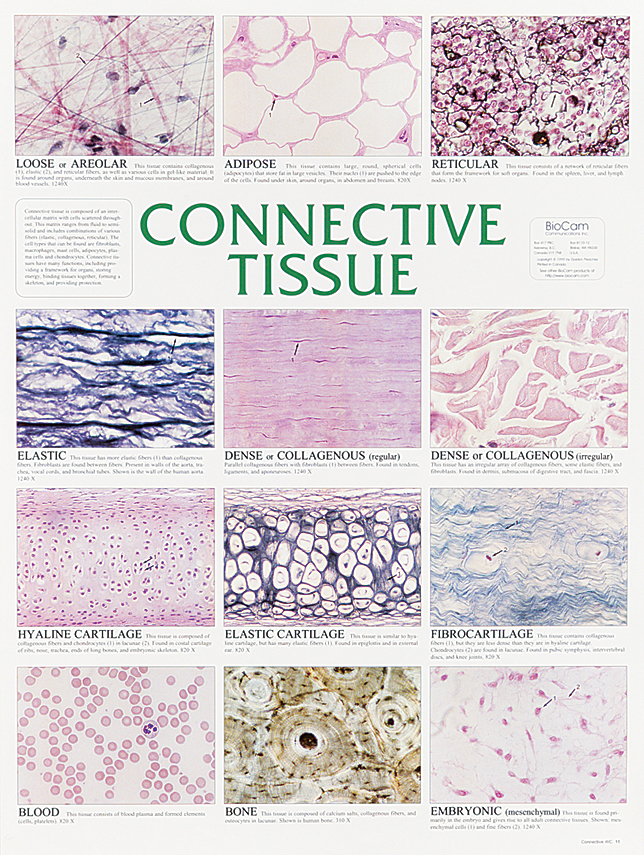
Anatomy Connective Tissue
Connective tissue proper includes loose connective tissue and dense connective tissue. These fibers form an irregular network with spaces between the fibers.
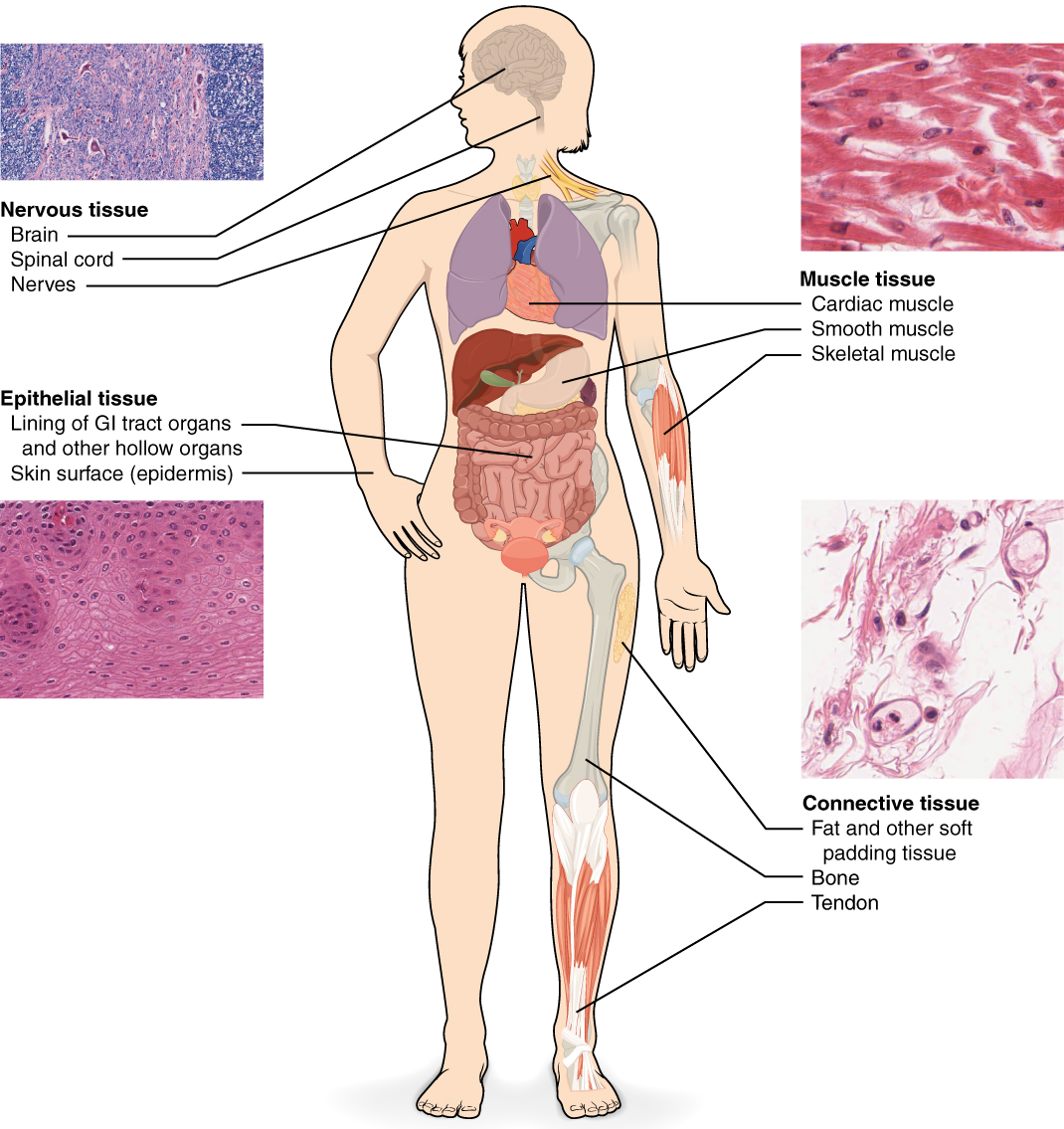 4 1 Types Of Tissues Anatomy And Physiology
4 1 Types Of Tissues Anatomy And Physiology
A type of loose connective tissue proper.
Anatomy connective tissue. Adipocytes account for most of volume. This tissue resembles areolar connective tissue but the only fibers in its matrix are the reticular fibers which form a delicate network. These canals consist of blood vessels that branch off the central vessels.
Both tissues have a variety of cell types and protein fibers suspended in a viscous ground substance. Four types of connective tissue 2342 all develop from mesenchyme 3295 different degrees of blood flow 3457 extracellular matrix full of ground substance and fibers 3594. Dense regular connective tissue fibers are parallel to each other enhancing tensile strength and resistance to stretching in the direction of the fiber orientations.
Most widely distributed connective tissue variety in the body looks cobwebby beansprouts contains elastic fibers collgen fibers reticular fibers fibroblasts macrophages mast cells some white blood cells. Ligaments and tendons are made of dense regular connective tissue. Main component of ligaments tendons aeroneurosis and fascia.
Eachosteon consists of a central canal which contains blood vessels and nerves surrounded by concentric rings lamellae of hard matrix and collagen fibers. The reticular tissue is limited to certain sites in the body such as internal frameworks that can support lymph nodes spleen and bone marrow. Dense regular connective tissue drct all collagen fibers in the matrix run in the same direction separated by rows of fibroblasts parallel to the direction of the pull.
Nearly all the fat in the body. There are three major categories of dense connective tissue. Regular irregular and elastic.
Highly vascularized fat that breaks down to provide heat to the blood. Loose connective tissue is named so because of the weave and type of its constituent fibers. Dense connective tissue is reinforced by bundles of fibers that provide tensile strength elasticity and protection.
It holds organs in place and attaches epithelial tissue to other underlying tissues. In vertebrates the most common type of connective tissue is loose connective tissue. Branching off the central canal at right angles are perforating canals.
