Face Anatomy Nerves
Several structures of the facial nervedescribed as nuclei segments and branchesproduce the four components of facial nerve function. Choose from 500 different sets of nerves of face anatomy flashcards on quizlet.
 Bell Palsy Clinical Examination And Management Cleveland
Bell Palsy Clinical Examination And Management Cleveland
The facial nerve is the seventh cranial nerve or simply cn vii.
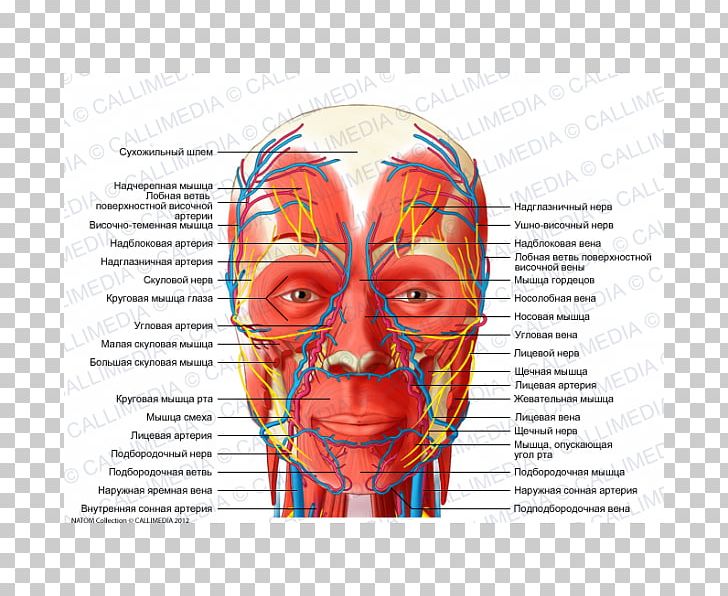
Face anatomy nerves. This part of face stays normal because lower motor neurons supplying this part of face get corticonuclear fibres upper motor neurons from cerebral cortex of the both sides. Its three branches are the ophthalmic v1 maxillary v2 and mandibular v3. It conveys some sensory information from the tongue and the interior of the mouth.
The facial nerve is the nerve associated with the second pharyngeal arch. This nerve performs two major functions. Learn nerves of face anatomy with free interactive flashcards.
It is one of the longest cranial nerves extending from the brainstem to the terminal end branches which are located throughout the face. Anatomically the course of the facial nerve can be divided into two parts. The facial nerve is one of the key cranial nerves with a complex and broad range of functions.
The facial nerve is one of a group of nerves called the cranial nerves cn twelve pairs of nerves that with the exception of the spinal accessory nerve cn xi originate in the brain and contribute to the peripheral nervous system pns. The specific bones and muscles derived from the second pharyngeal arch are shown below. The facial nerve is also known as the seventh cranial nerve cn7.
Intracranial the course of the nerve through the cranial cavity and the cranium itself. The facial nerve has a complex anatomy. Each of those branches supplies the corresponding region on the face.
It emerges from the pons of the brainstem controls the muscles of facial expression and functions in the conveyance of taste sensations from the anterior two thirds of the tongue. Although at first glance it is the motor nerve of facial expression which begins as a trunk and emerges from the parotid gland as five branches see facial nerve branches mnemonic it has taste and parasympathetic fibers that relay in a complex manner. Cutaneous nerves in upper motor neuron type paralysis of facial muscles because of engagement of the pyramidal tract the upper part of the face isnt changed.
The sensory innervation to the face comes from the trigeminal nerve which is the only cranial nerve that arises directly from the pons. Extracranial the course of the nerve outside the cranium through the face and neck.
