Homeostasis Definition Anatomy
A system used to control the level of a variable in which there is an identifiable receptor sensor control center integrator or comparator effectors and methods of communication. Homeostasis is a healthy state that is maintained by the constant adjustment of biochemical and physiological pathways.
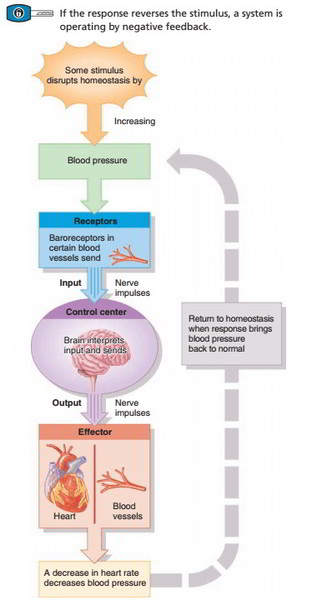 Homeostasis Regulation Positive And Negative Feedback
Homeostasis Regulation Positive And Negative Feedback
Maintaining homeostasis requires that the body continuously monitors its internal conditions.
Homeostasis definition anatomy. Homeostasis the principle of self regulating information feedback by which constant conditions are maintained in a biological system such as the human body. Homeostasis is the dynamic equilibrium that maintains health within the body in spite of the continual changes taking place both internally and in the external environment. The biological definition of homeostasis is the tendency of an organism or cell to regulate its internal environment and maintain equilibrium usually by a system of feedback controls so as to stabilize health and functioning.