 Anatomy And Cell Biology 3309 Lecture Notes Summer 2017
Anatomy And Cell Biology 3309 Lecture Notes Summer 2017
 Anatomy And Physiology Connective Tissue Notes
Anatomy And Physiology Connective Tissue Notes
 Quiz Worksheet Structure Of Adipose Loose Connective
Quiz Worksheet Structure Of Adipose Loose Connective
 Crafton Hills Anatomy Physiology Epithelial Tissues A
Crafton Hills Anatomy Physiology Epithelial Tissues A
 Connective Tissue Types Functions Disorders
Connective Tissue Types Functions Disorders
Ch04 Mineralized Connective Tissues
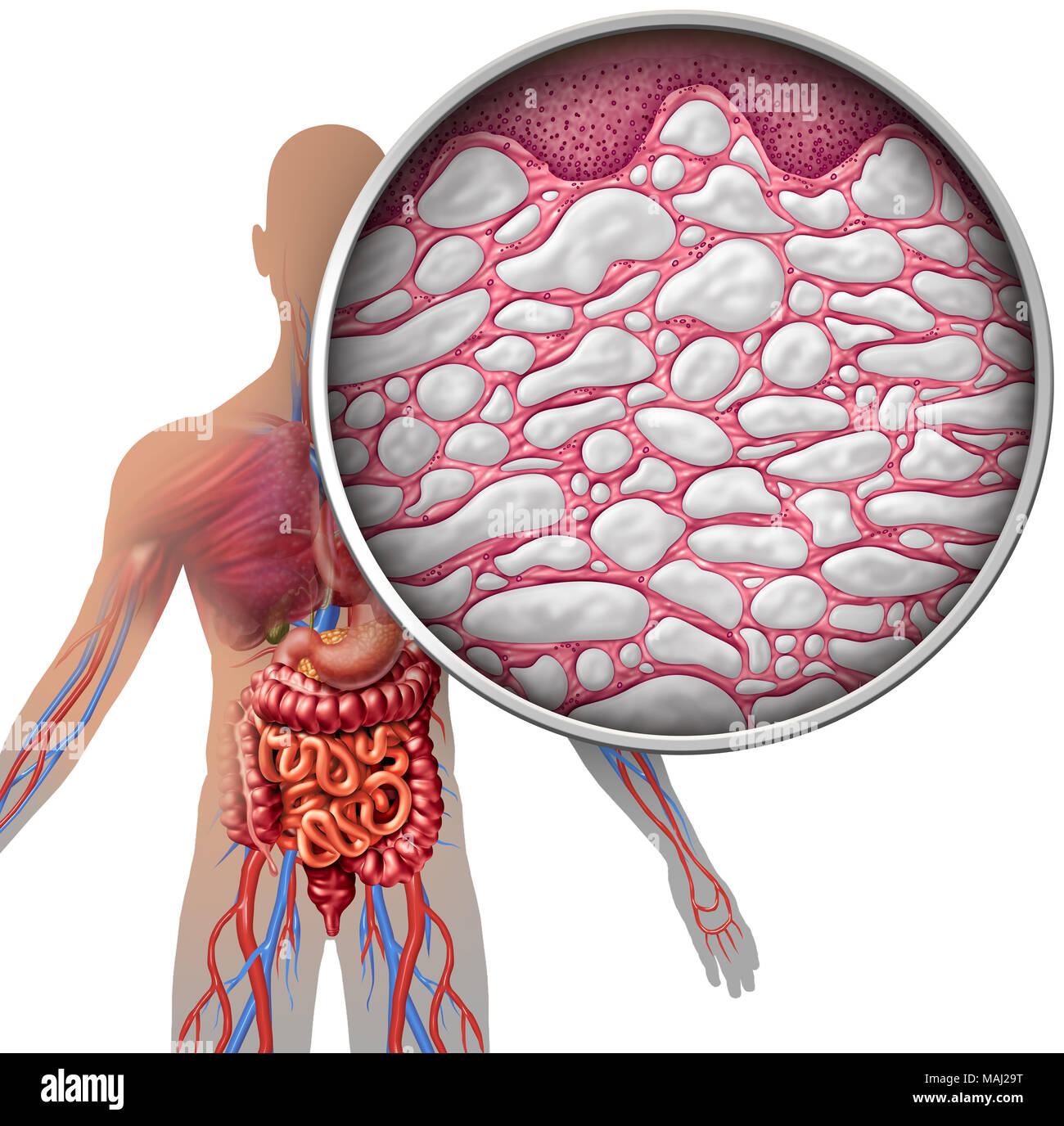 Interstitium Human Body Anatomy With Organs Concept As
Interstitium Human Body Anatomy With Organs Concept As
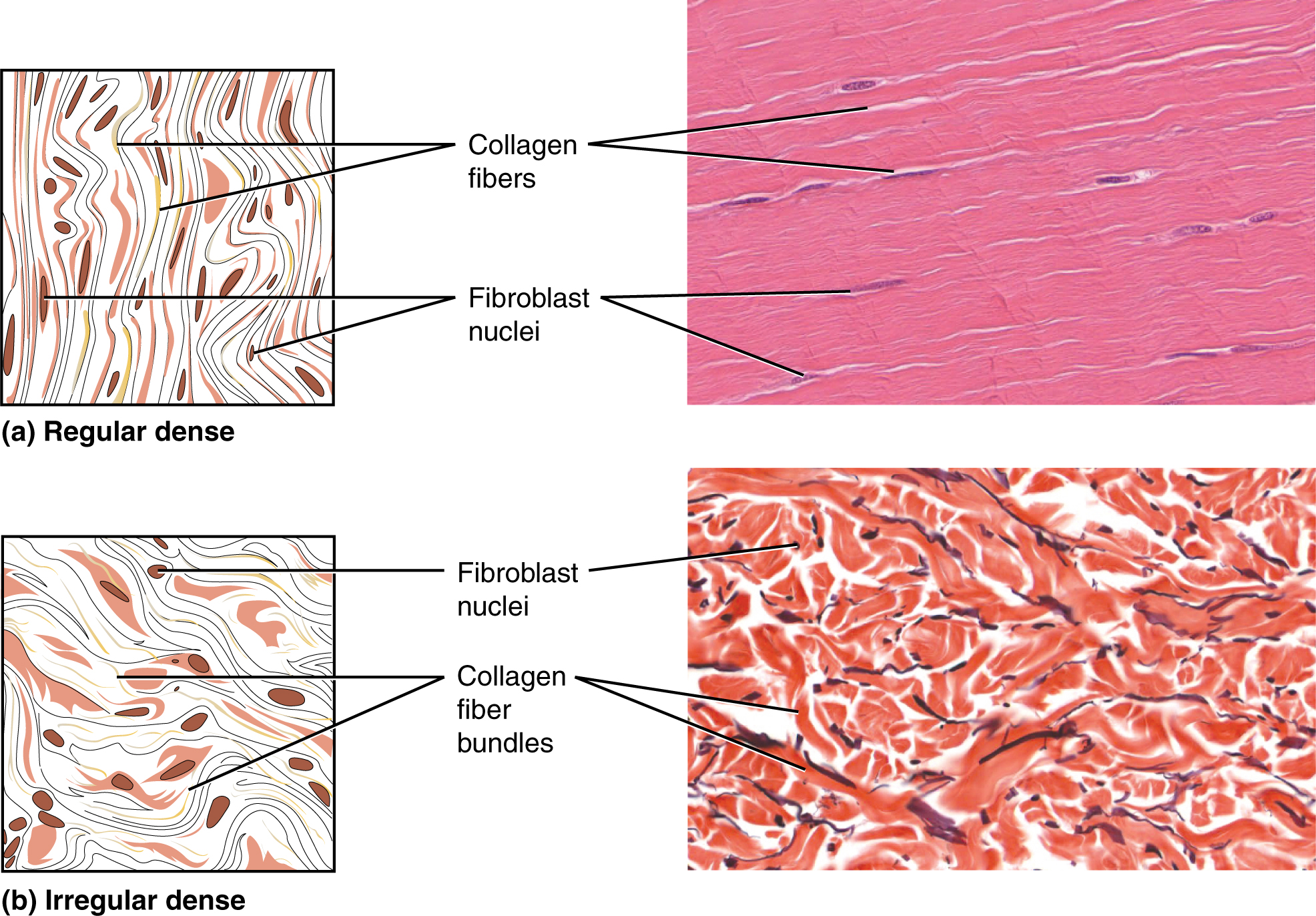 4 3 Connective Tissue Supports And Protects Anatomy And