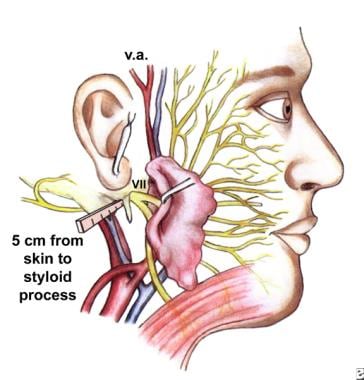 Facial Nerve Embryology Overview The Mature Facial Nerve
Facial Nerve Embryology Overview The Mature Facial Nerve
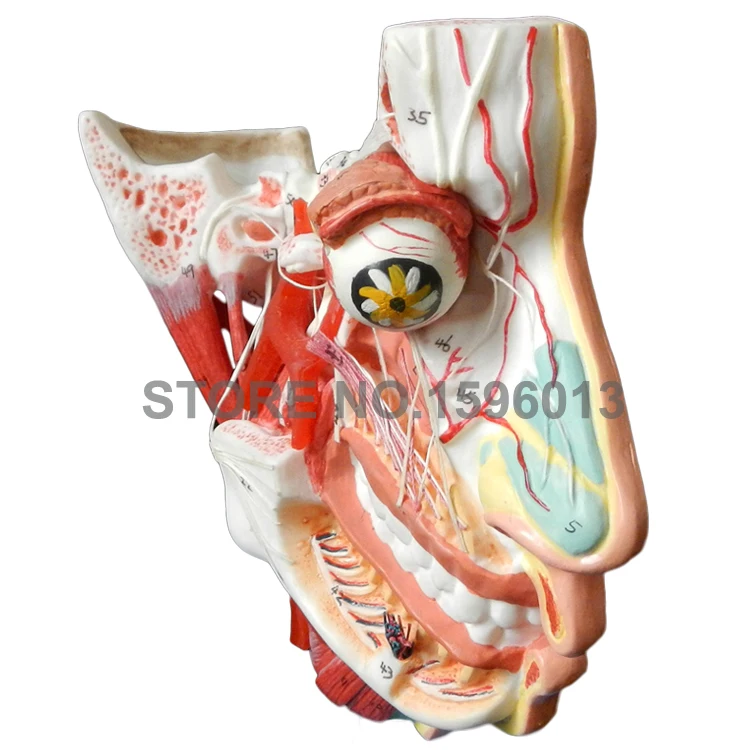 Us 130 0 Two Sides Head And Face Anatomy Model Muscles Nerves And Vessels In Facial Skull Model In Medical Science From Office School Supplies On
Us 130 0 Two Sides Head And Face Anatomy Model Muscles Nerves And Vessels In Facial Skull Model In Medical Science From Office School Supplies On
 Facial Artery An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Facial Artery An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
 Facial Reanimation Surgery Head And Neck Cancer Treatment
Facial Reanimation Surgery Head And Neck Cancer Treatment
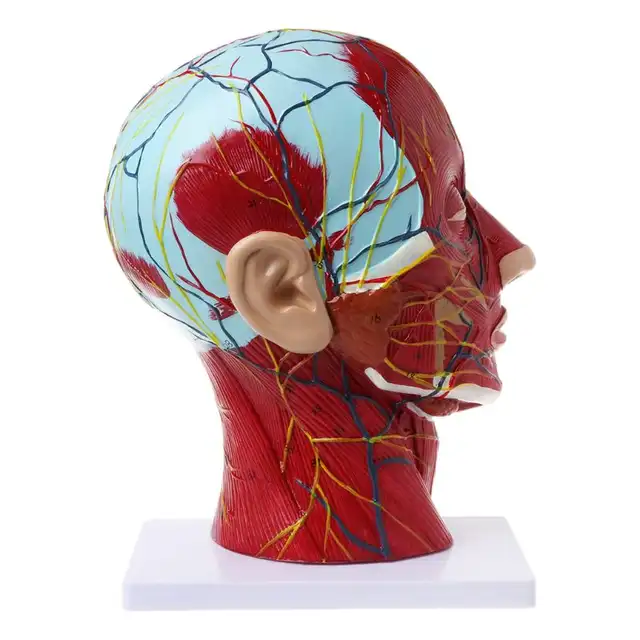 Human Anatomical Half Head Face Anatomy Medical Brain Neck Median Section Study Model Nerve Blood Vessel For Teaching
Human Anatomical Half Head Face Anatomy Medical Brain Neck Median Section Study Model Nerve Blood Vessel For Teaching