Homeostasis is regulated by negative feedback loops and much less frequently by positive feedback loops. The word homeostasis derives from greek homeo meaning similar and stasis meaning stable when used as an adjective it is homeostatic. Homeostasis is essential to life and applies to thousands of bodily parameters.
Homeostasis is an organisms process of maintaining a stable internal environment suitable for sustaining life. Generally the body is in homeostasis when its needs are met and its functioning properly. The maintenance of homeostasis in the body typically occurs through the use of feedback loops that control the bodys internal conditions.
Homeostasis refers to the bodys ability to maintain a stable internal environment regulating hormones body temp water balance etc. This is achieved by attempting to maintain a constant internal state and all the systems of the body are involved in the effort. Homeostasis is the activity of cells throughout the body to maintain the physiological state within a narrow range that is compatible with life.
An example of homeostasis is the maintenance of a constant blood pressure in the human body through a series of fine adjustments in the normal range of function of the hormonal neuromuscular and cardiovascular systems. These adjustments allow the maintenance of blood pressure needed for body function despite environmental changes and changes in a persons activity level.
 What Is Homeostasis Definition Examples Video
What Is Homeostasis Definition Examples Video
Difference Between Hemostasis And Homeostasis Definition
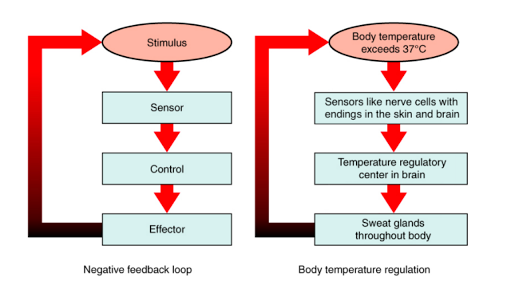
Main Mechanisms Of Homeostasis Homeostasis
 Positive And Negative Feedback Homeostasis Biology Dictionary
Positive And Negative Feedback Homeostasis Biology Dictionary
Difference Between Hemostasis And Homeostasis Definition
 1 Definition Of Physiology Study Of The Functions Of The
1 Definition Of Physiology Study Of The Functions Of The
 How Does The Nervous System Maintain Homeostasis Biology
How Does The Nervous System Maintain Homeostasis Biology
 Introduction To Anatomy Physiology Chapter 1 Introduction
Introduction To Anatomy Physiology Chapter 1 Introduction
 Ch103 Chapter 8 Homeostasis And Cellular Function Chemistry
Ch103 Chapter 8 Homeostasis And Cellular Function Chemistry
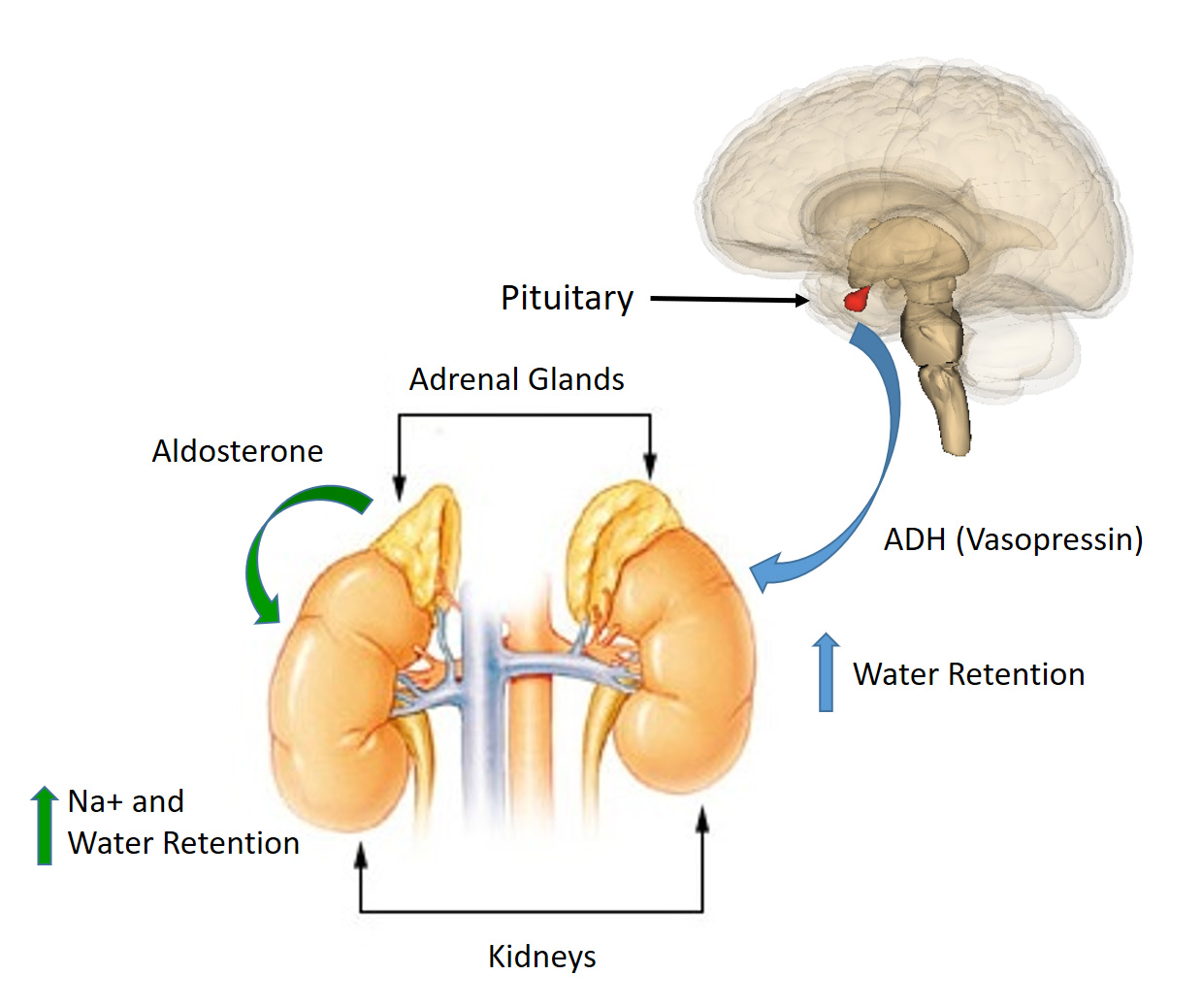
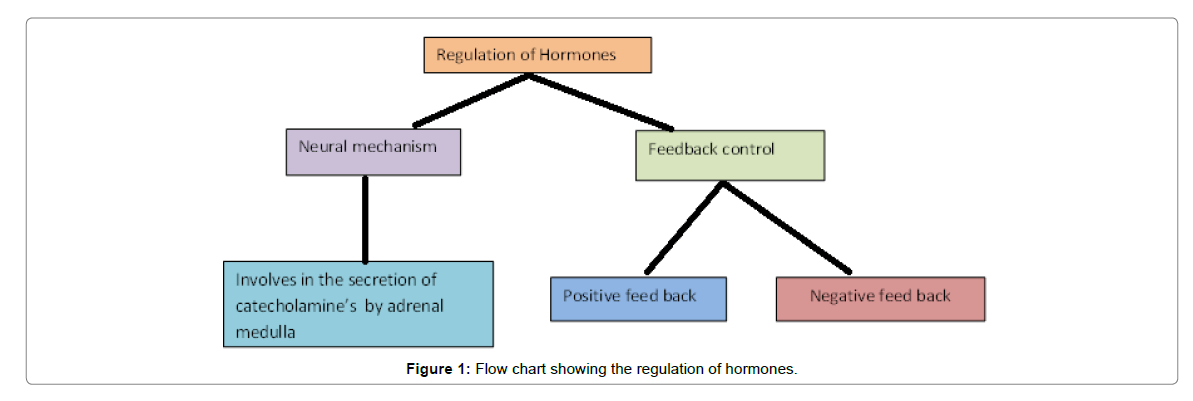 Role Of Homeostasis In Human Physiology A Review
Role Of Homeostasis In Human Physiology A Review
 Solved Understand The Topics Of Physiology Know The D
Solved Understand The Topics Of Physiology Know The D