4 3 Connective Tissue Supports And Protects Anatomy And
Connective Tissue L2 Microscopic Anatomy Flashcards Memorang
 Human Anatomy Connective Tissue Diagrams By Julie Ridge
Human Anatomy Connective Tissue Diagrams By Julie Ridge
 Joints Ligaments And Connective Tissues Advanced Anatomy
Joints Ligaments And Connective Tissues Advanced Anatomy
 The Plantar Fascia Is A Thick Band Of Connective Tissue That
The Plantar Fascia Is A Thick Band Of Connective Tissue That
 Connectivetissue Connective Tissues Directions Insert And
Connectivetissue Connective Tissues Directions Insert And
 Anatomy And Physiology Connective Tissue Notes
Anatomy And Physiology Connective Tissue Notes
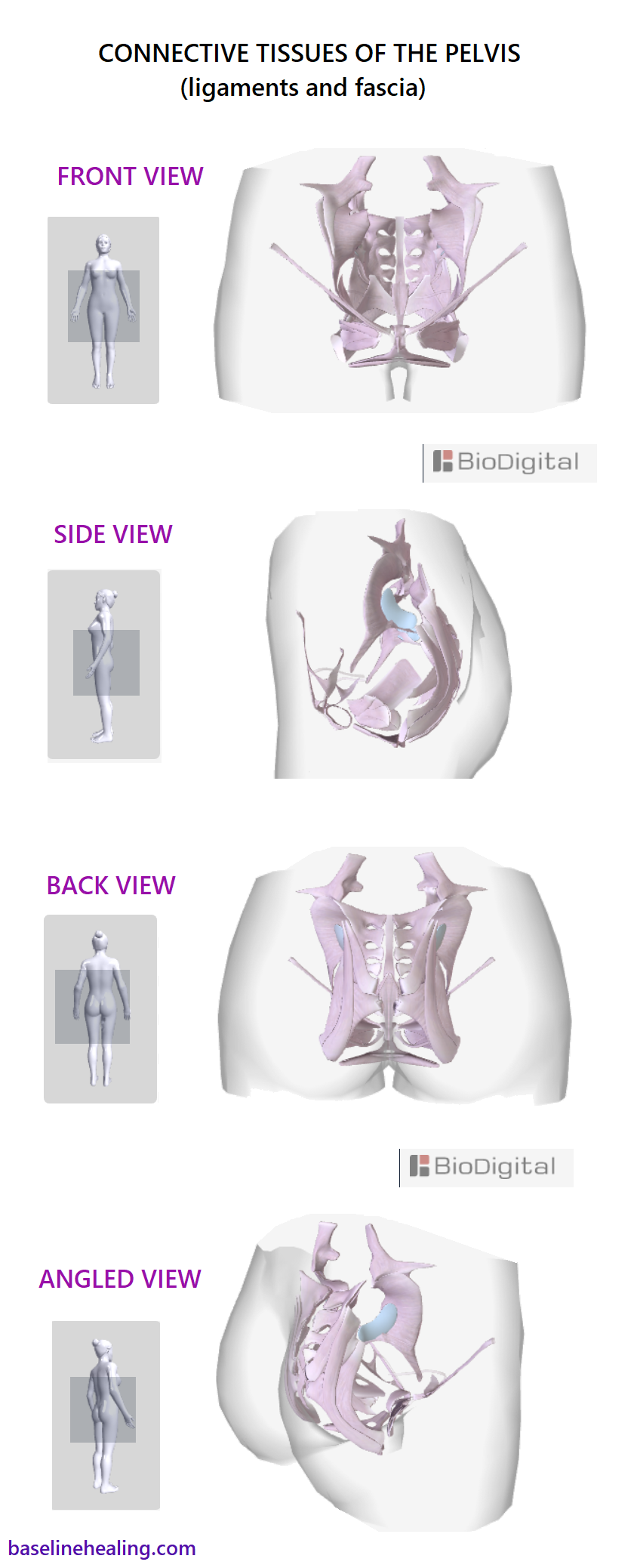 The Pelvis Anatomy Images Pelvic Floor Connective Tissues
The Pelvis Anatomy Images Pelvic Floor Connective Tissues
 Anatomy Review Skeletal Muscle Tissue Sinoe Medical Homepage
Anatomy Review Skeletal Muscle Tissue Sinoe Medical Homepage
Skeletal Muscle Anatomy And Physiology Openstax
 Anatomy Of The Abdomen And Groin Articles Mount Nittany
Anatomy Of The Abdomen And Groin Articles Mount Nittany
 Pin By Dorothy Jenkins On Health Fitness That I Love
Pin By Dorothy Jenkins On Health Fitness That I Love
 Animal Primary Tissues Boundless Biology
Animal Primary Tissues Boundless Biology
 Anatomy And Physiology Tissues Connective Tissue V2 0
Anatomy And Physiology Tissues Connective Tissue V2 0
 Anatomy Of The Abdomen And Groin
Anatomy Of The Abdomen And Groin
 Anatomy And Physiology Connective Tissue Notes
Anatomy And Physiology Connective Tissue Notes



Belum ada Komentar untuk "Anatomy Connective Tissue"
Posting Komentar