The Trigeminal And Facial Nerves
 The Proprioception In The Muscles Supplied By The Facial
The Proprioception In The Muscles Supplied By The Facial
 The Facial Nerve Cn Vii Course Functions Teachmeanatomy
The Facial Nerve Cn Vii Course Functions Teachmeanatomy
 Trigeminal Nerve An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Trigeminal Nerve An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
 Head And Neck Anatomy Nerve Human Body Nervous System Png
Head And Neck Anatomy Nerve Human Body Nervous System Png

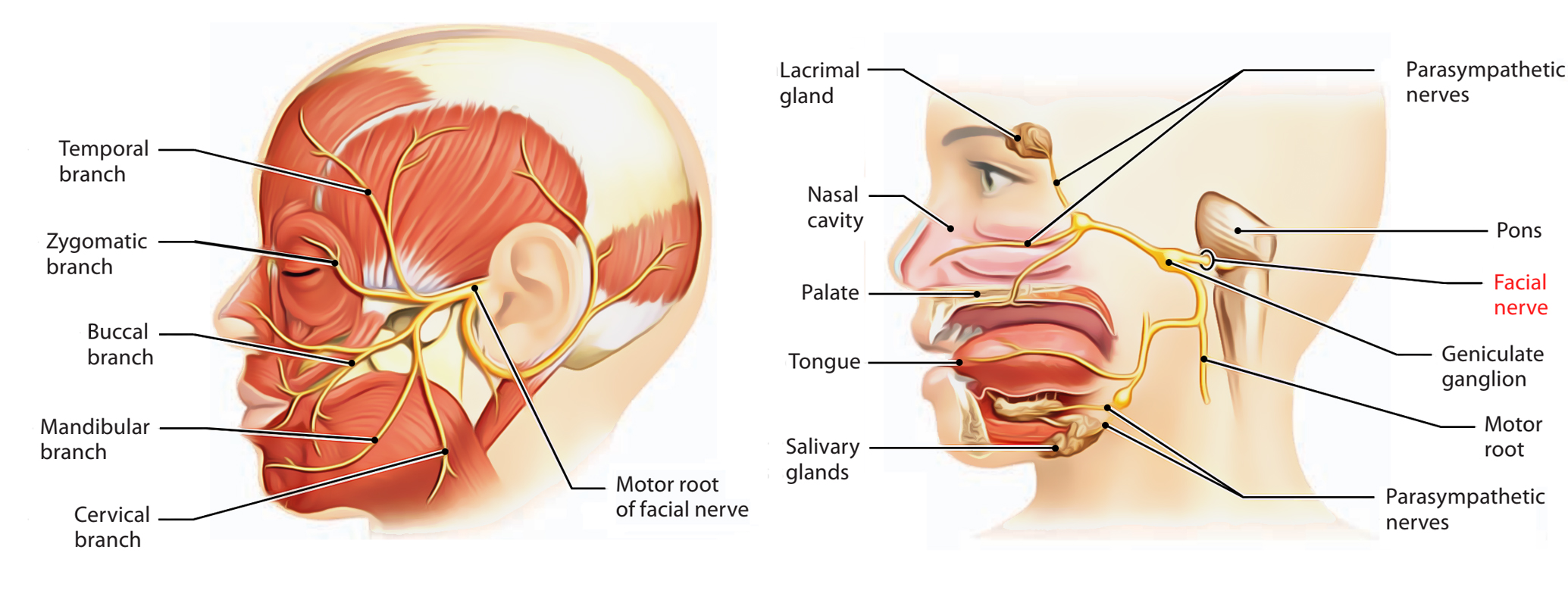 Easy Notes On Facial Nerve Learn In Just 4 Minutes
Easy Notes On Facial Nerve Learn In Just 4 Minutes
Facial Nerve Nervous System Anatomyzone
 Nerves Of The Head And Neck Interactive Anatomy Guide
Nerves Of The Head And Neck Interactive Anatomy Guide
 Facial Nerve Branches And Course Preview Human Neuroanatomy Kenhub
Facial Nerve Branches And Course Preview Human Neuroanatomy Kenhub
