C05 Head And Neck Musculature 3 4 Full Size 5 Part 3b Smart Anatomy
 Free Anatomy Quiz Muscles Of The Head And Neck Locations
Free Anatomy Quiz Muscles Of The Head And Neck Locations
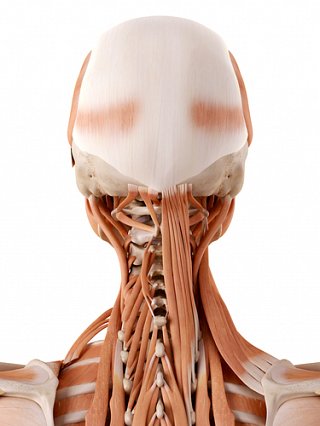 Neck Anatomy Simply Guide To Your Neck
Neck Anatomy Simply Guide To Your Neck

 Muscles Of The Head And Neck Anatomy Pictures And Information
Muscles Of The Head And Neck Anatomy Pictures And Information
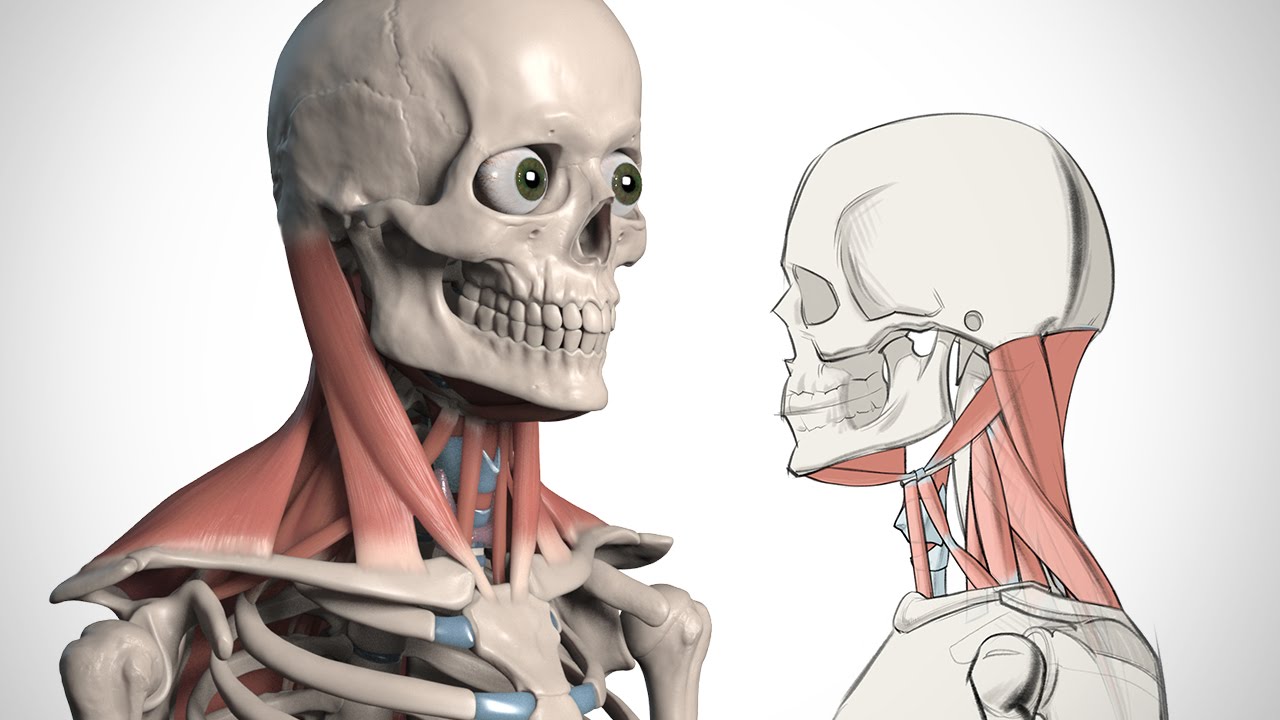 How To Draw The Neck Anatomy For Artists Proko
How To Draw The Neck Anatomy For Artists Proko
 Muscular Anatomy And Soft Tissue Headandcervicalspine
Muscular Anatomy And Soft Tissue Headandcervicalspine
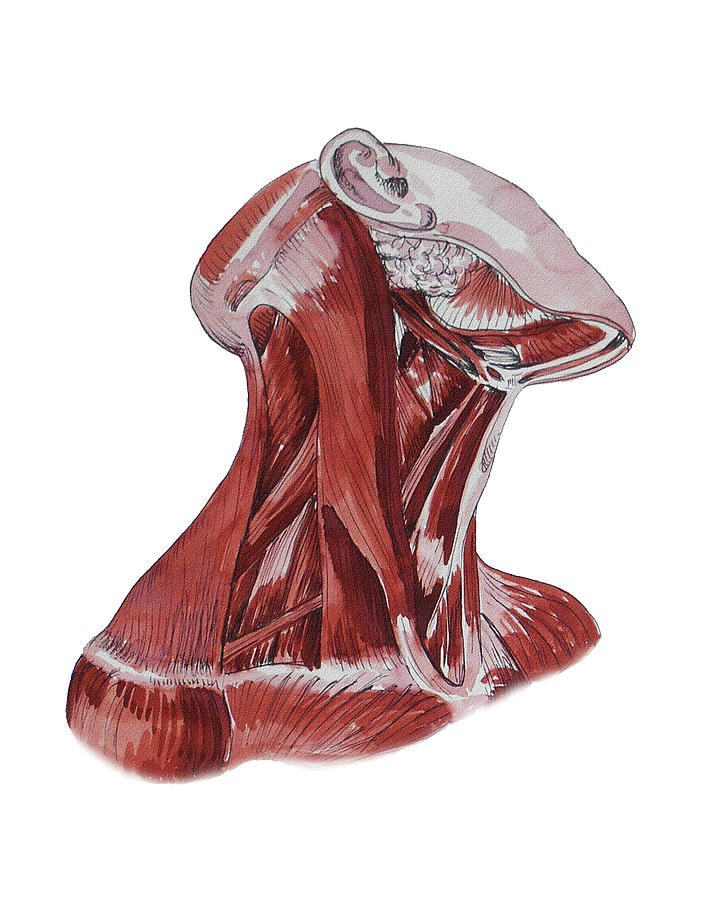




Belum ada Komentar untuk "Anatomy Neck Muscles"
Posting Komentar