 Feedback Inhibition Definition And Examples Biology
Feedback Inhibition Definition And Examples Biology
Homeostasis And Regulation In The Human Body Opencurriculum
 Lecture Notes Homeostasis The Foundation Of Physiology
Lecture Notes Homeostasis The Foundation Of Physiology
 Human Body Levels Of Organization And Homeostasis Task Cards
Human Body Levels Of Organization And Homeostasis Task Cards
 Homeostasis And Feedback Loops Anatomy And Physiology I
Homeostasis And Feedback Loops Anatomy And Physiology I
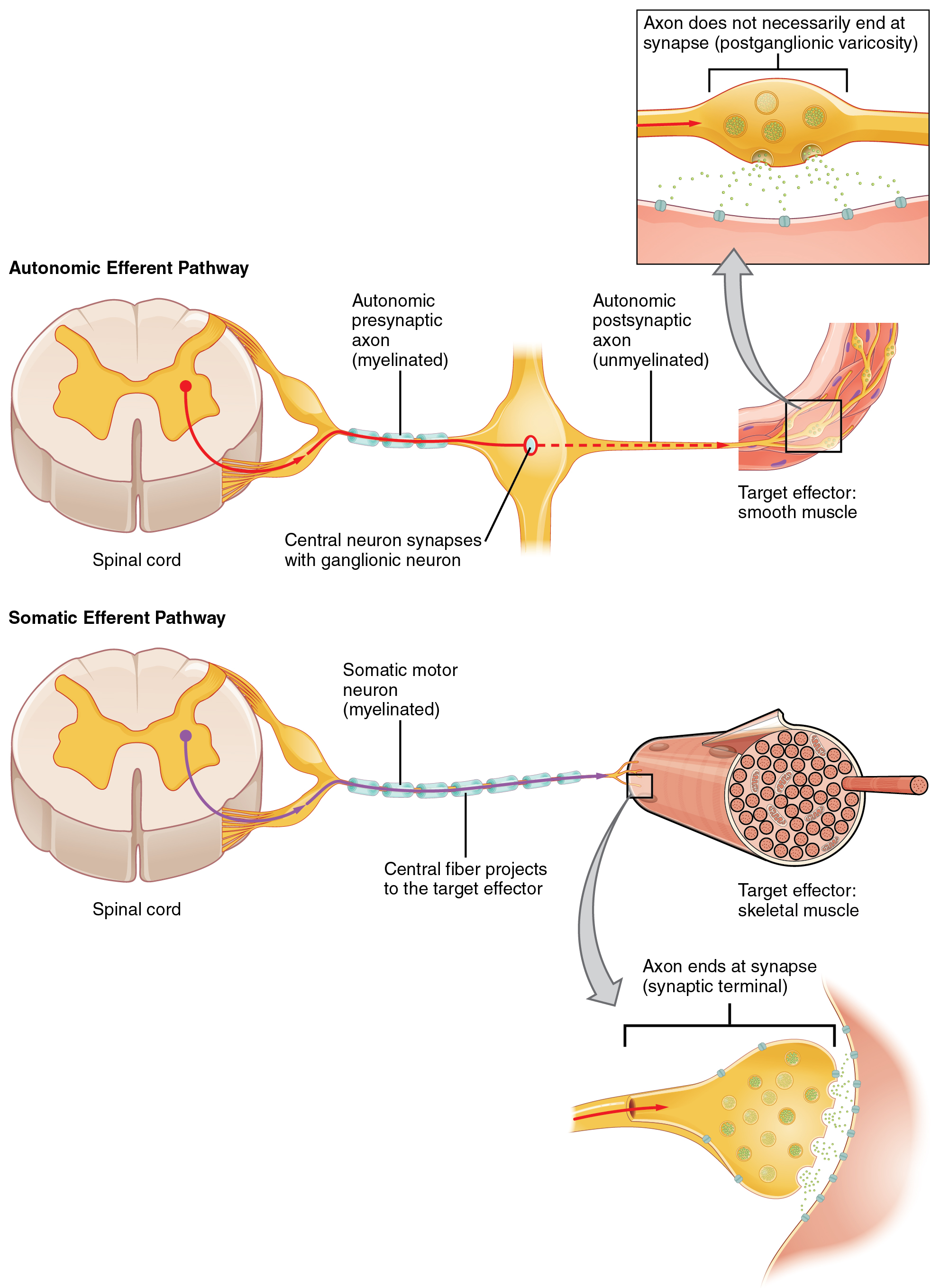 15 2 Autonomic Reflexes And Homeostasis Anatomy And Physiology
15 2 Autonomic Reflexes And Homeostasis Anatomy And Physiology
 Organ System Definition And Examples Biology Dictionary
Organ System Definition And Examples Biology Dictionary
Homeostasis Anatomy Physiology A Level Biology
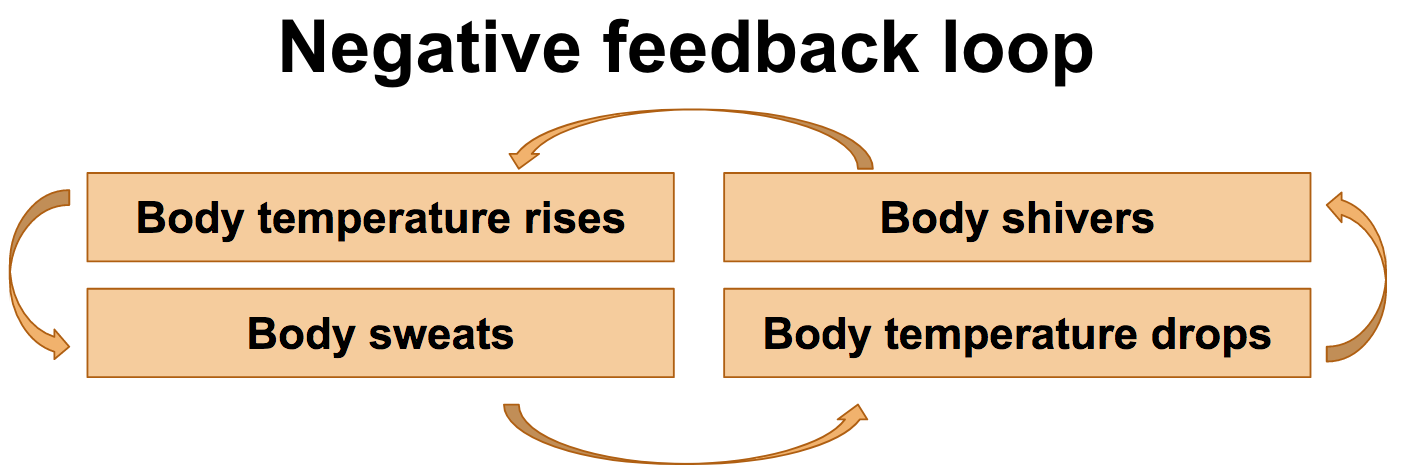 Body Structure And Homeostasis Review Article Khan Academy
Body Structure And Homeostasis Review Article Khan Academy
Human Biology Online Lab Homeostasis And The
 03 Homeostasis Anatomy Physiology Biol121 With Morris
03 Homeostasis Anatomy Physiology Biol121 With Morris





Belum ada Komentar untuk "Homeostasis Definition Anatomy"
Posting Komentar