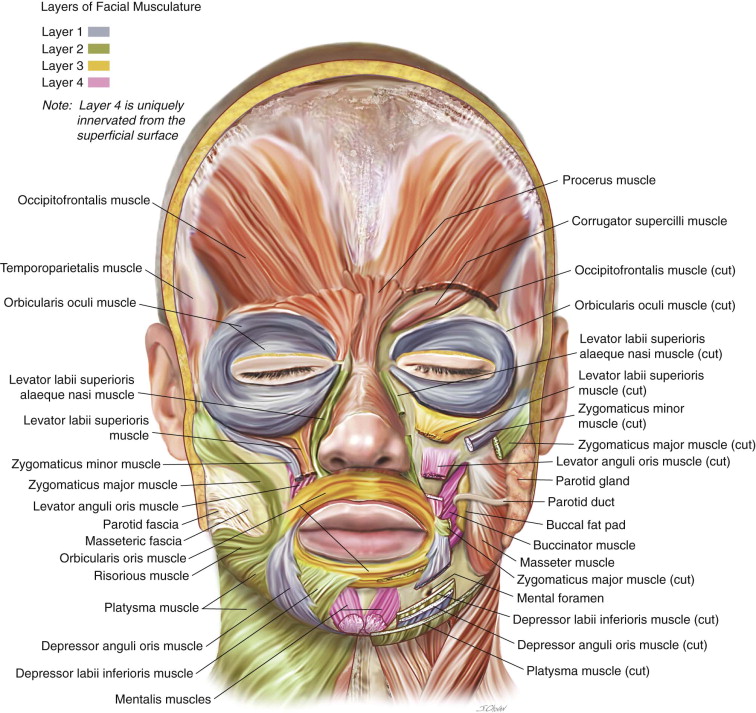 The Anatomy Of The Face Mouth And Jaws Pocket Dentistry
The Anatomy Of The Face Mouth And Jaws Pocket Dentistry
 Us 298 0 Head And Neck With Vessels Nerves And Brain Medical Model Anatomical Model Head And Face Muscle Nerve Model Gasen Nsj004 In Medical
Us 298 0 Head And Neck With Vessels Nerves And Brain Medical Model Anatomical Model Head And Face Muscle Nerve Model Gasen Nsj004 In Medical
 Facial Nerve Preservation Dr Larian
Facial Nerve Preservation Dr Larian
 Parapharyngeal Space Wikipedia
Parapharyngeal Space Wikipedia
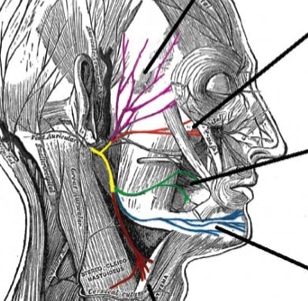 Facial Palsy Causes Differential Diagnosis Management
Facial Palsy Causes Differential Diagnosis Management
 Reconstruction St Louis Childrens Hospital
Reconstruction St Louis Childrens Hospital
 5삼차신경 7안면신경 Facial Nerve Cranial Nerves Nerve
5삼차신경 7안면신경 Facial Nerve Cranial Nerves Nerve
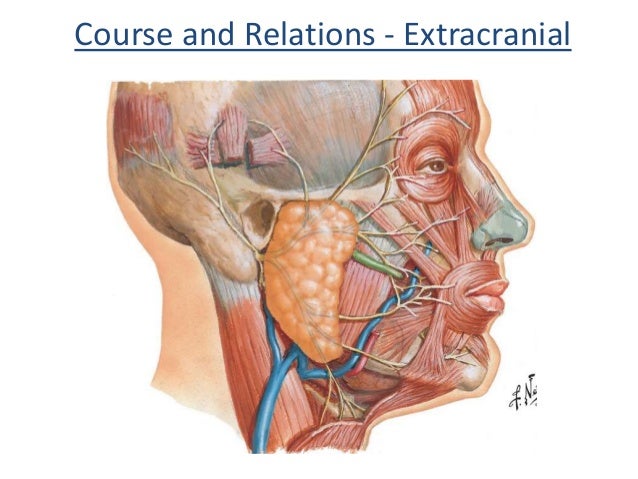
Ringing The Infection Bell About Facial Nerve Palsy

Belum ada Komentar untuk "Face Anatomy Nerves"
Posting Komentar